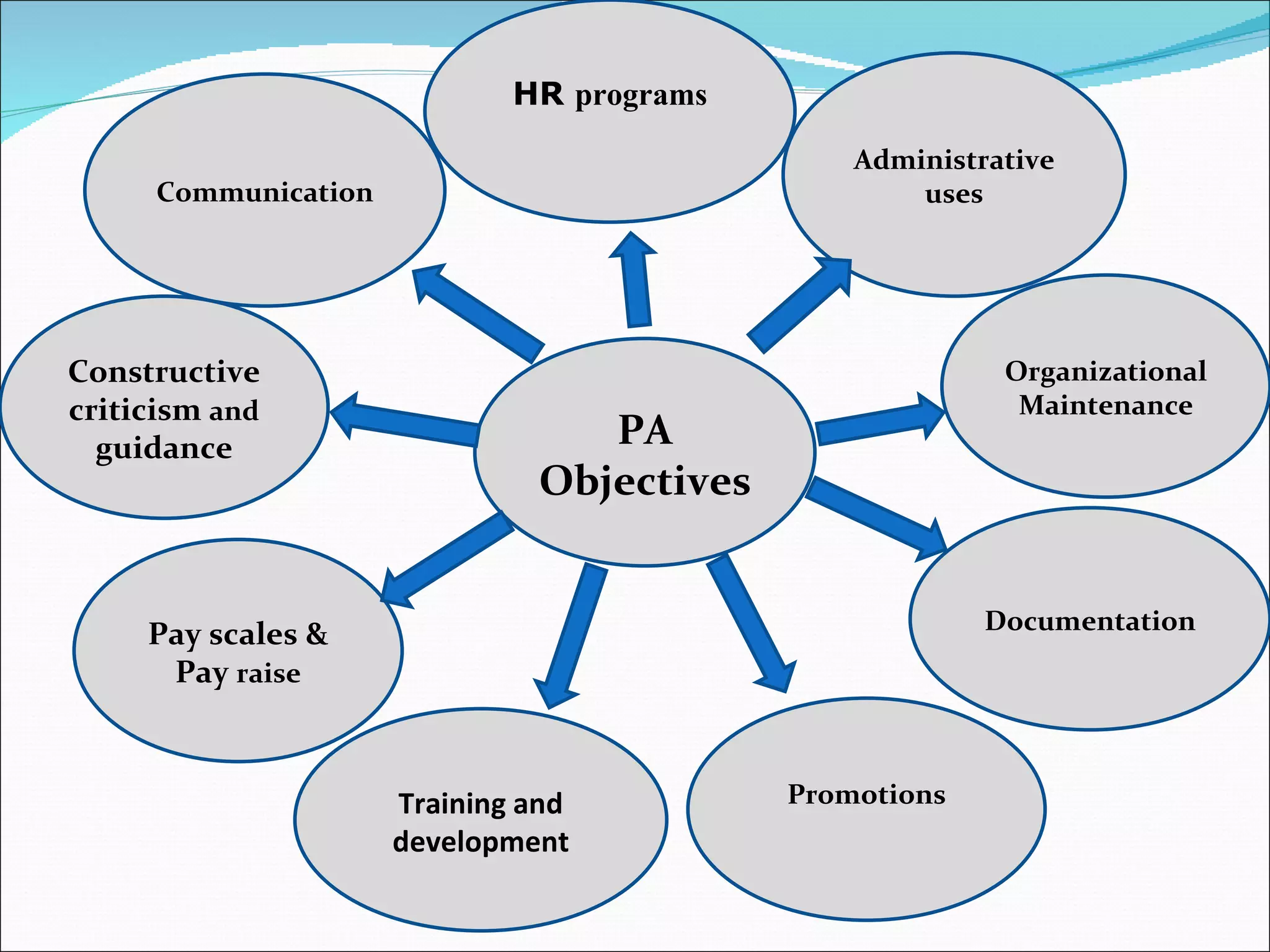
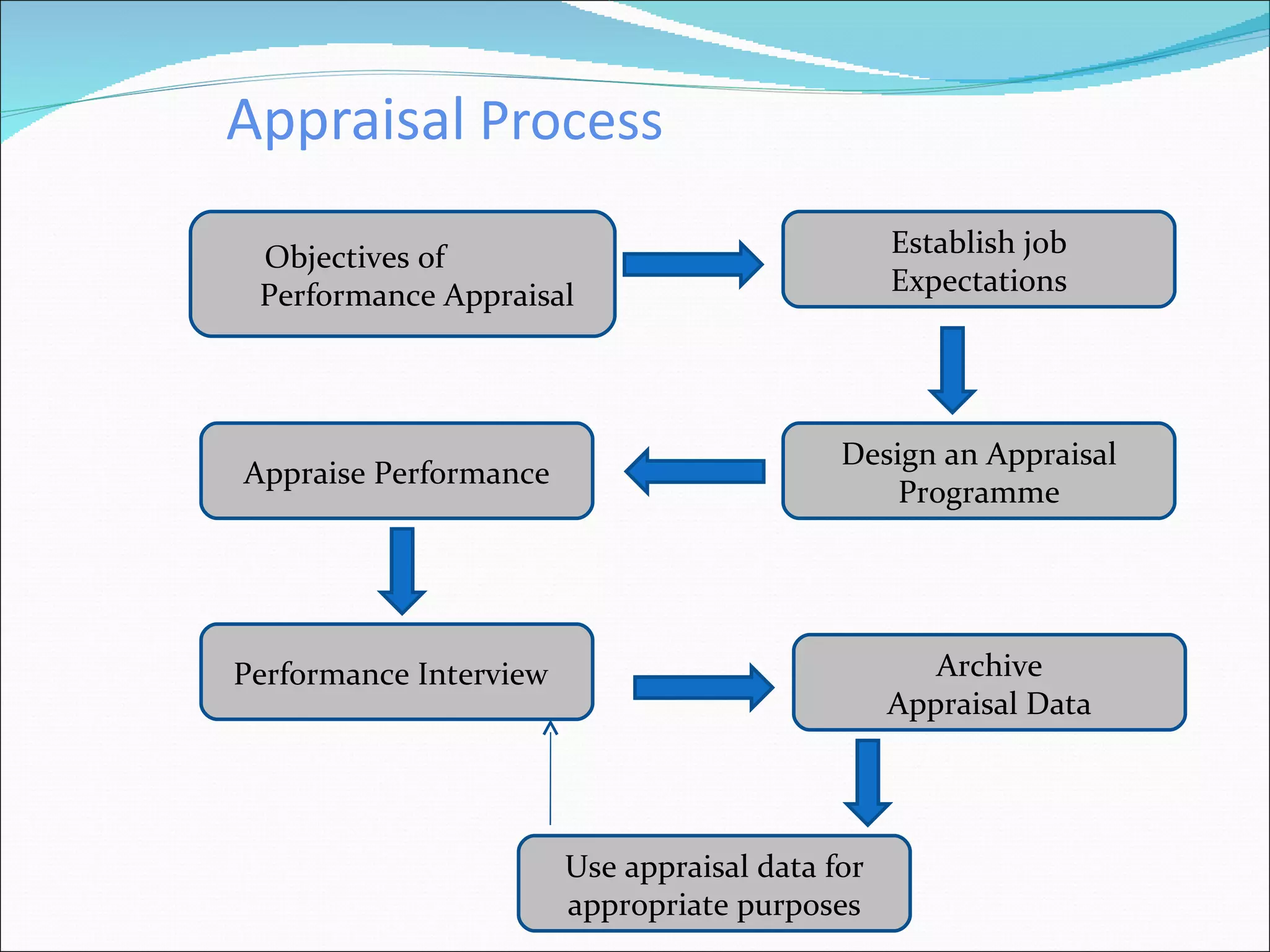
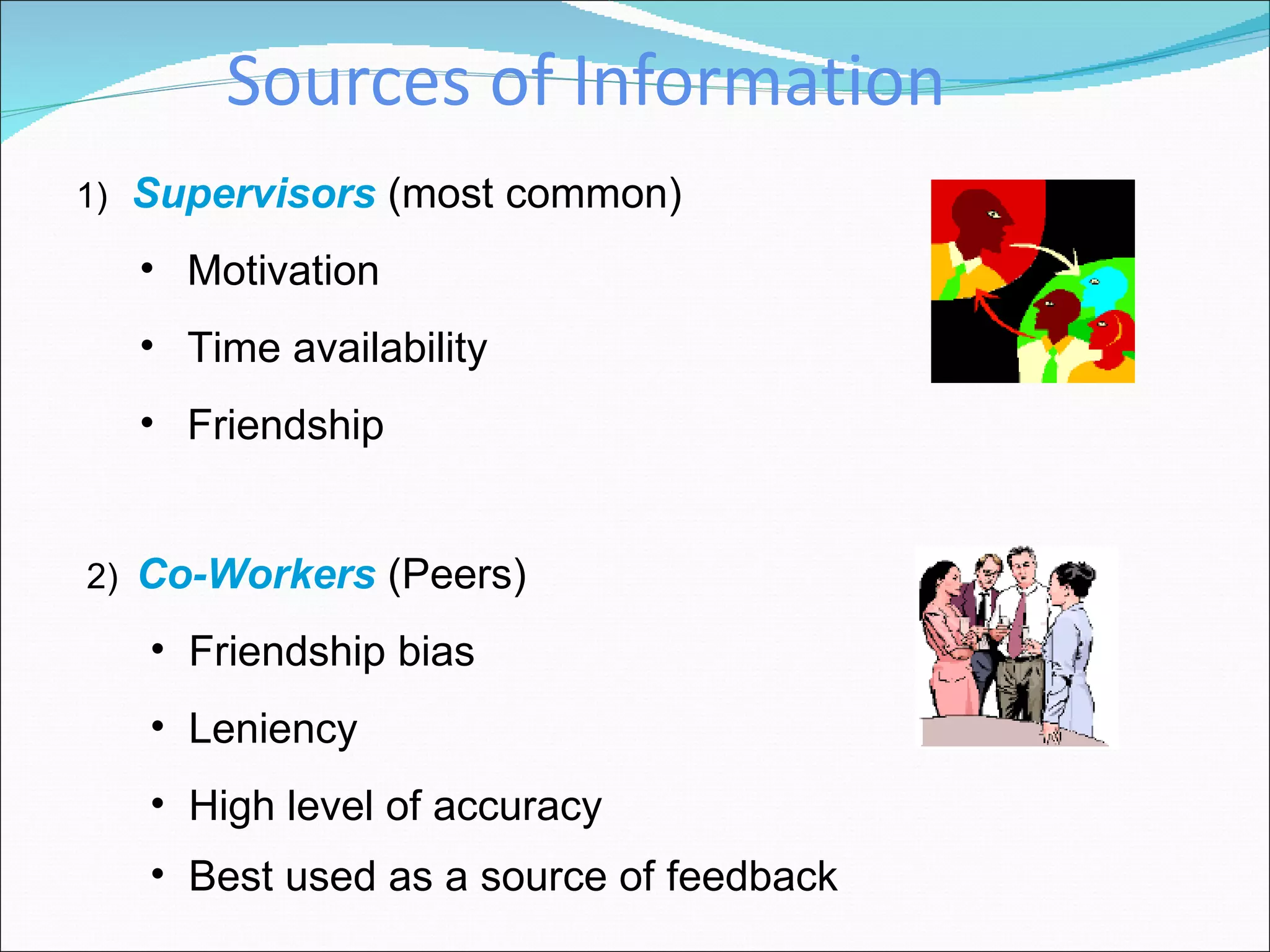
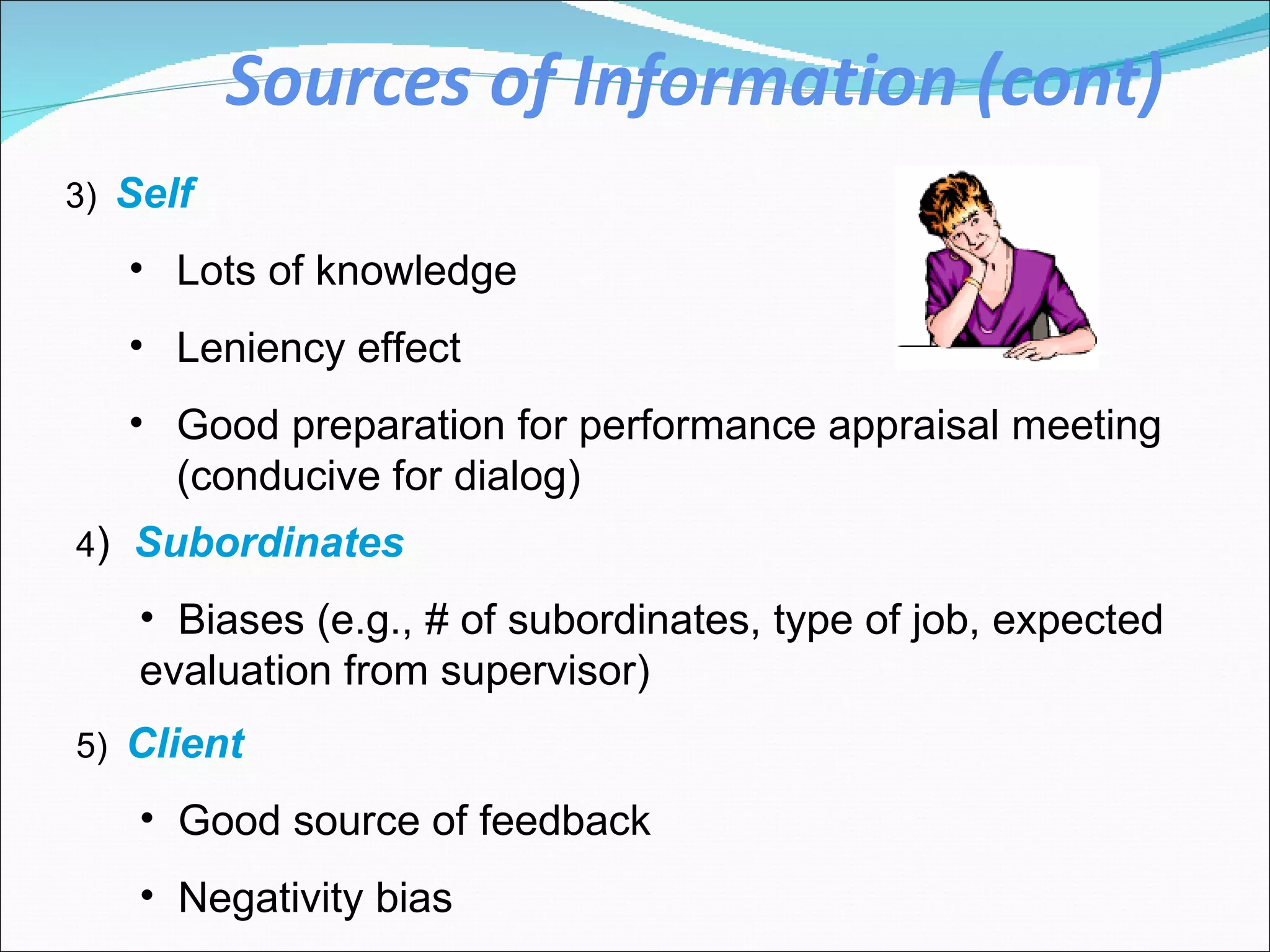
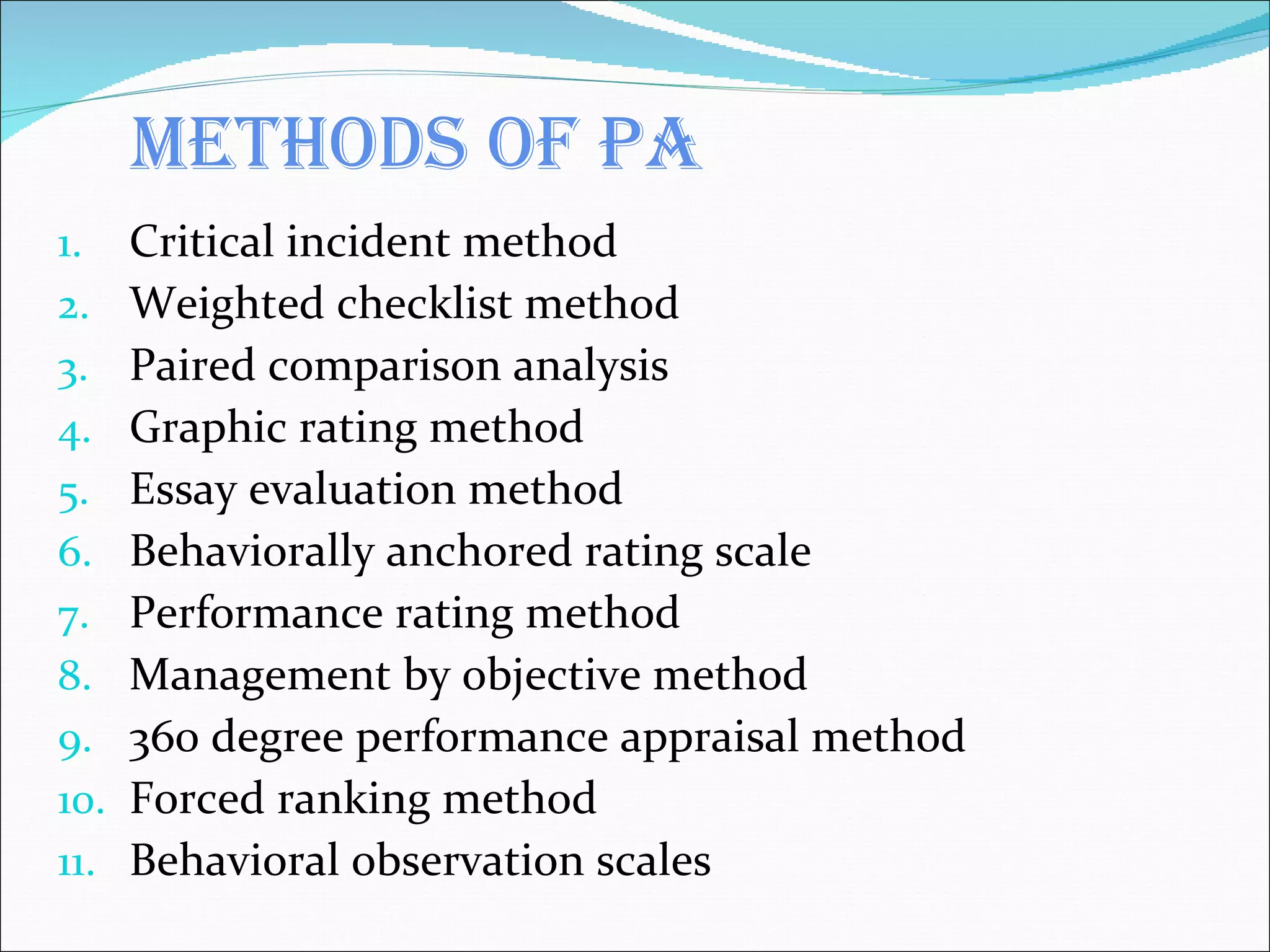
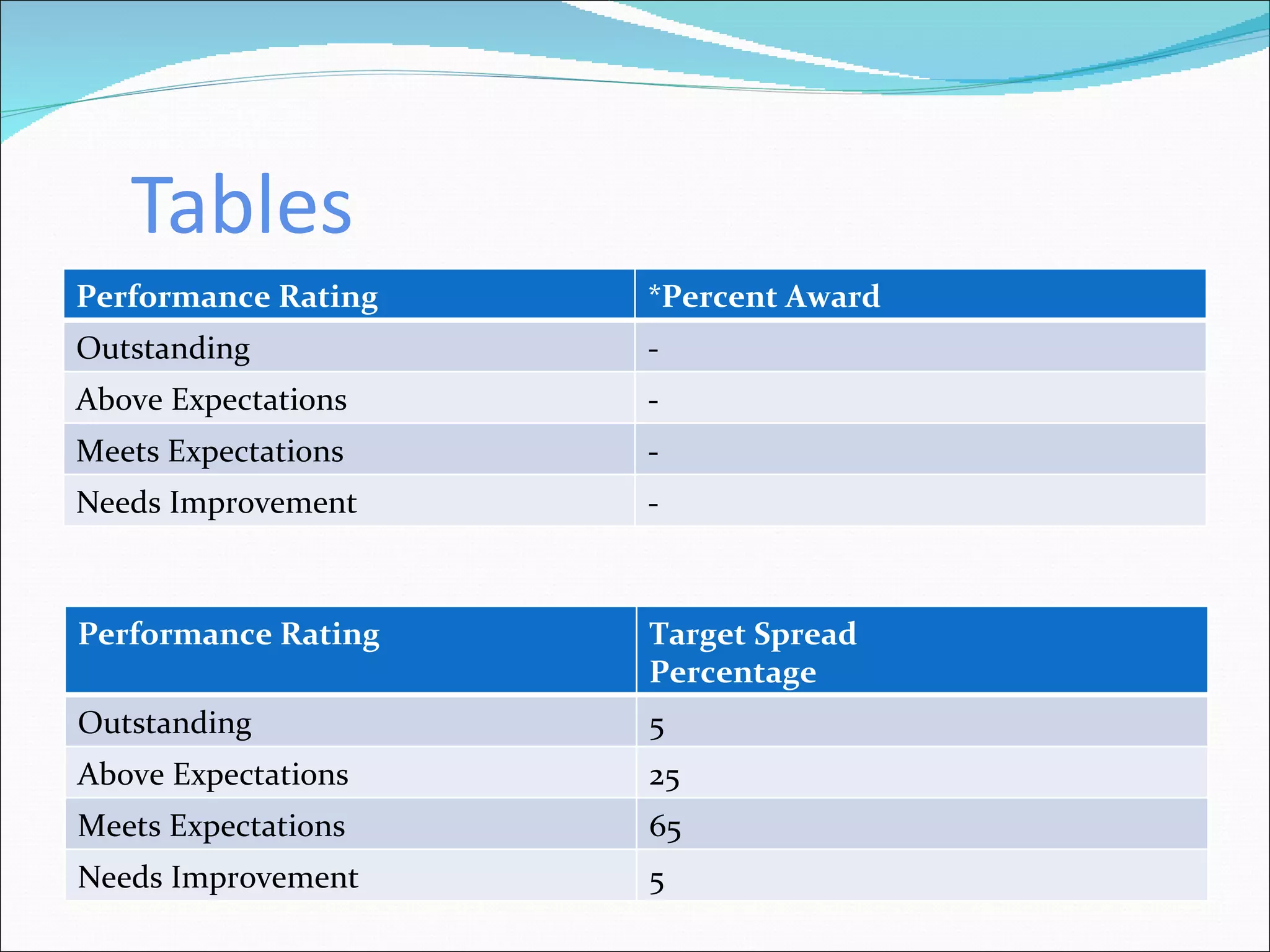
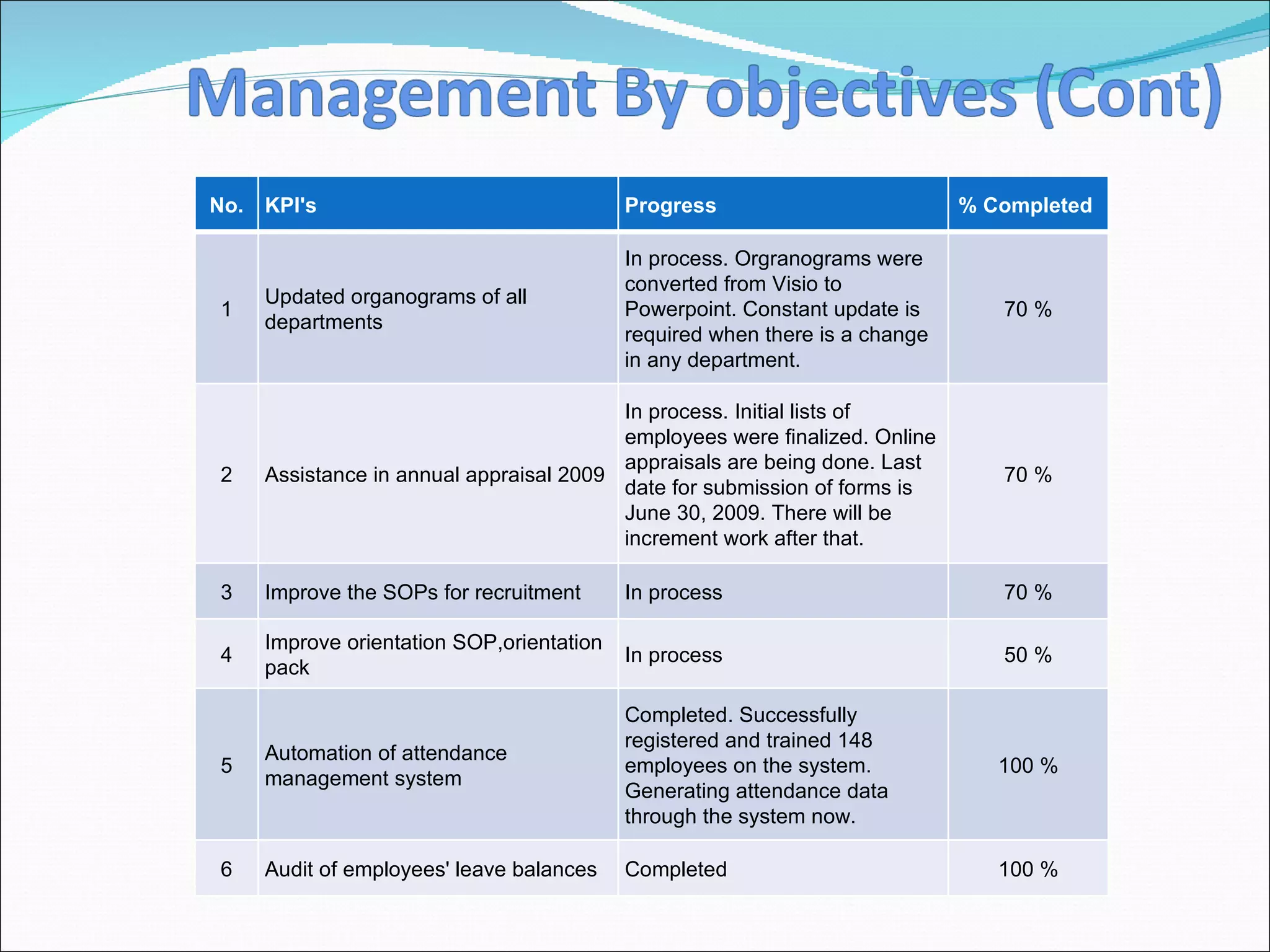
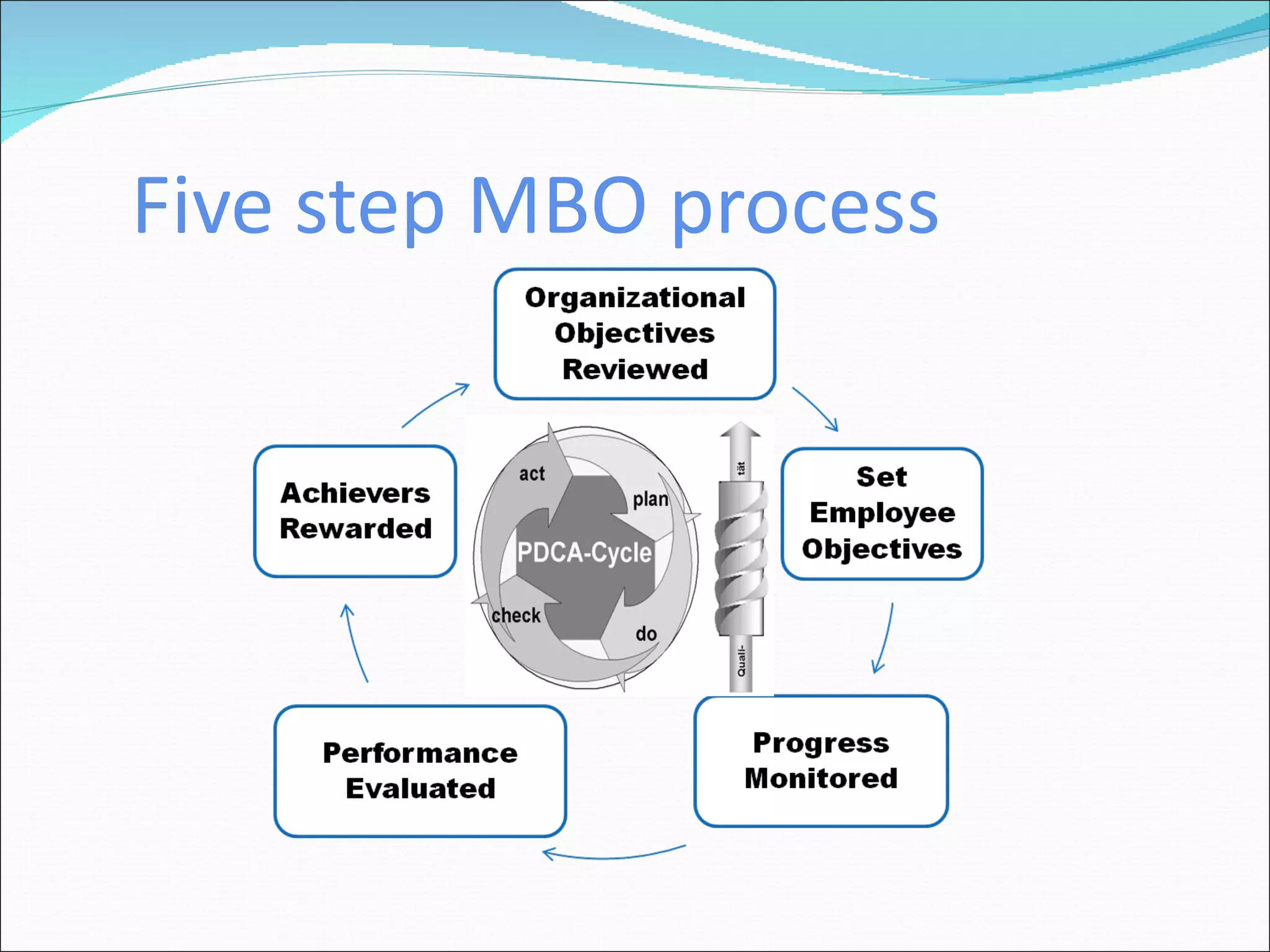
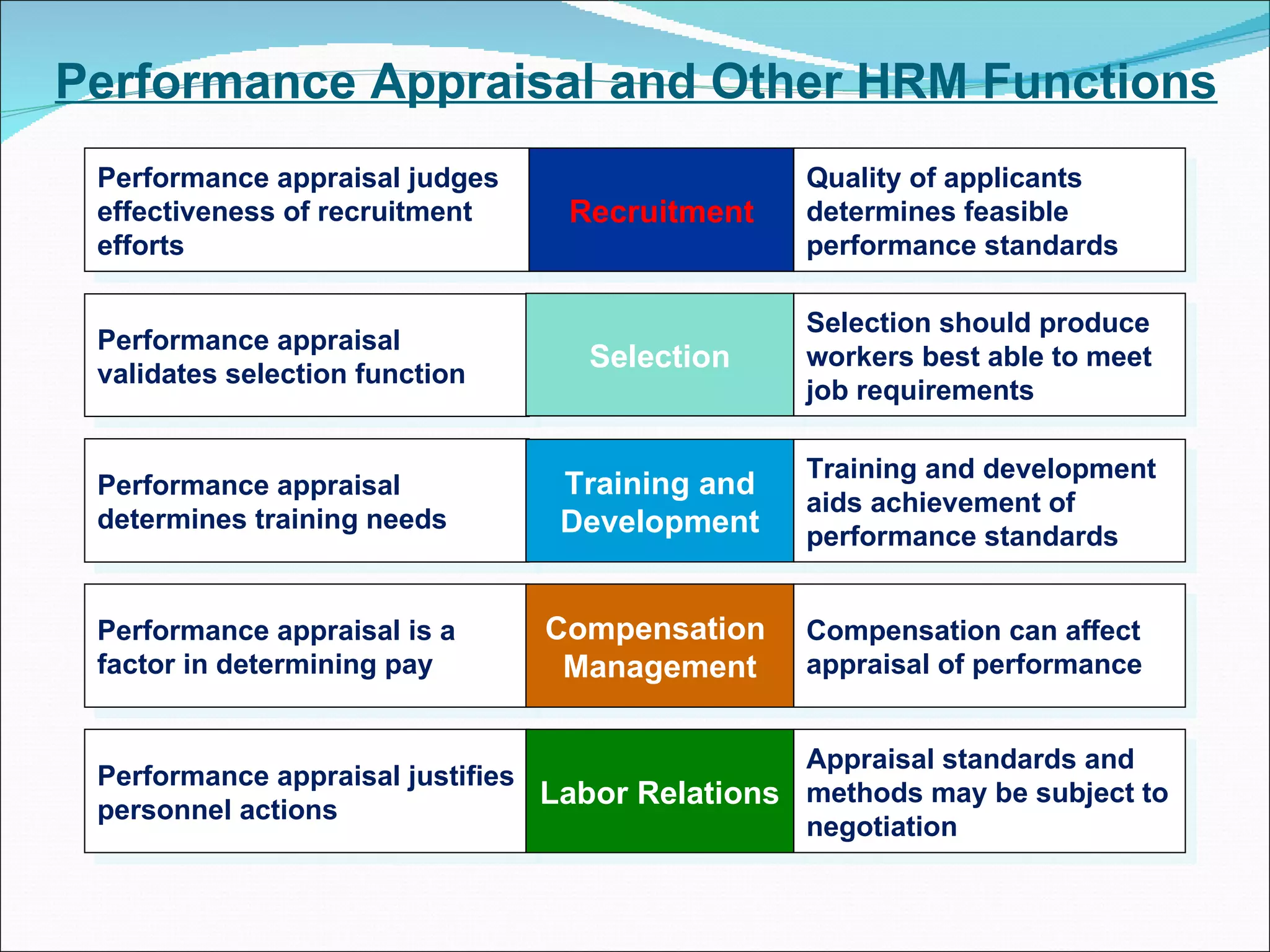
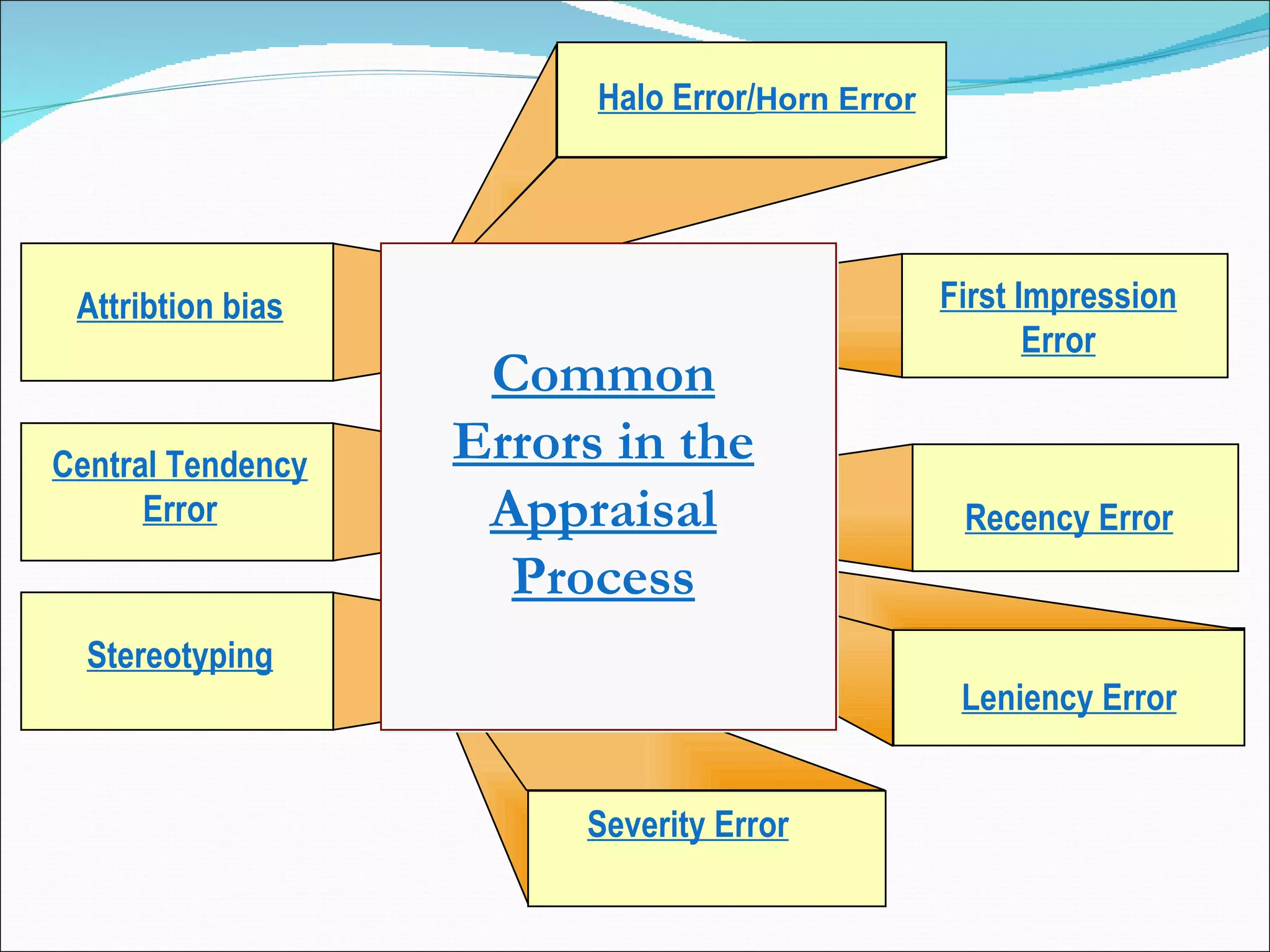
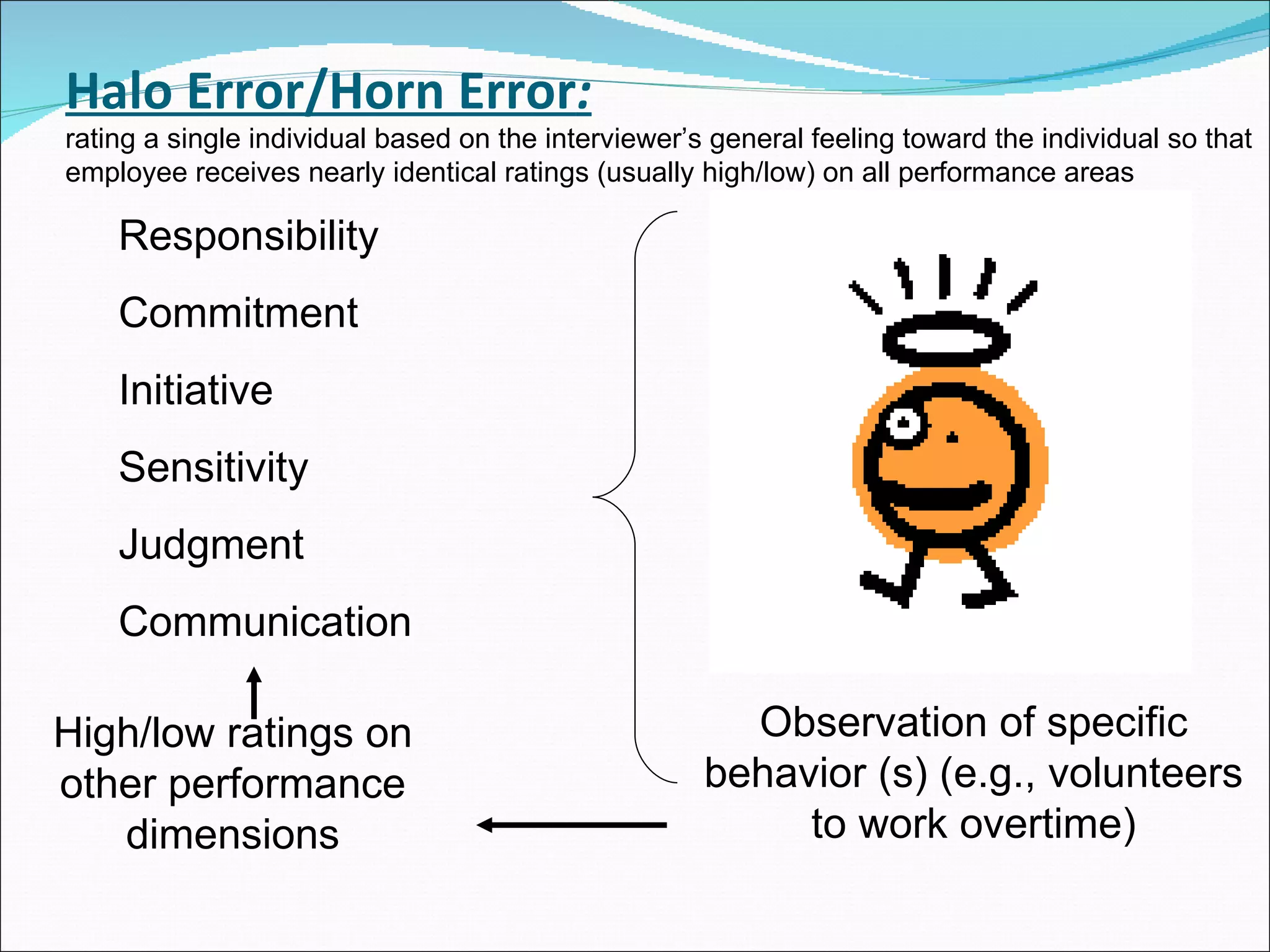
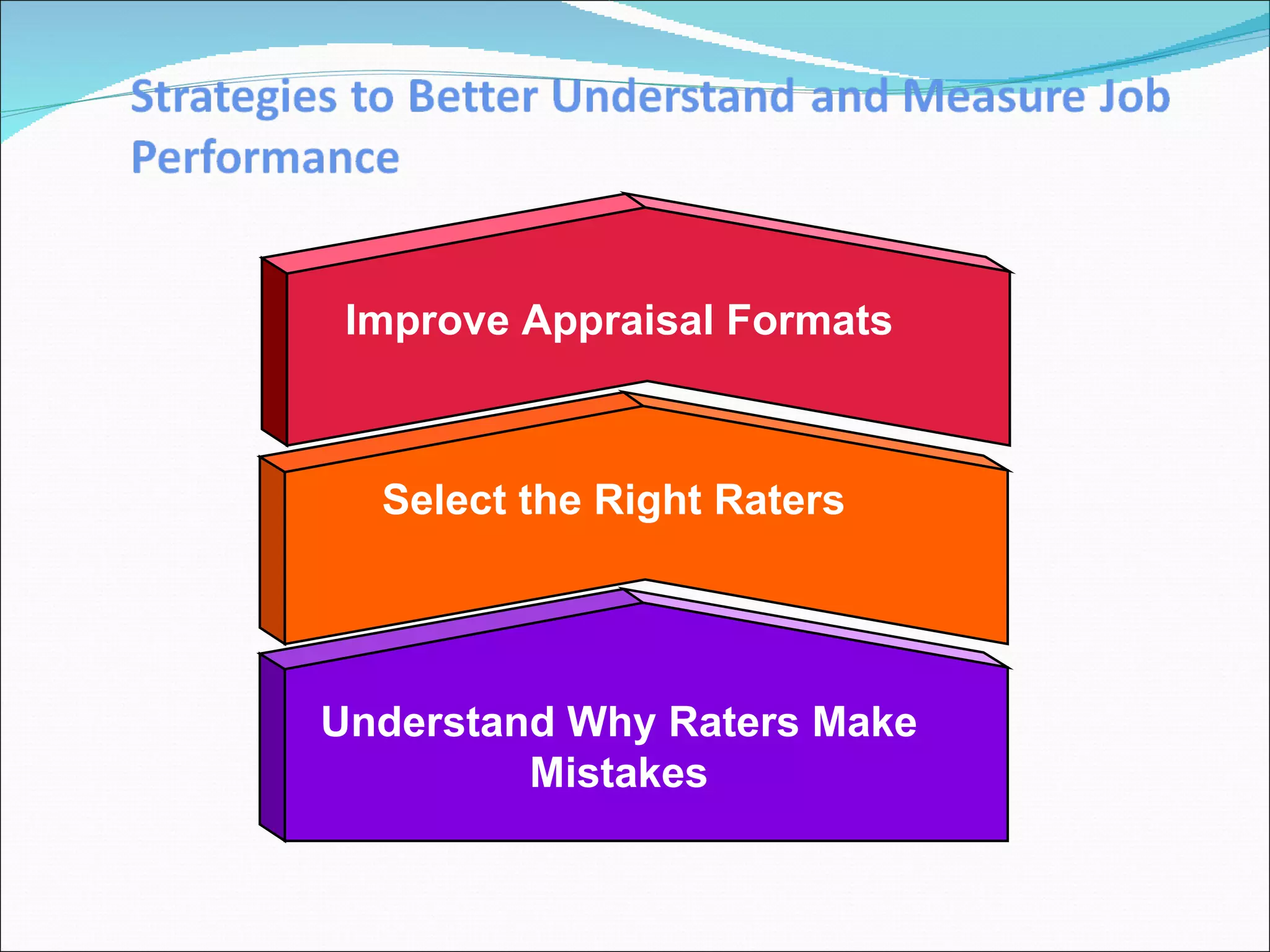
The document discusses performance management and performance appraisals. It covers various topics related to performance appraisals including definitions, objectives, processes, methods, common errors and ways to improve appraisal systems. Specifically, it discusses establishing standards and linking appraisals to business objectives. It also describes different appraisal methods like forced ranking, management by objectives and essay evaluations. Common errors like halo effects and ways to reduce errors through rater training are also outlined.