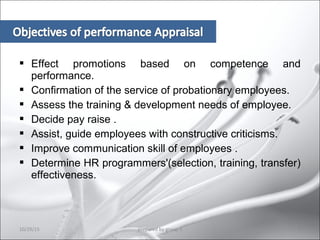
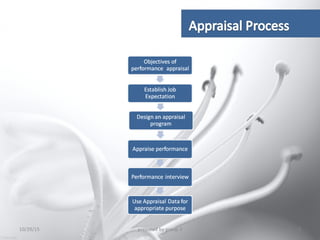
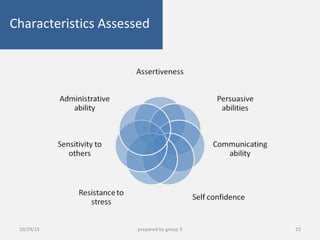
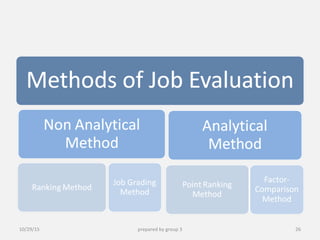
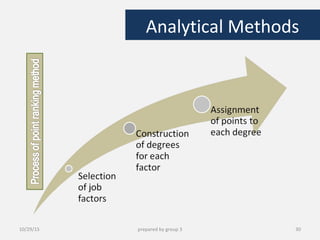
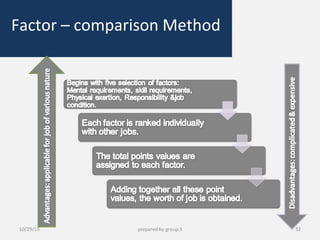
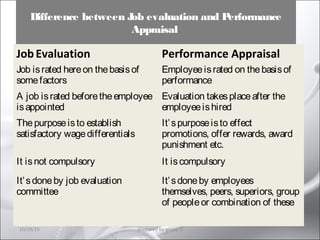
This document provides information about performance appraisal. It discusses the objectives, process, methods, and errors of performance appraisal. It also covers topics like job evaluation, organizational strategies related to appraisal, psychological appraisal and assessment centers. Different analytical and non-analytical methods of job evaluation are described along with the process of employee classification. The document is presented by Group 3 and contains an outline and explanations of key areas regarding performance appraisal.