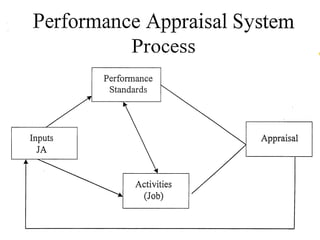
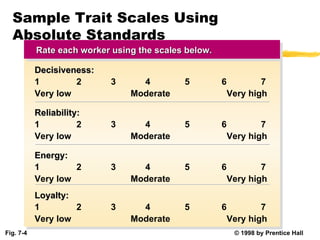
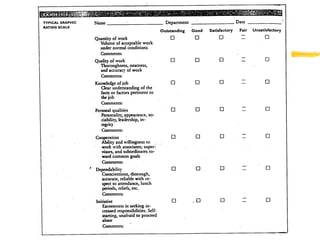
Performance management involves systematically evaluating employee job performance and providing feedback to improve performance. It includes performance appraisals that measure performance relative to standards, as well as developmental feedback. Effective performance management benefits employees through improved performance, fairness, and motivation. It also provides administrative benefits to organizations and legal protections when implemented properly.