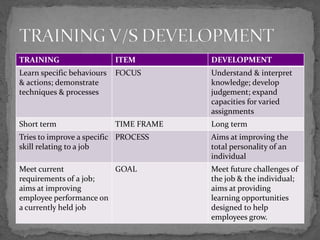
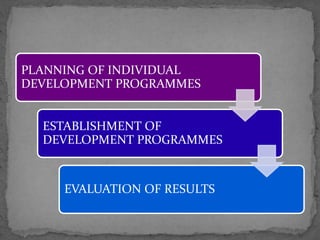
Development aims to enhance one's ability to understand and interpret knowledge, and results from experience and maturity. It differs from training, which focuses on learning specific behaviors and actions. Management development involves imparting knowledge, changing attitudes, or increasing skills to improve current or future management performance. It has a long-term focus on understanding knowledge, developing judgment, and expanding capacities, while training has a short-term focus on improving specific skills for a current job. Development measures effectiveness through having qualified people available when needed, promoting from within, and gaining a human resource competitive advantage.