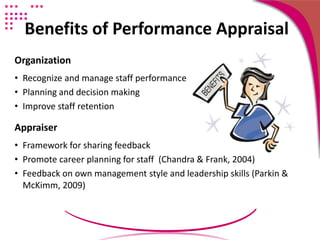
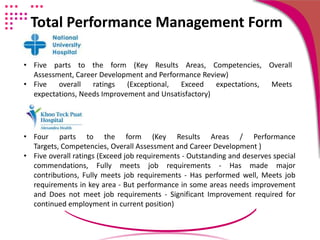
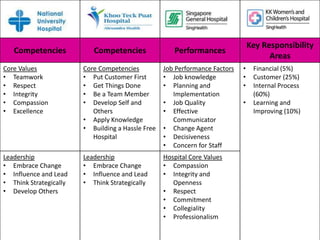
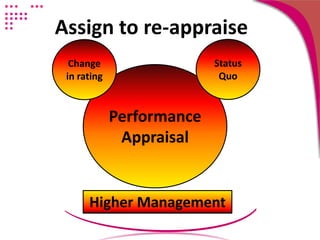
The document discusses strategies for conducting a fair performance appraisal of nurses who felt their previous appraisal was unfair. The new appraiser would:
1) Analyze objective and subjective performance data like records and interviews to substantiate any rating changes.
2) Interview staff and the previous appraiser to understand the reasons for grievances like personality clashes or errors in rating.
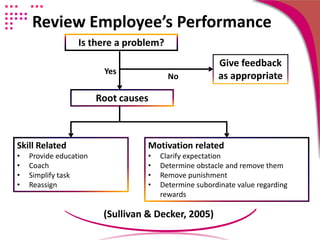
3) Address any performance issues by determining the root cause such as skills, motivation, or opportunity factors, and taking actions like training, coaching, clarifying expectations.
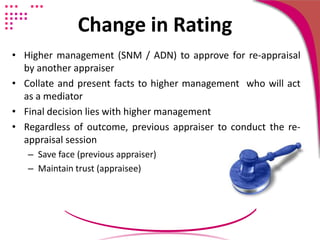
4) Conduct the re-appraisal with effective communication skills and an understanding of common rater errors to avoid inaccurate assessments. The focus would be on organizational objectives and
![[Business Communication]
[Company Name]
Performance Appraisal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performanceappraisal-131002075633-phpapp01/75/Performance-appraisal-1-2048.jpg)