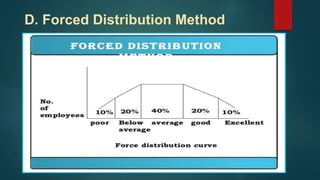
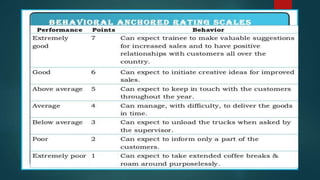
The document discusses various methods of performance appraisal used to evaluate employees. It describes past-oriented methods like rating scales, checklist methods and forced choice methods. Future-oriented methods discussed include management by objectives, psychological appraisal, assessment centers, and 360-degree feedback. Key factors measured in performance appraisals are listed as job knowledge, quality and quantity of work, initiative, and dependability. The purposes of performance appraisal are identified as communication of performance, training and development, and determining effectiveness of HR programs.