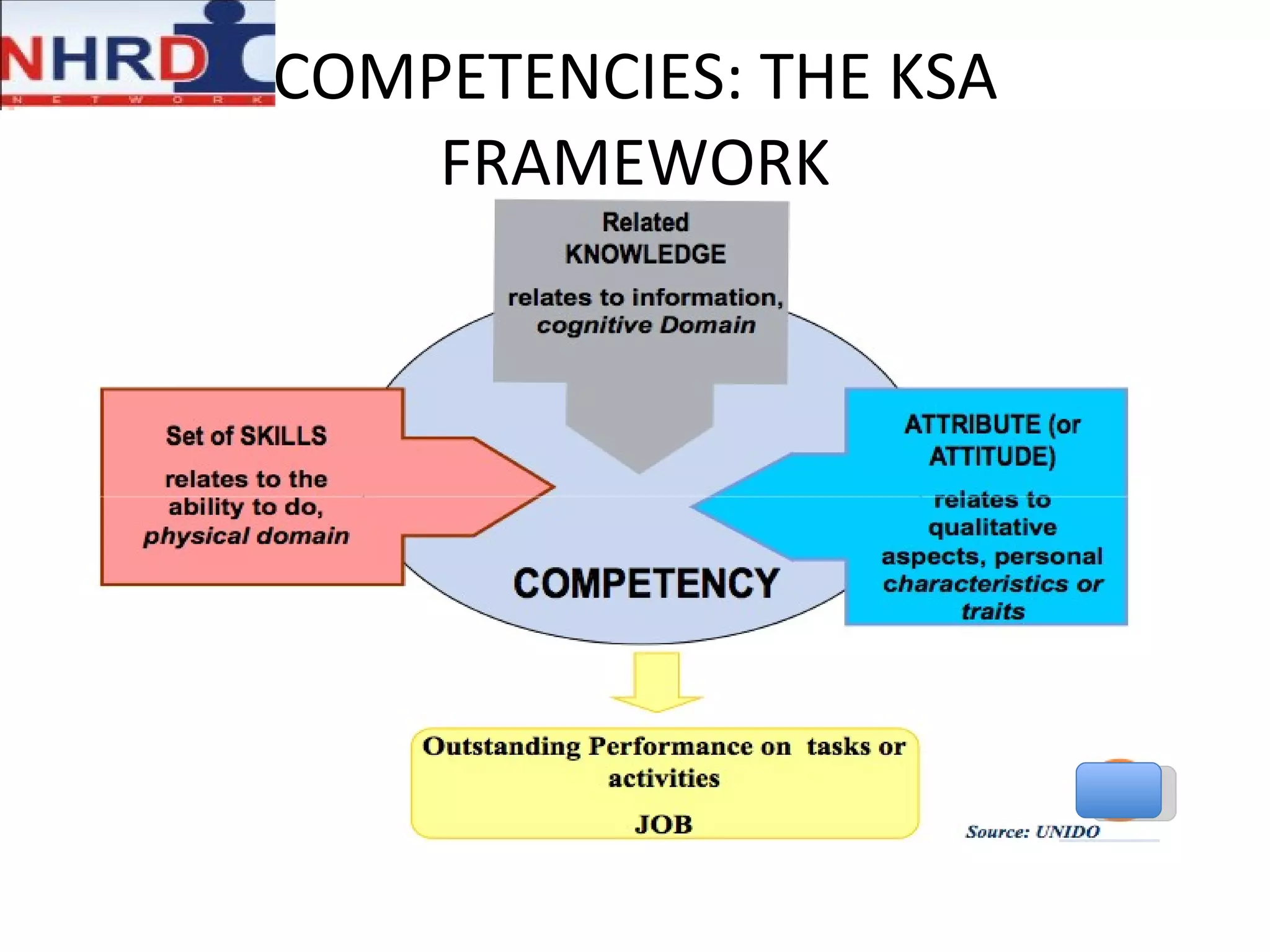
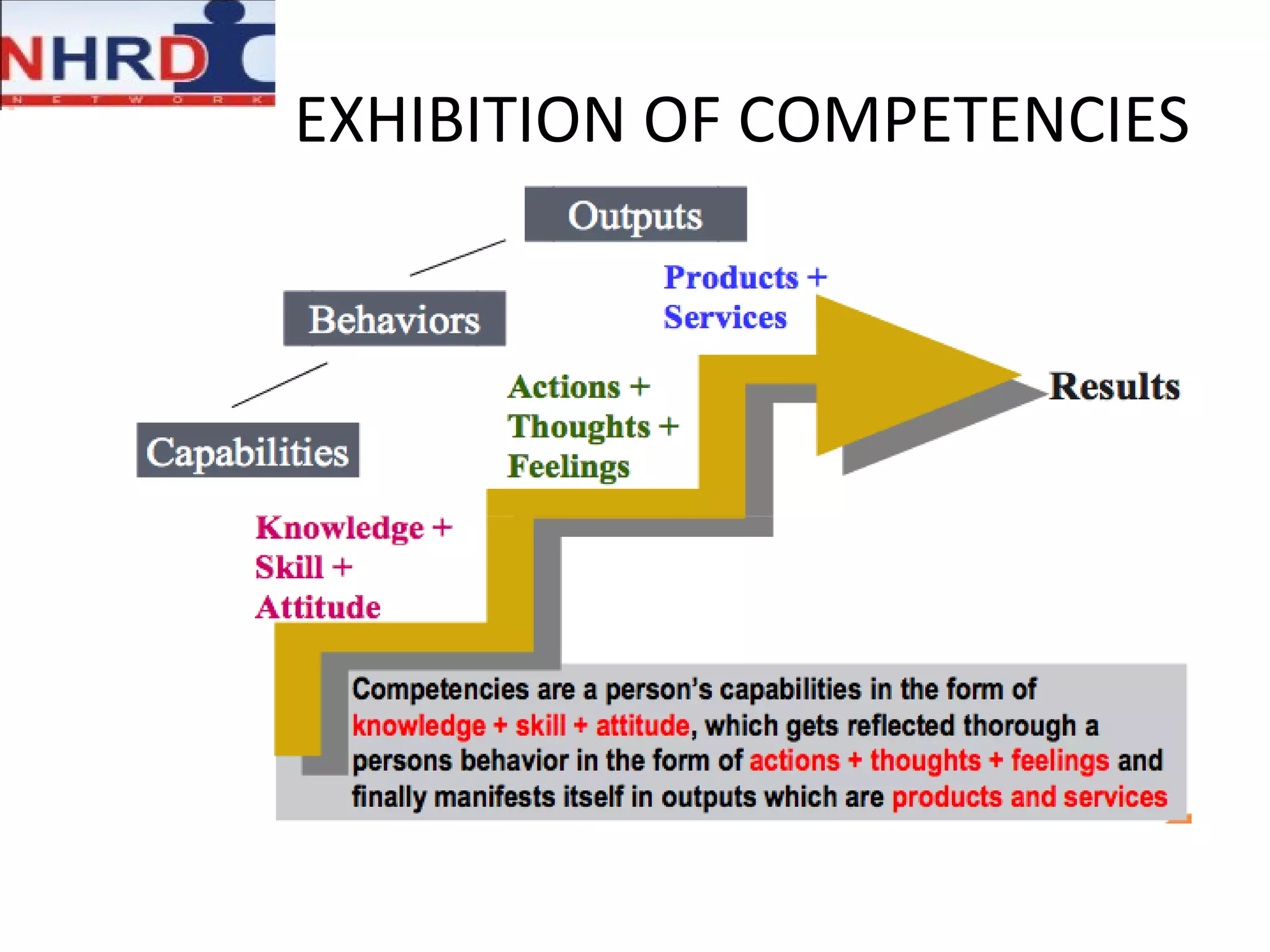
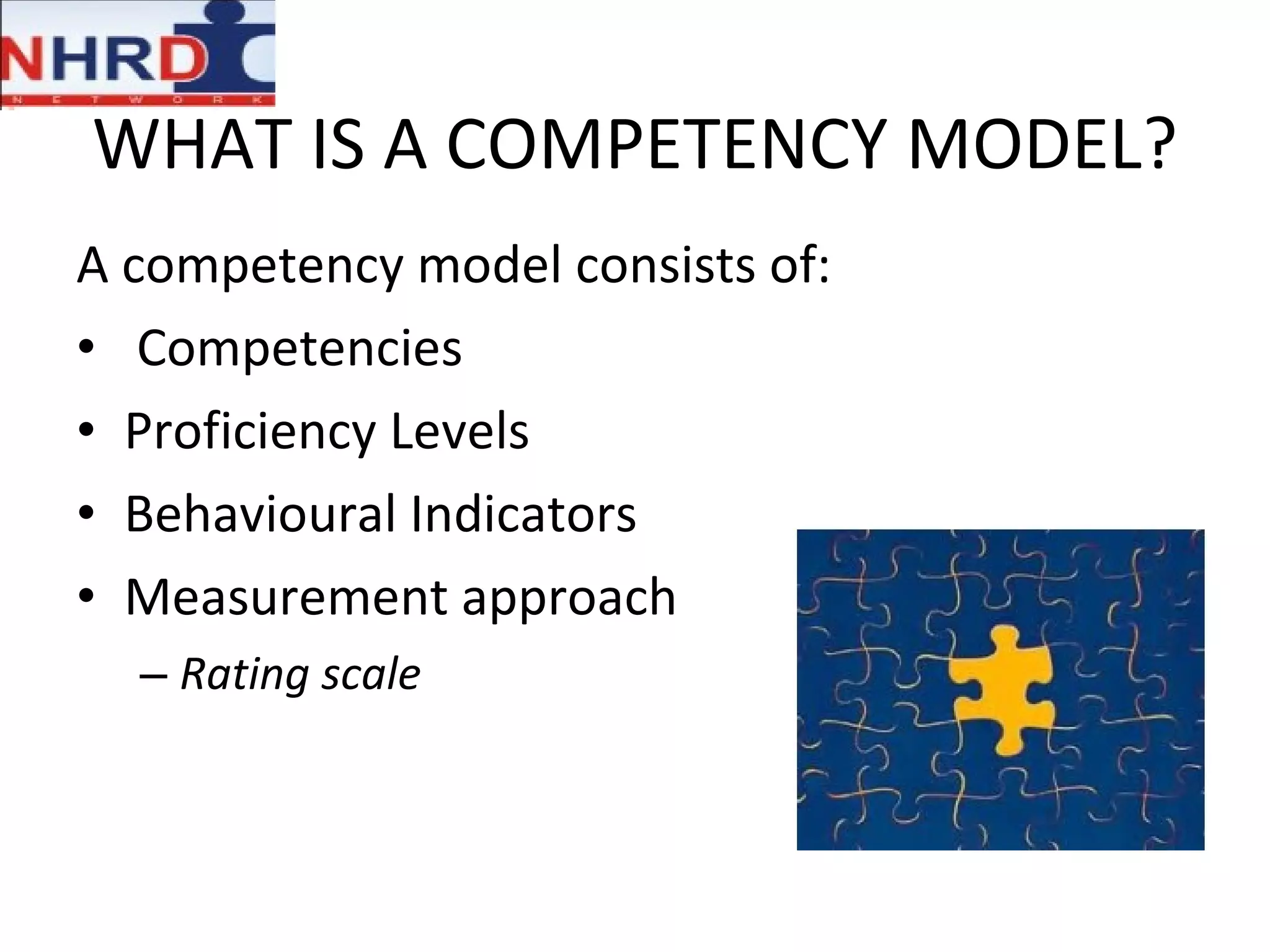
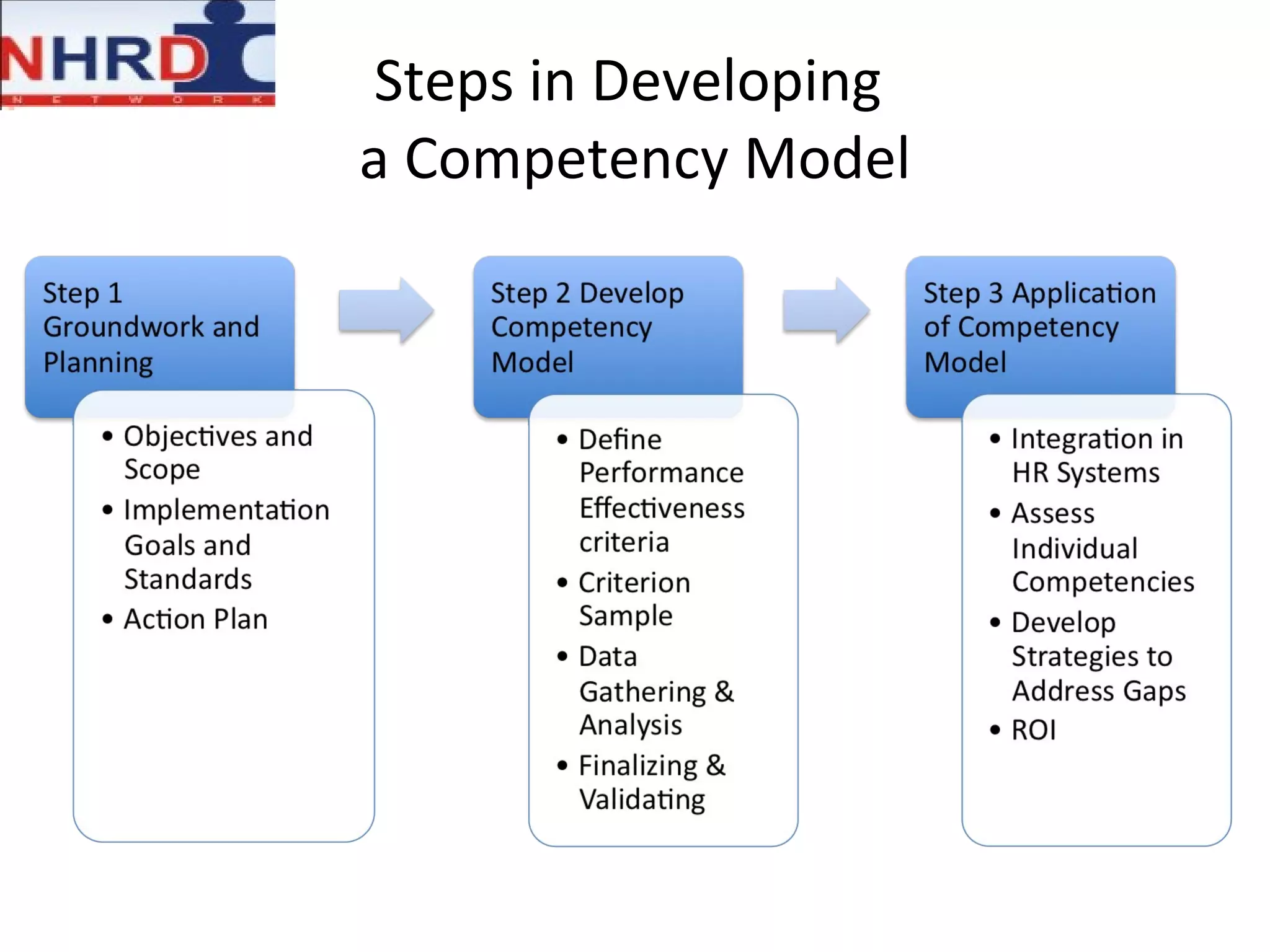
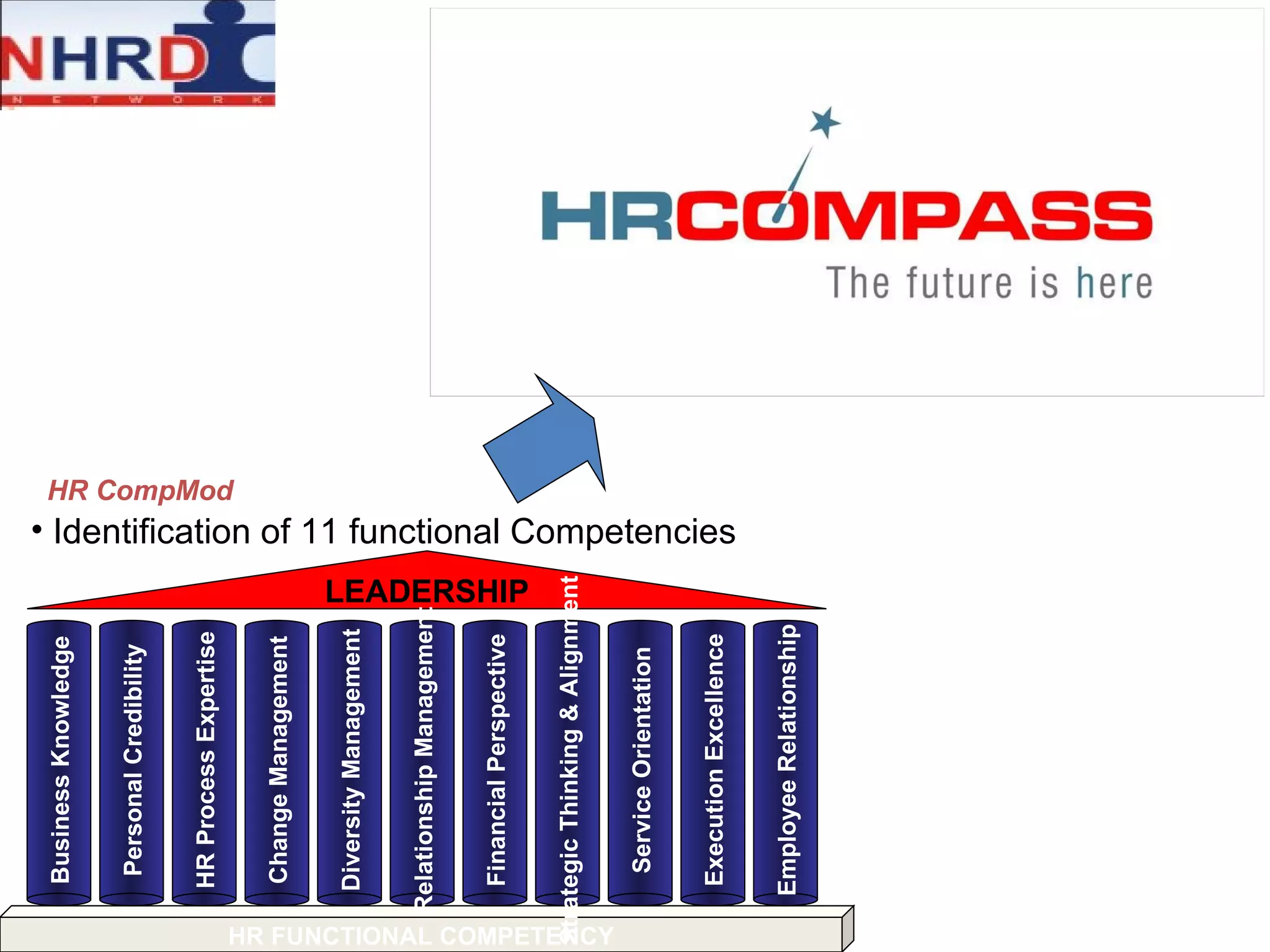
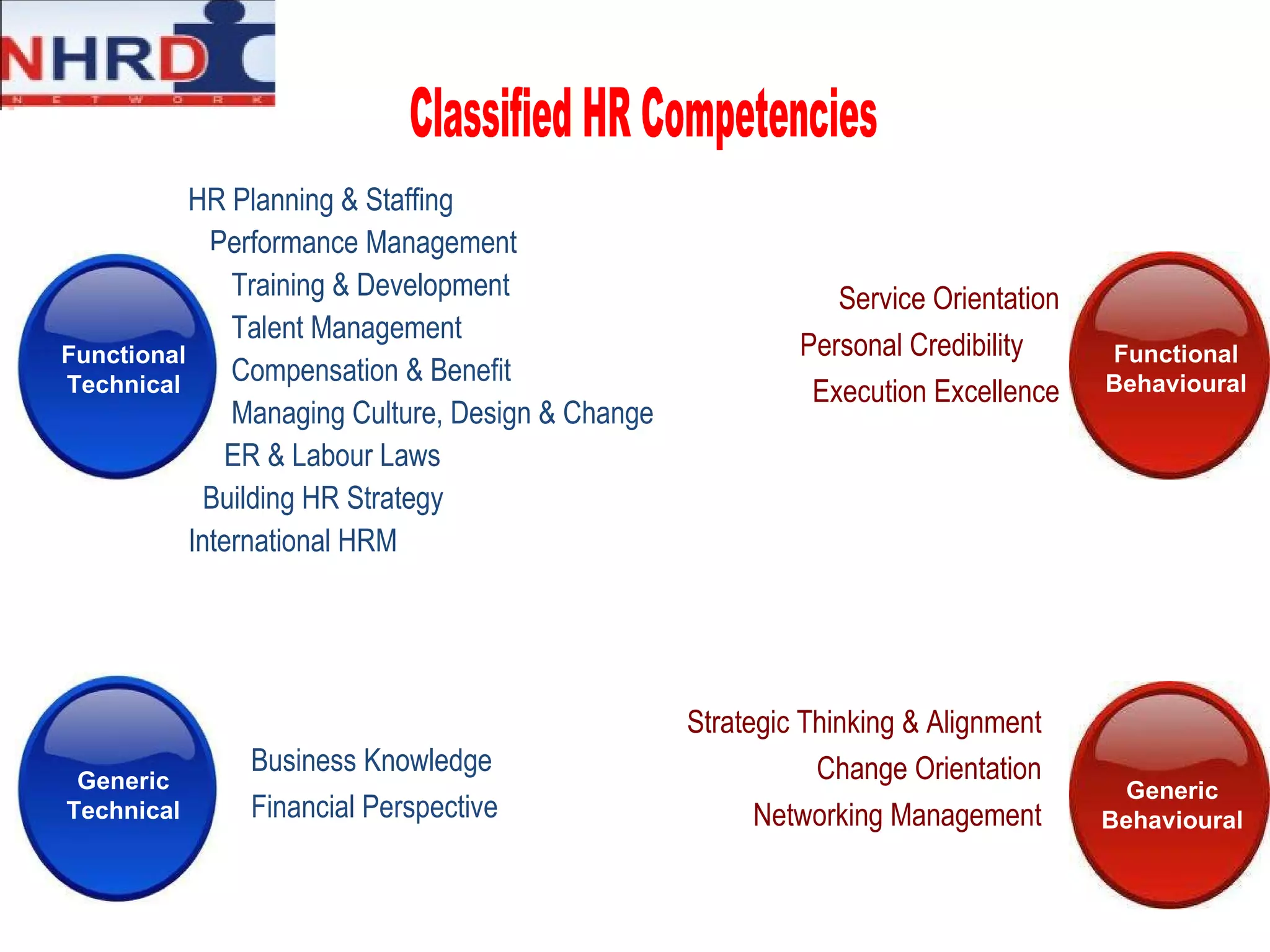
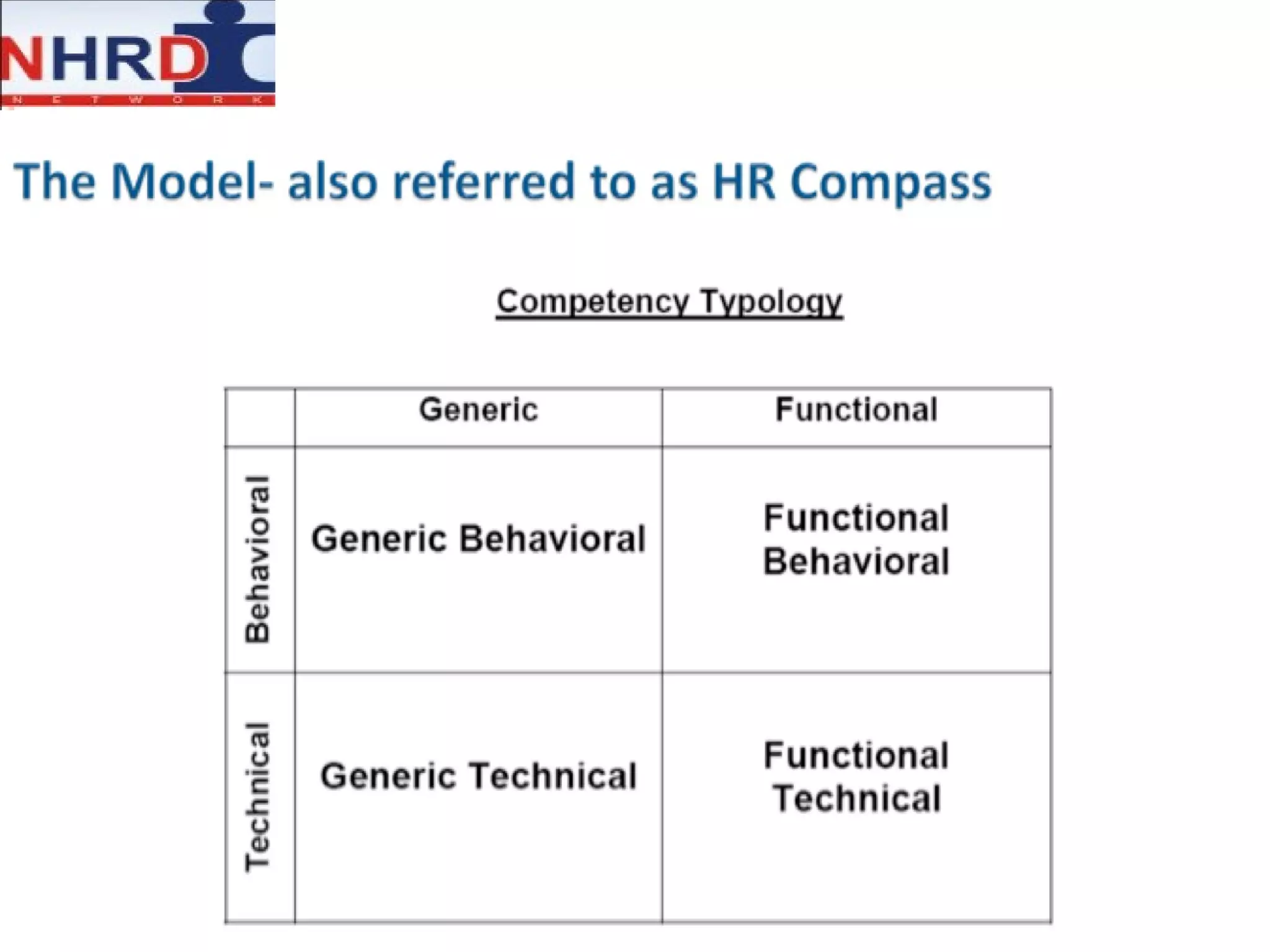
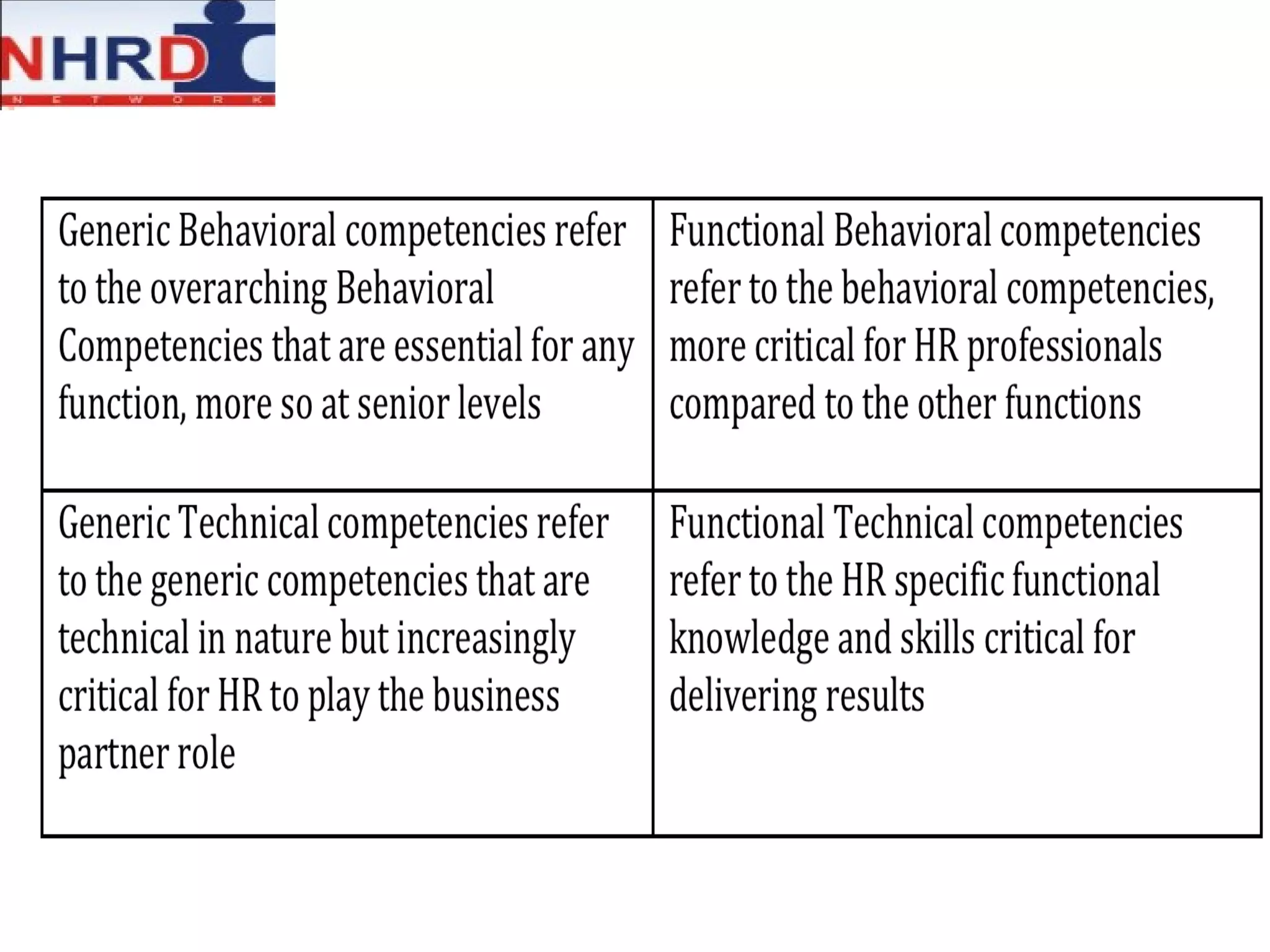
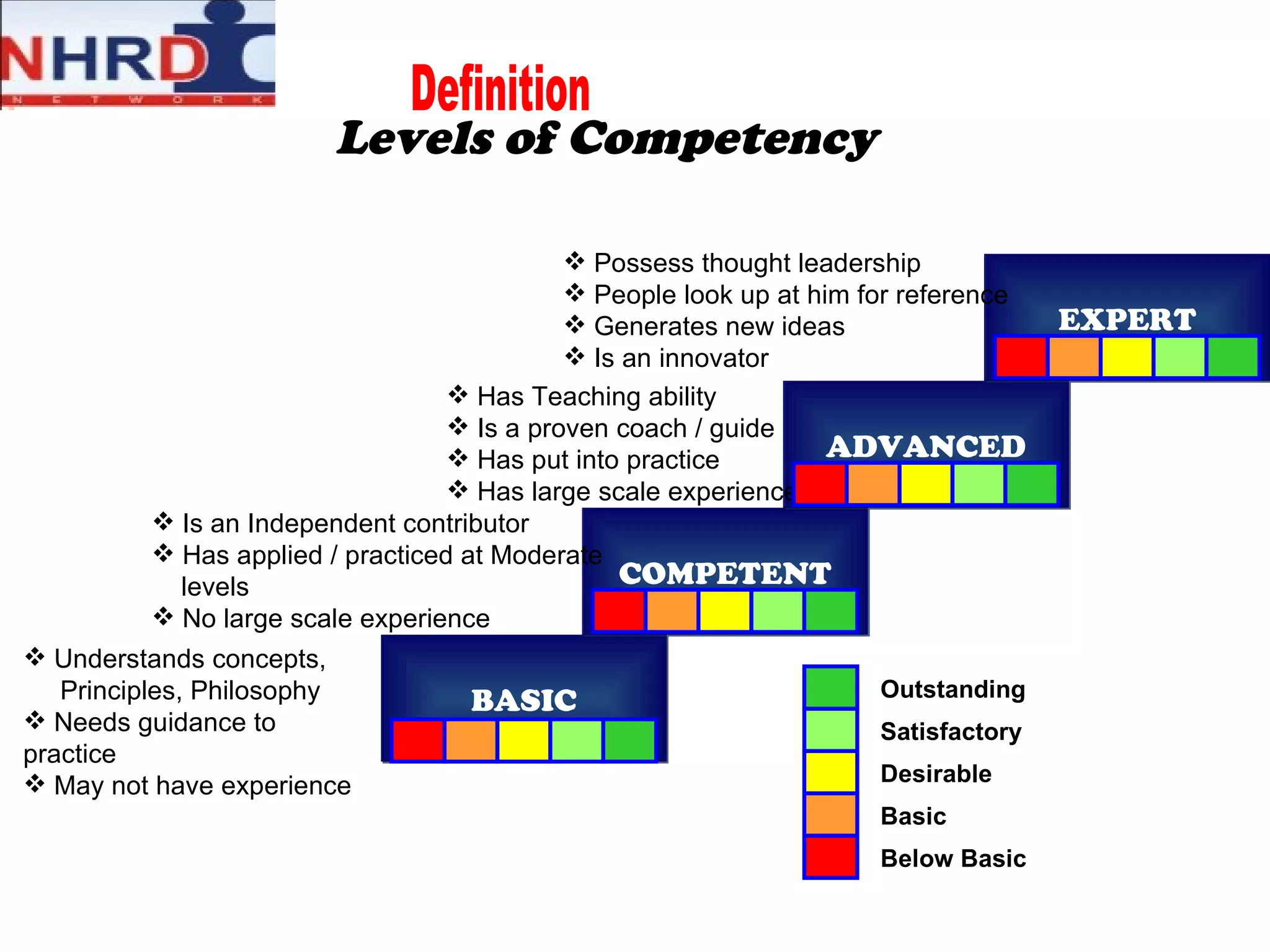
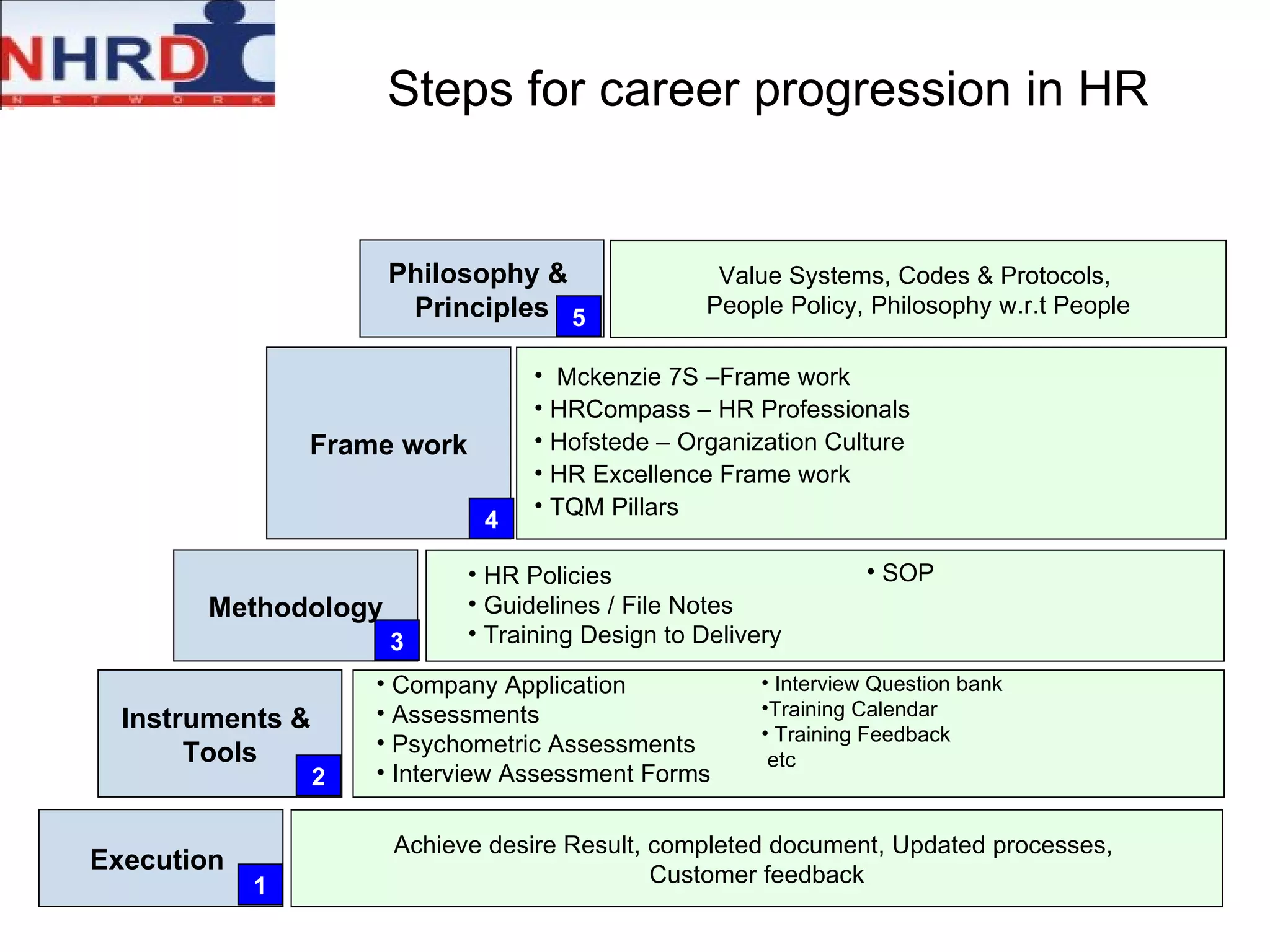
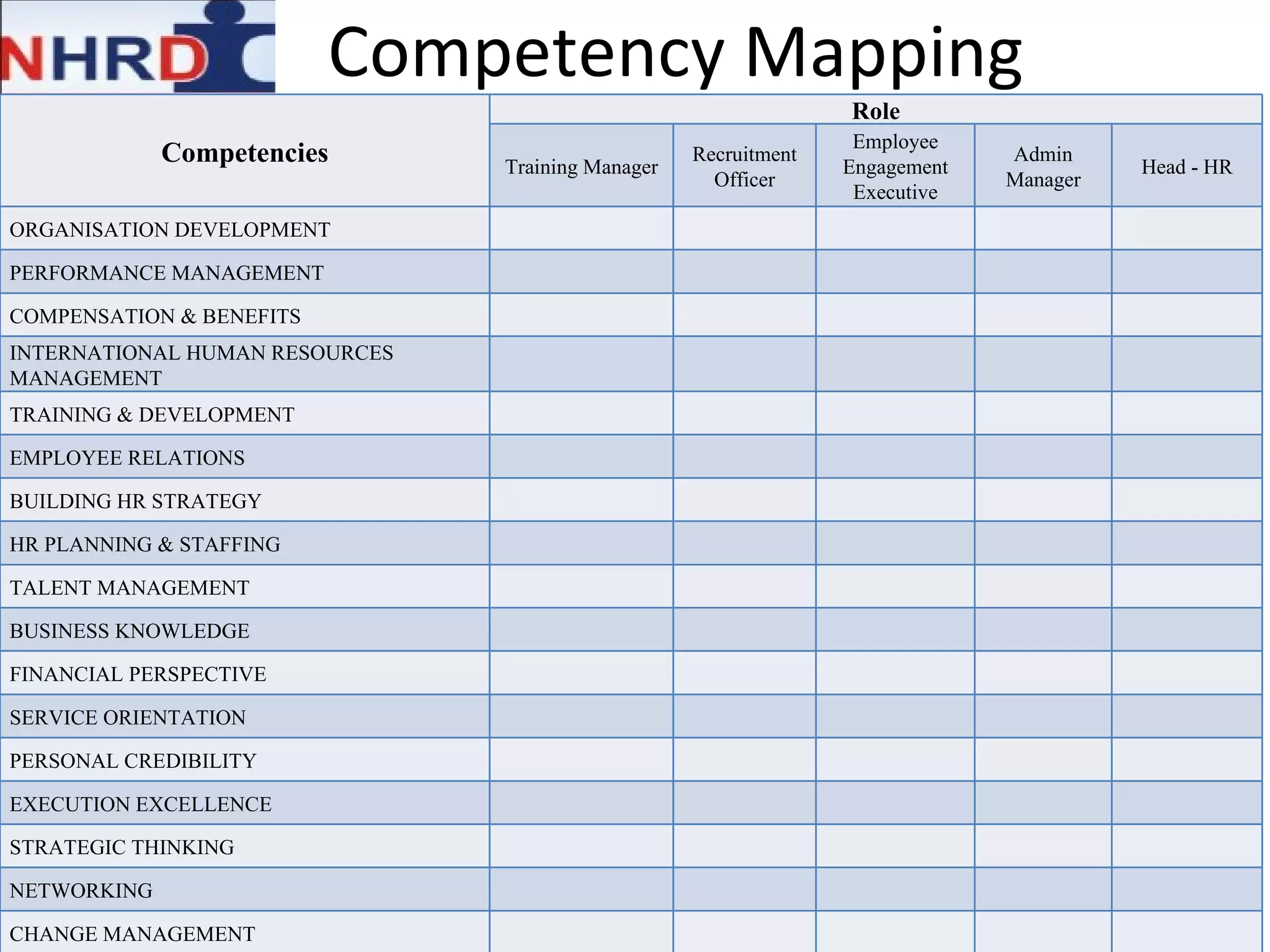
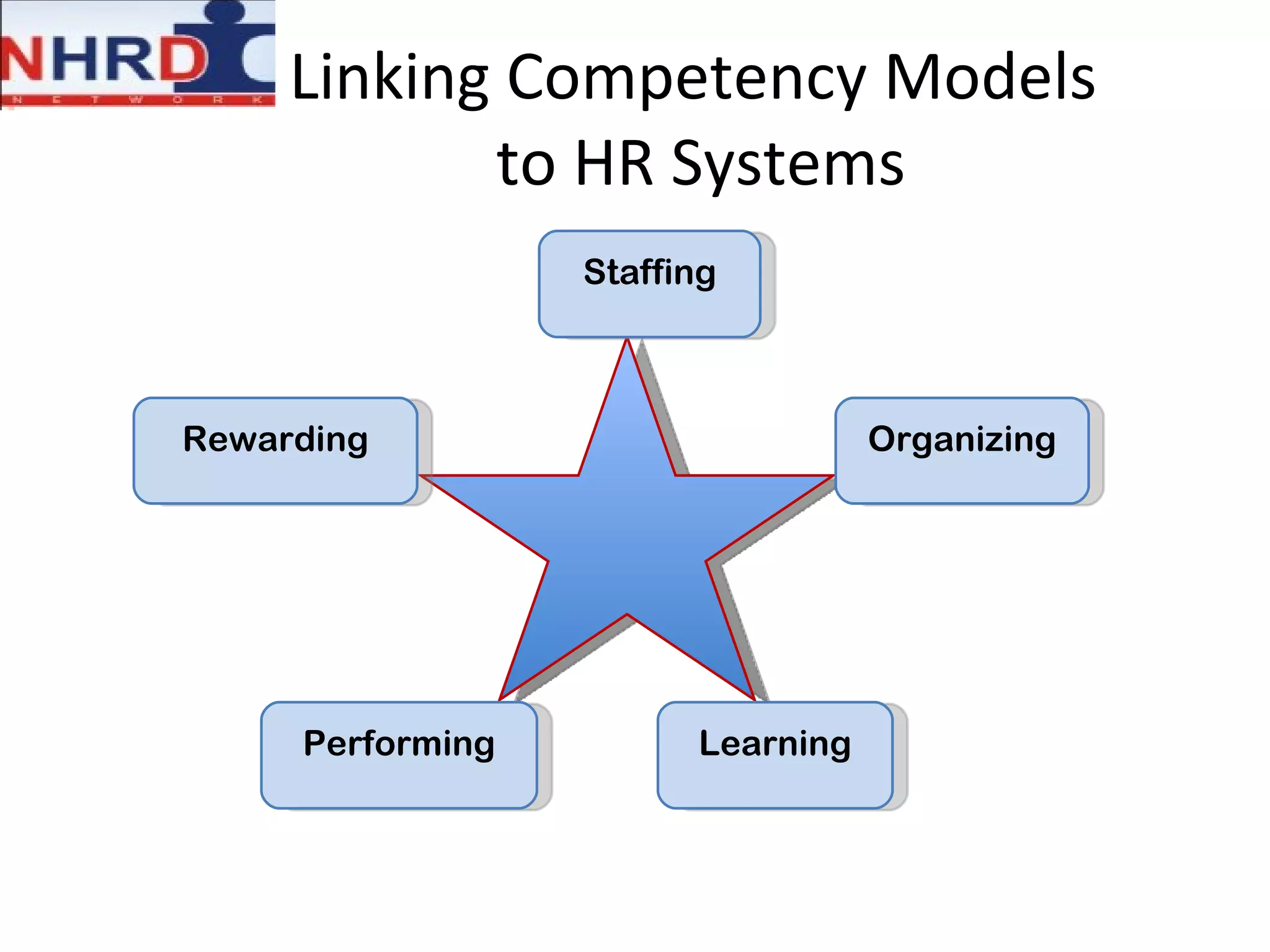
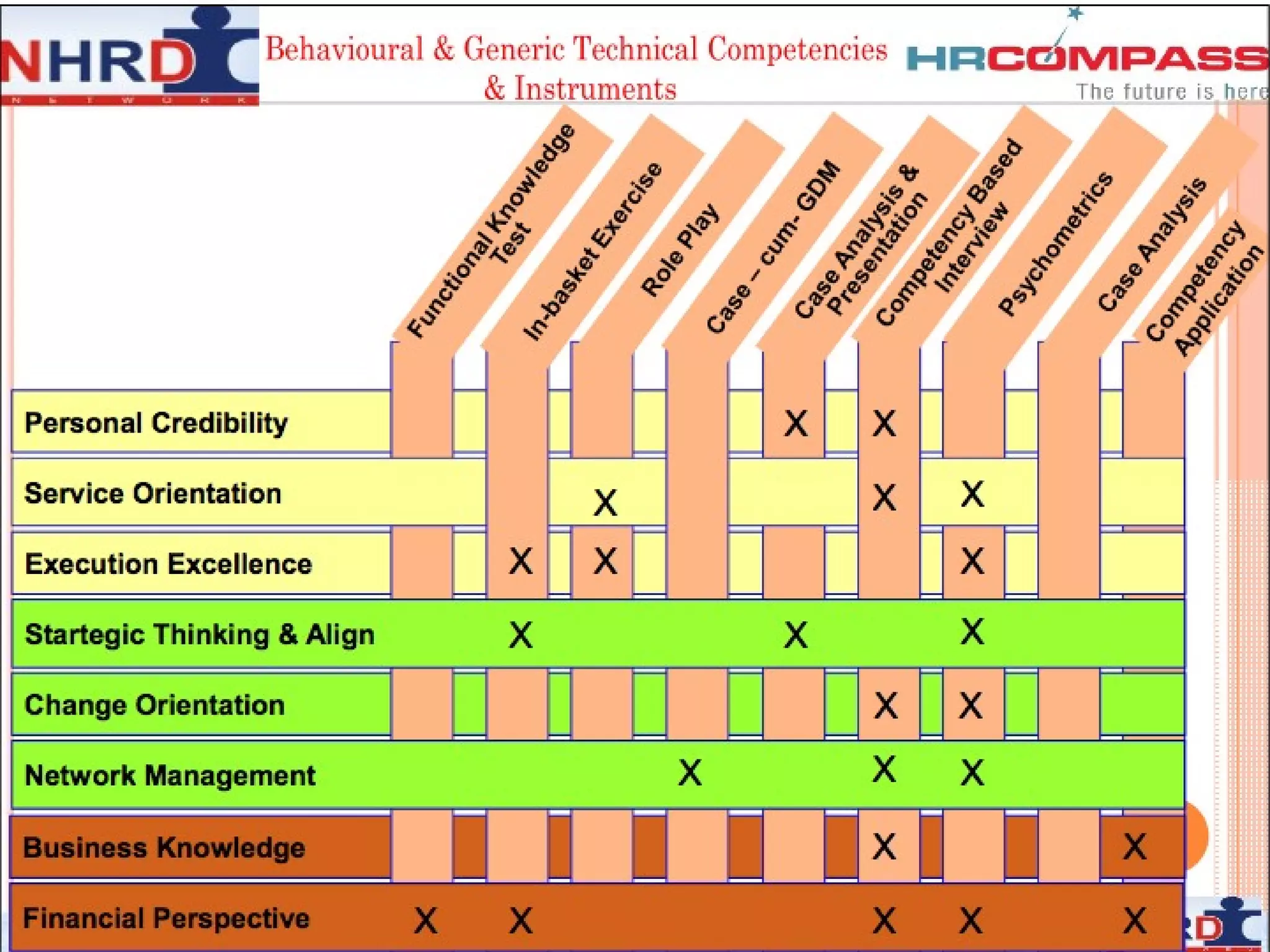
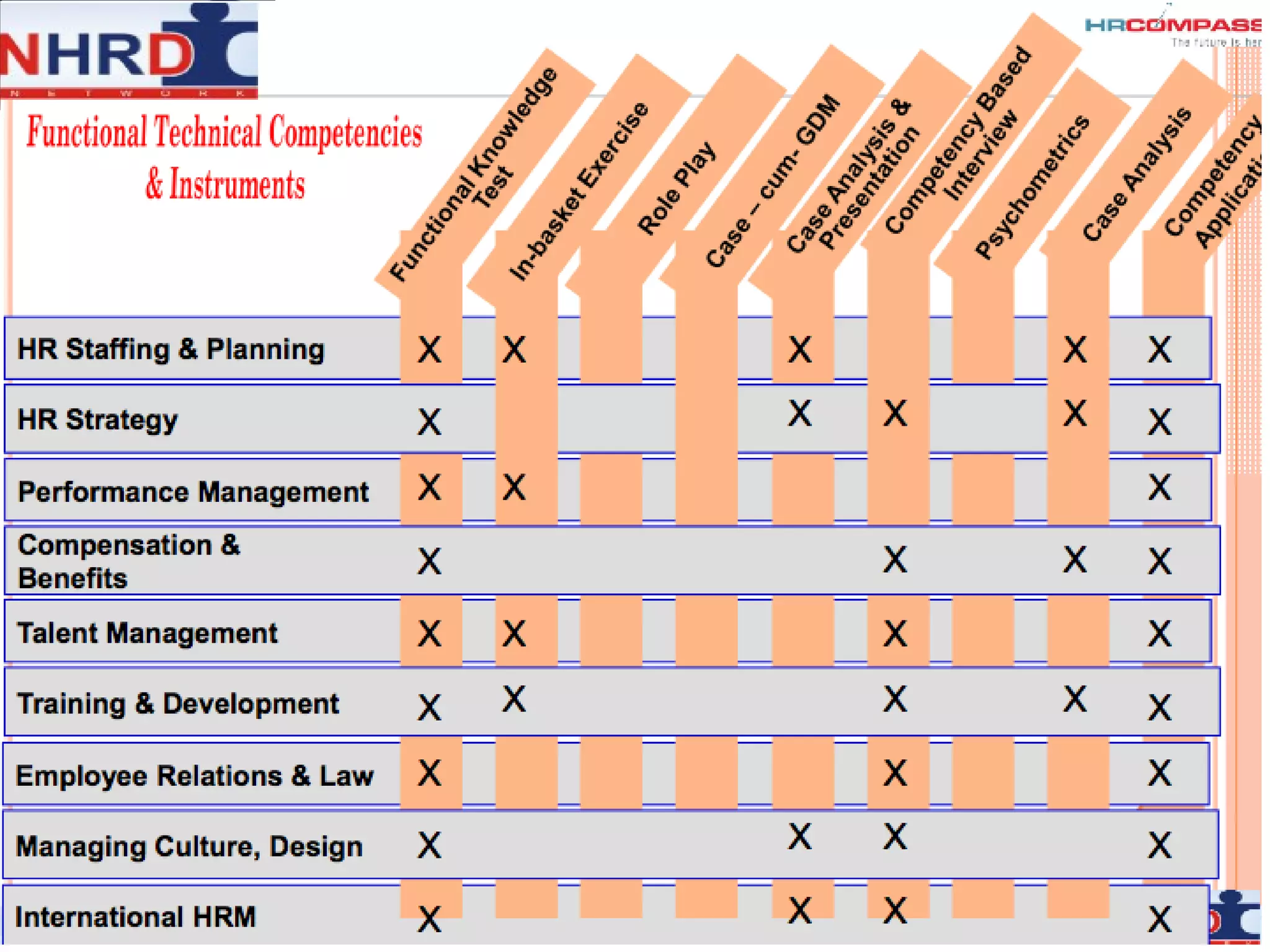
The document discusses competency frameworks and their importance for human resource management. It defines competencies as underlying characteristics that lead to effective performance. Developing competency models involves identifying the competencies, proficiency levels, behavioral indicators, and measurement approaches required for different jobs. Linking competency models to HR systems like staffing, learning, performance management and rewards helps organizations hire the right people, develop employees, set clear expectations, and align compensation with goals.