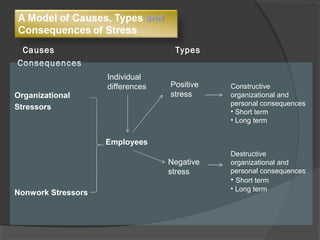
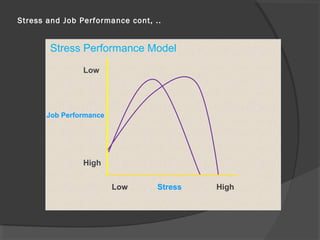
This document discusses stress in the workplace and employee counseling. It begins by defining stress and listing typical negative symptoms like physical, psychological, and behavioral issues. It then covers extreme forms of stress like burnout and trauma. Common causes of stress are discussed, including organizational stressors and non-work stressors. The relationship between stress and job performance is explained, noting that stress can be either helpful or harmful depending on its level. Approaches to managing stress are presented, such as preventing or reducing stressors, escaping stressful situations, and learning coping techniques. Finally, the document outlines different types of employee counseling including directive, nondirective, and participative counseling and discusses their objectives and functions.