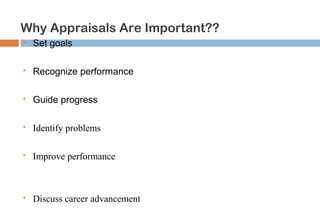
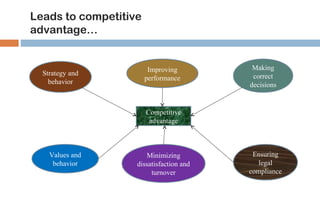
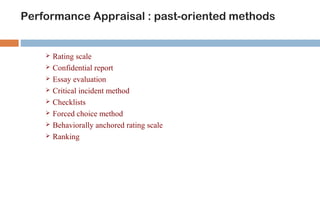
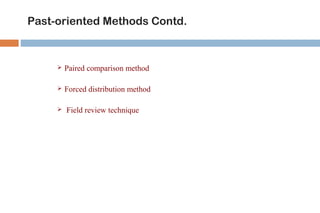
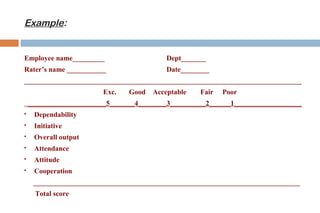
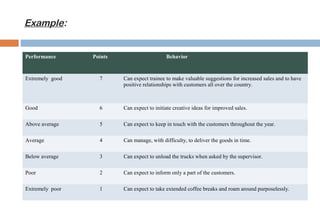
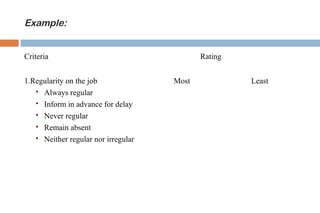
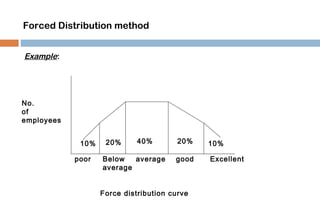
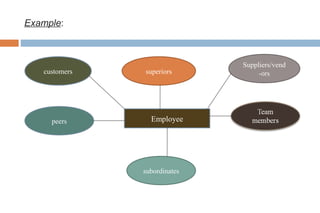
This document discusses various methods used for performance appraisal in organizations. It describes past-oriented methods like rating scales, confidential reports, essays and checklists that evaluate past performance. Future-oriented methods like management by objectives, 360-degree feedback, and assessment centers are aimed at setting goals and standards for future improvement. The document provides examples and limitations of different appraisal techniques to help organizations select the most appropriate method.