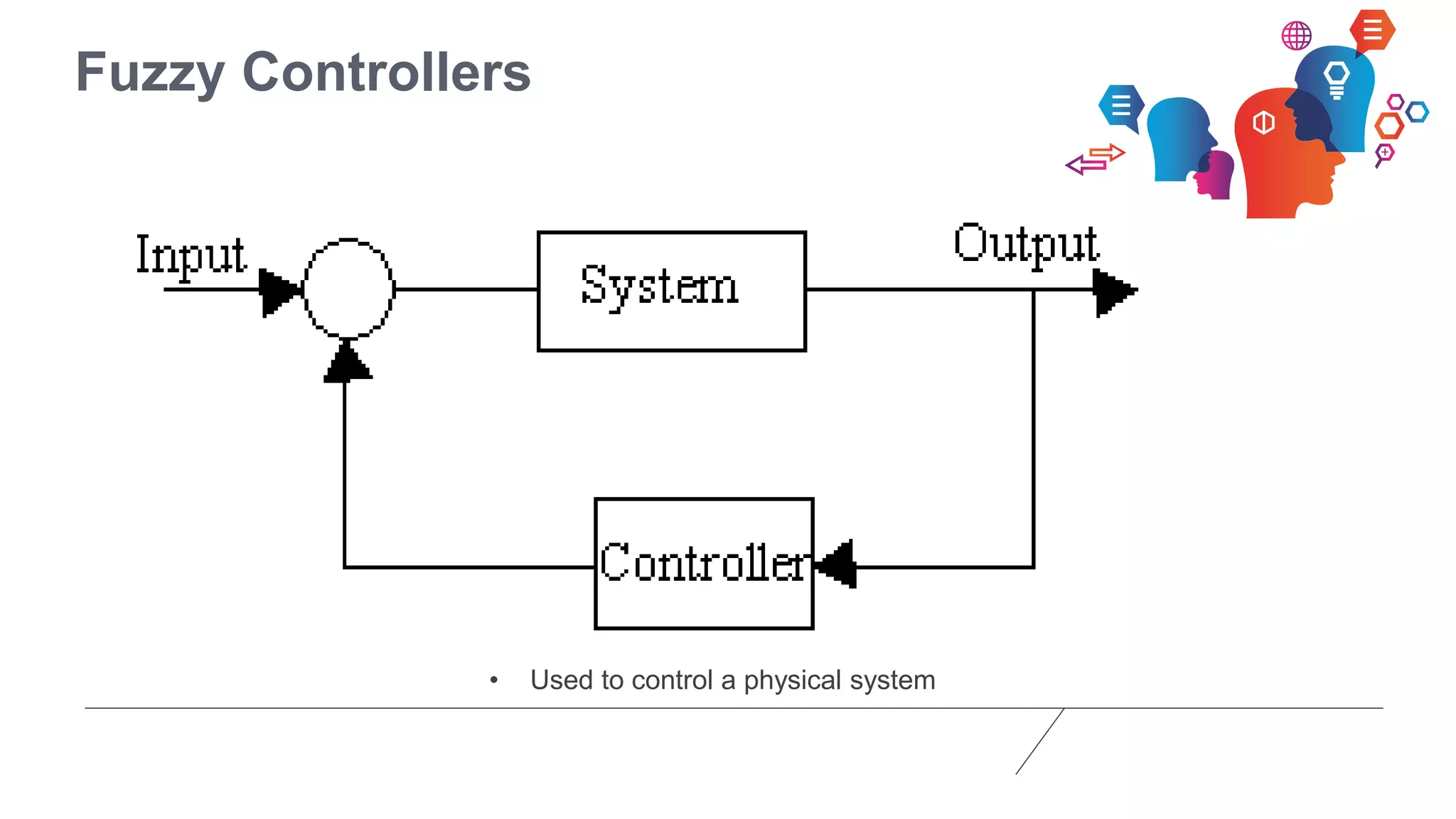
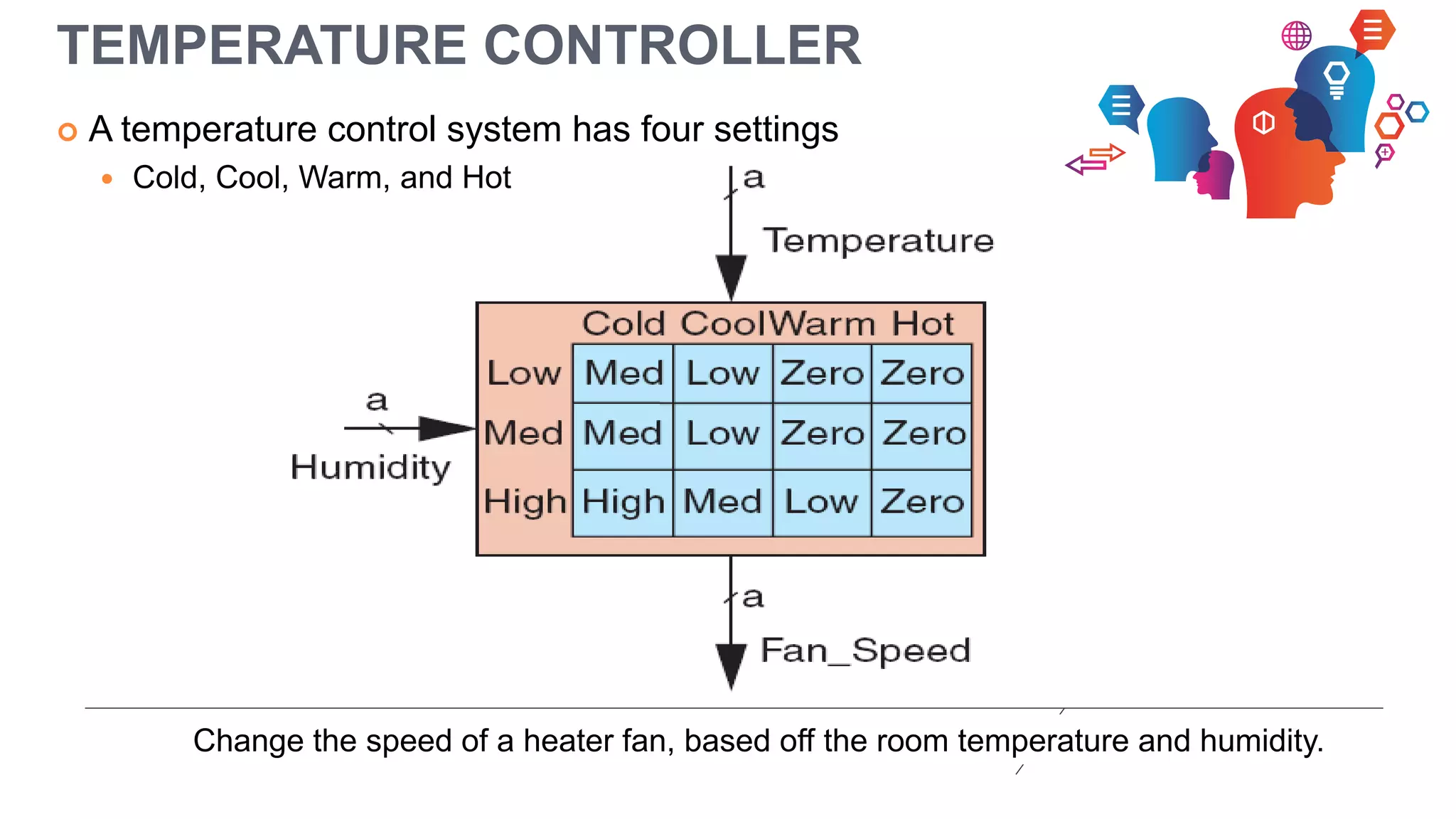
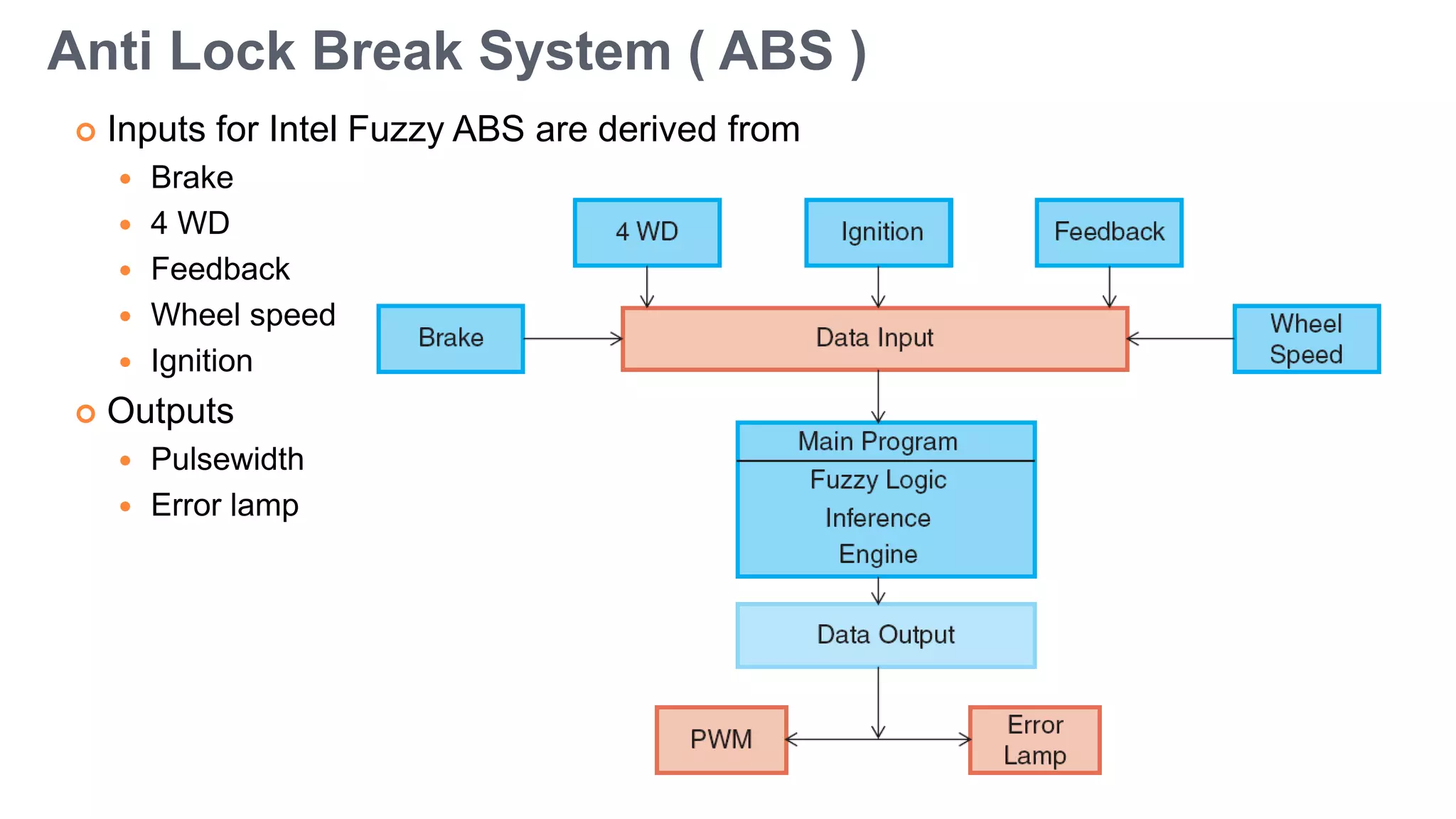
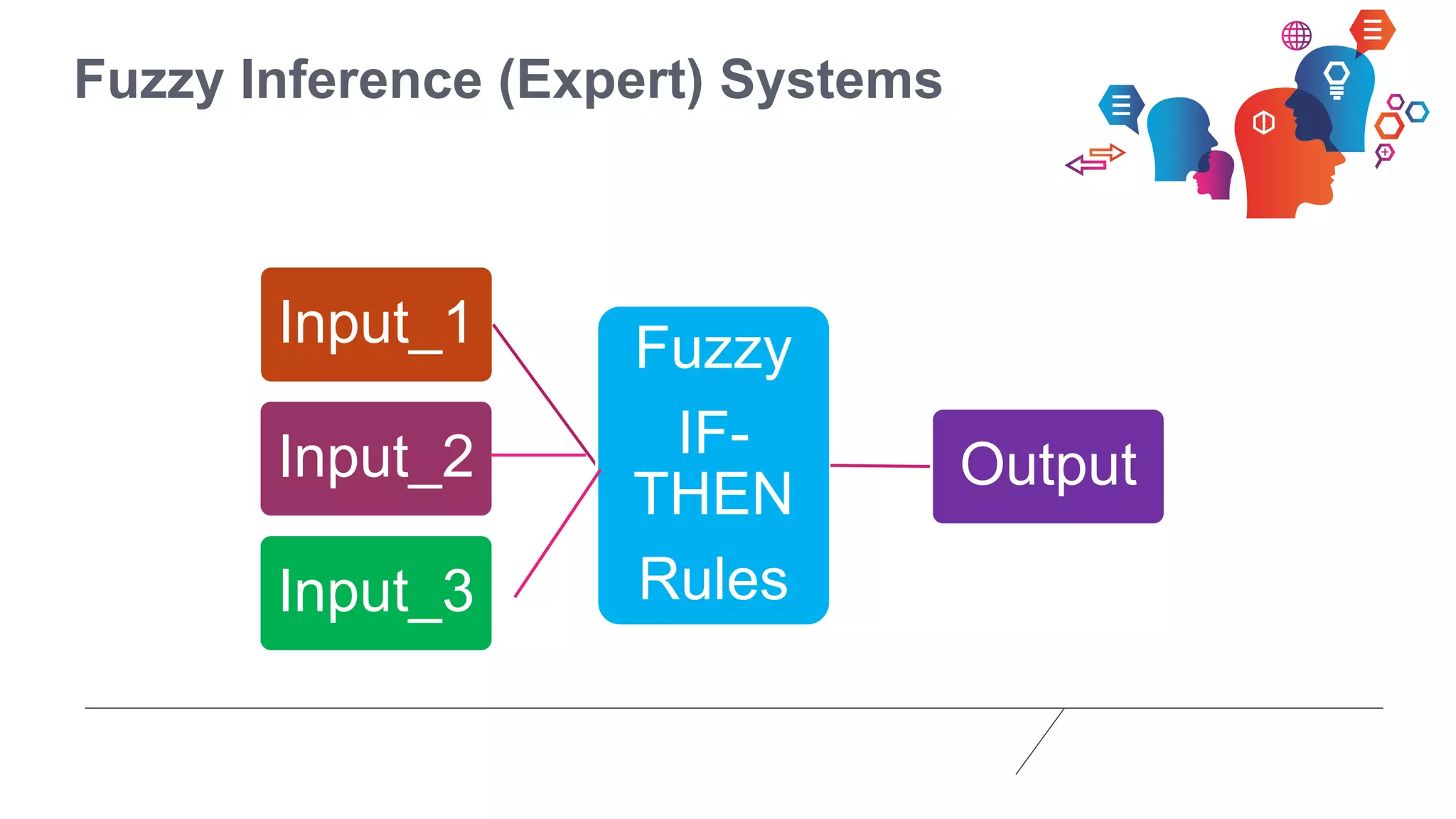
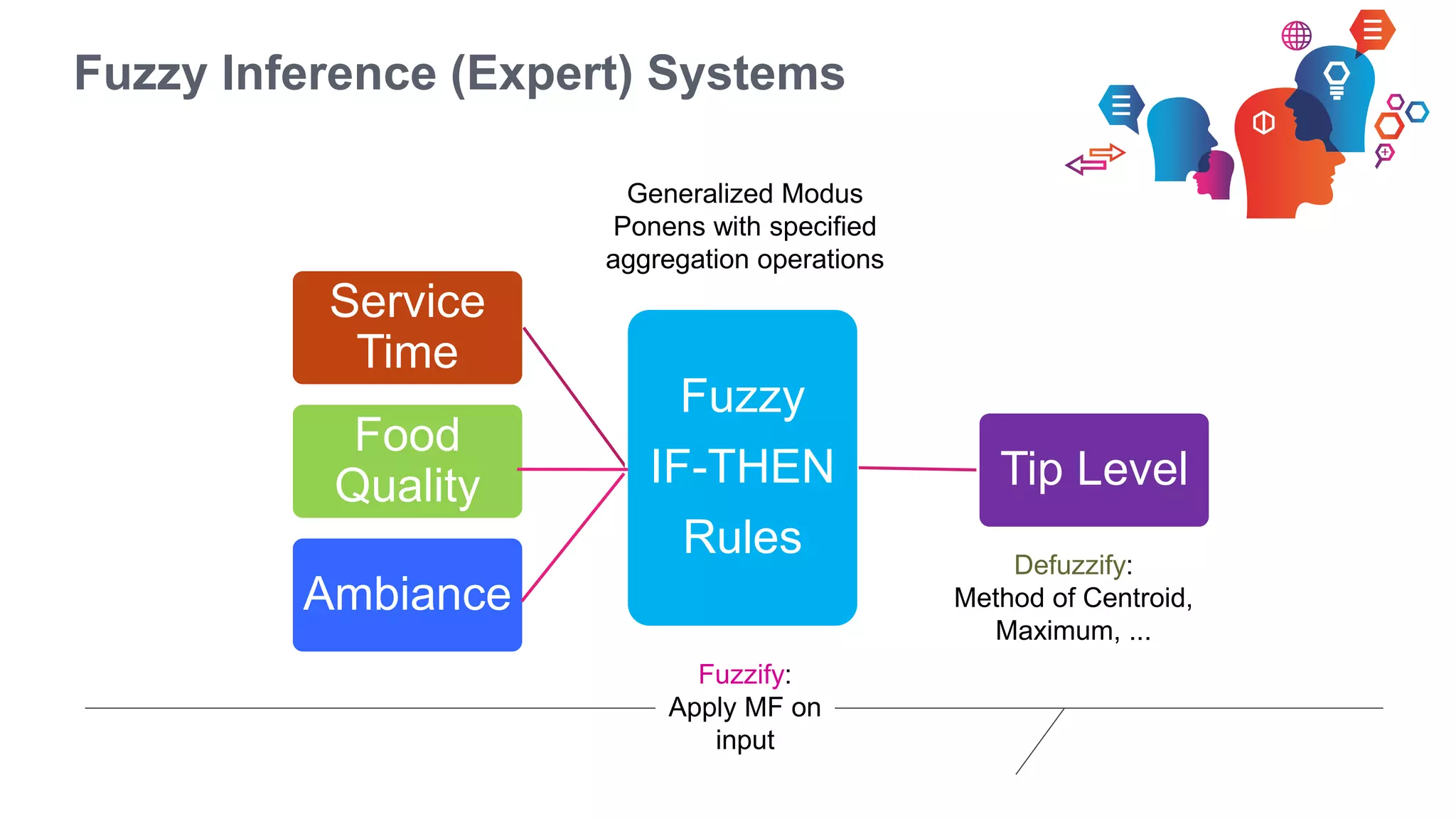
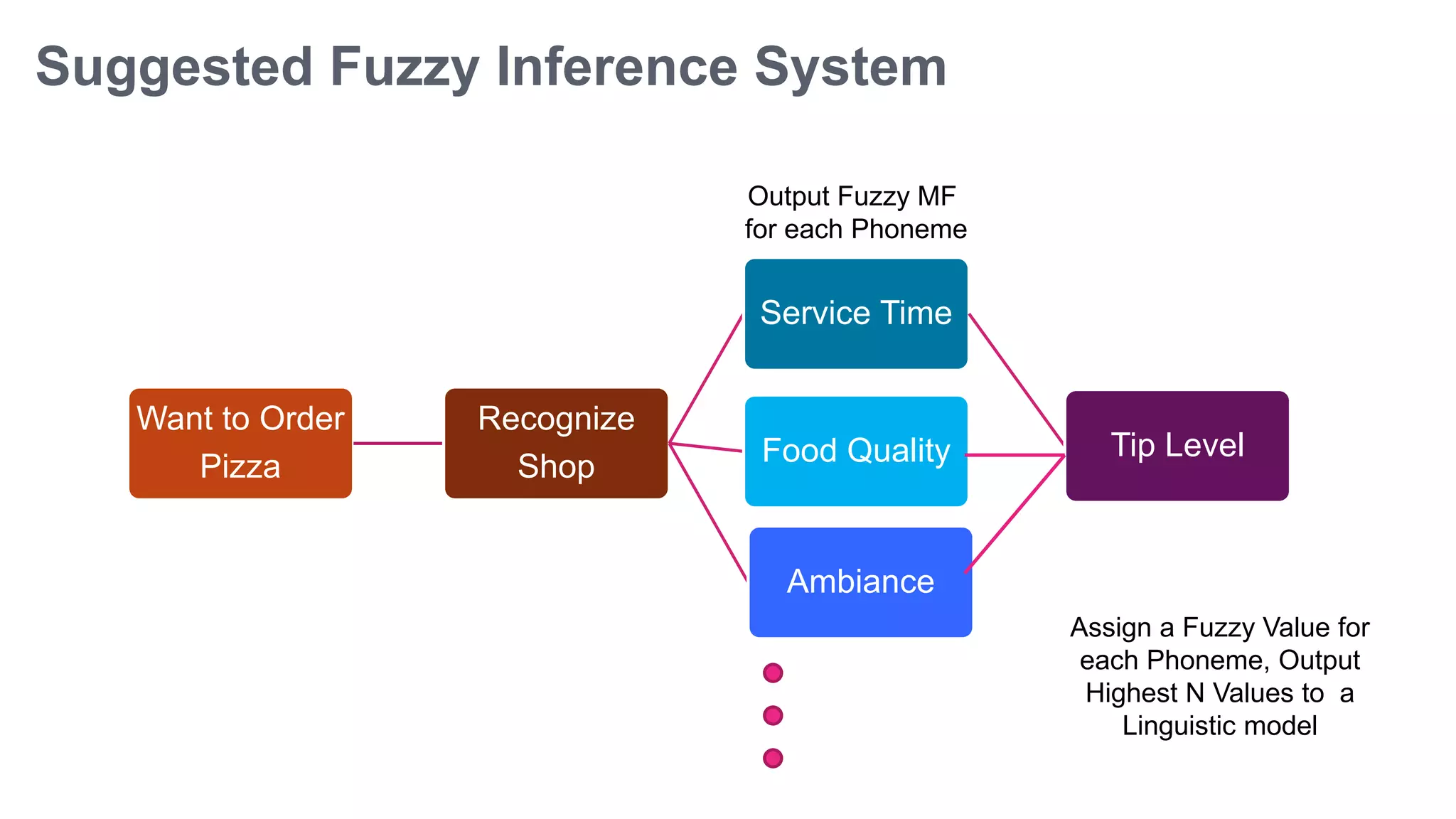
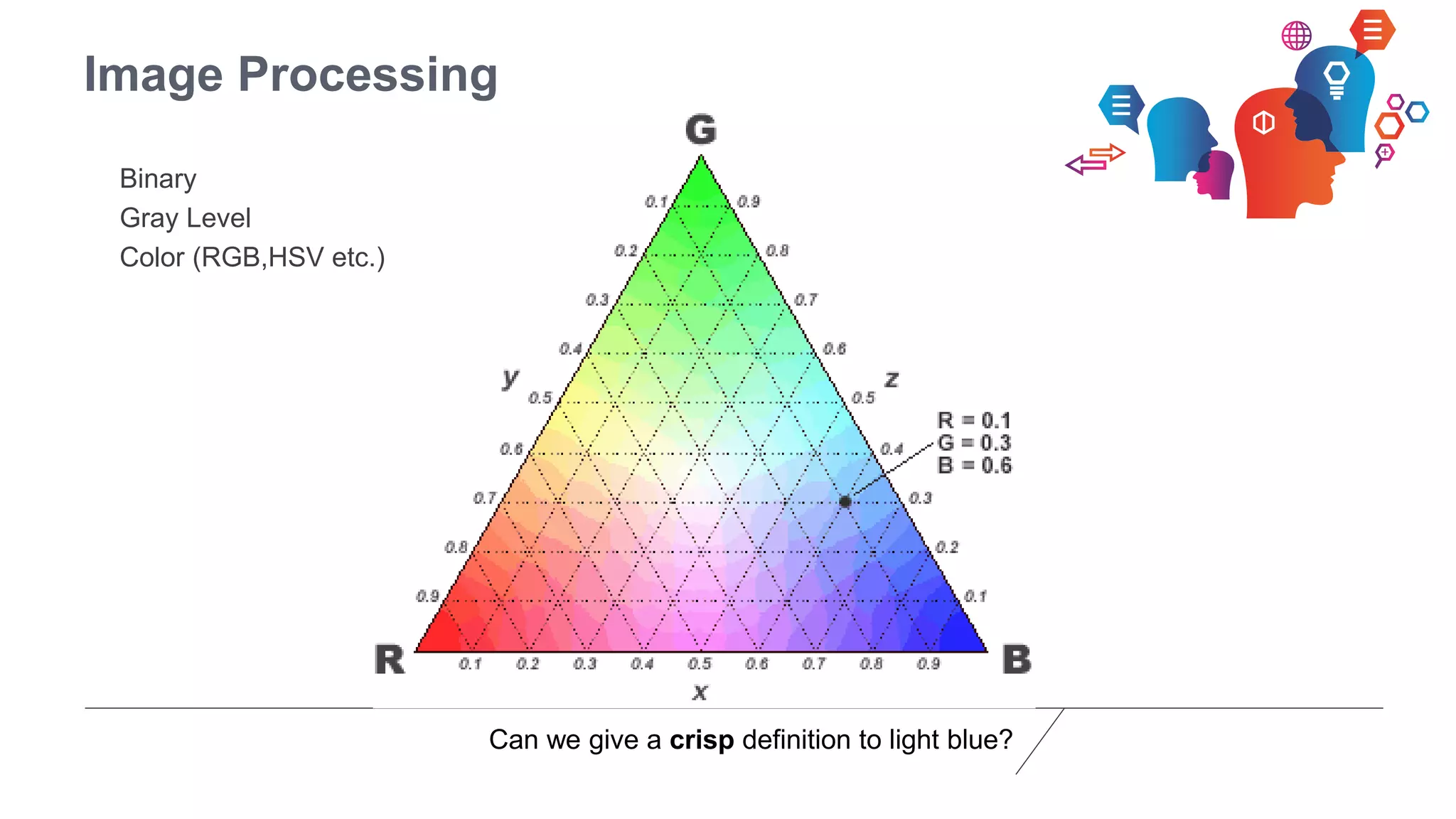
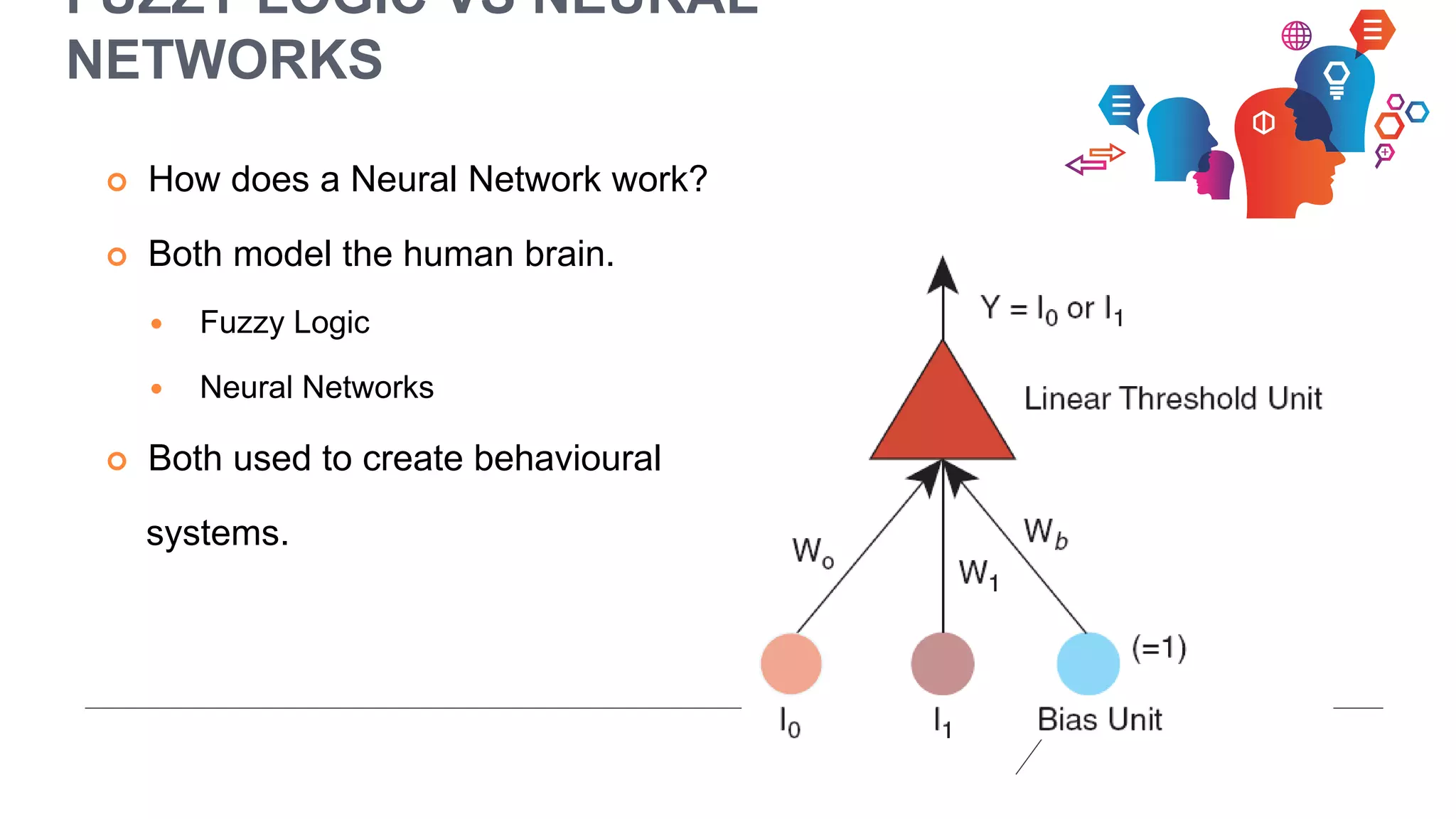
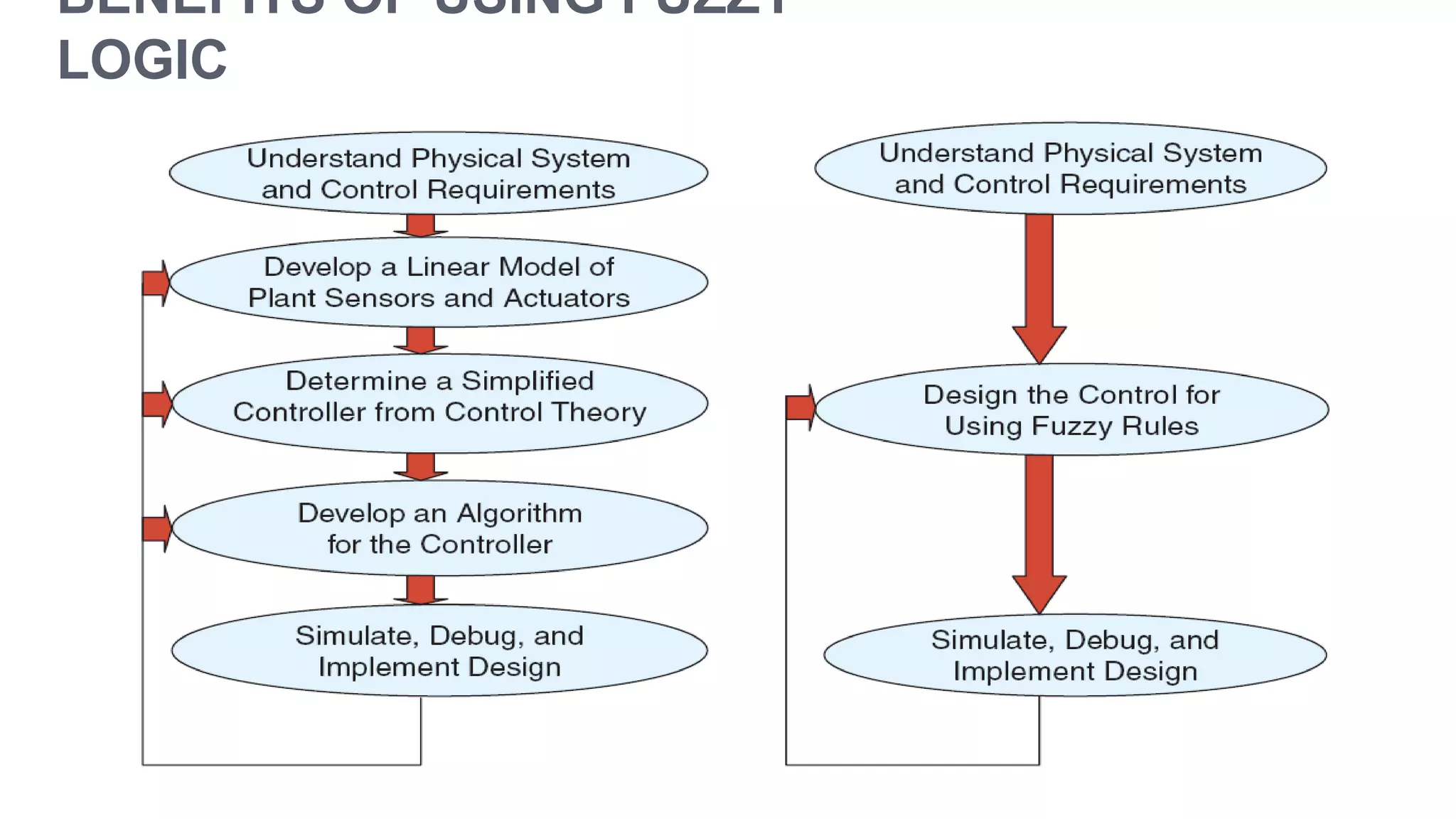
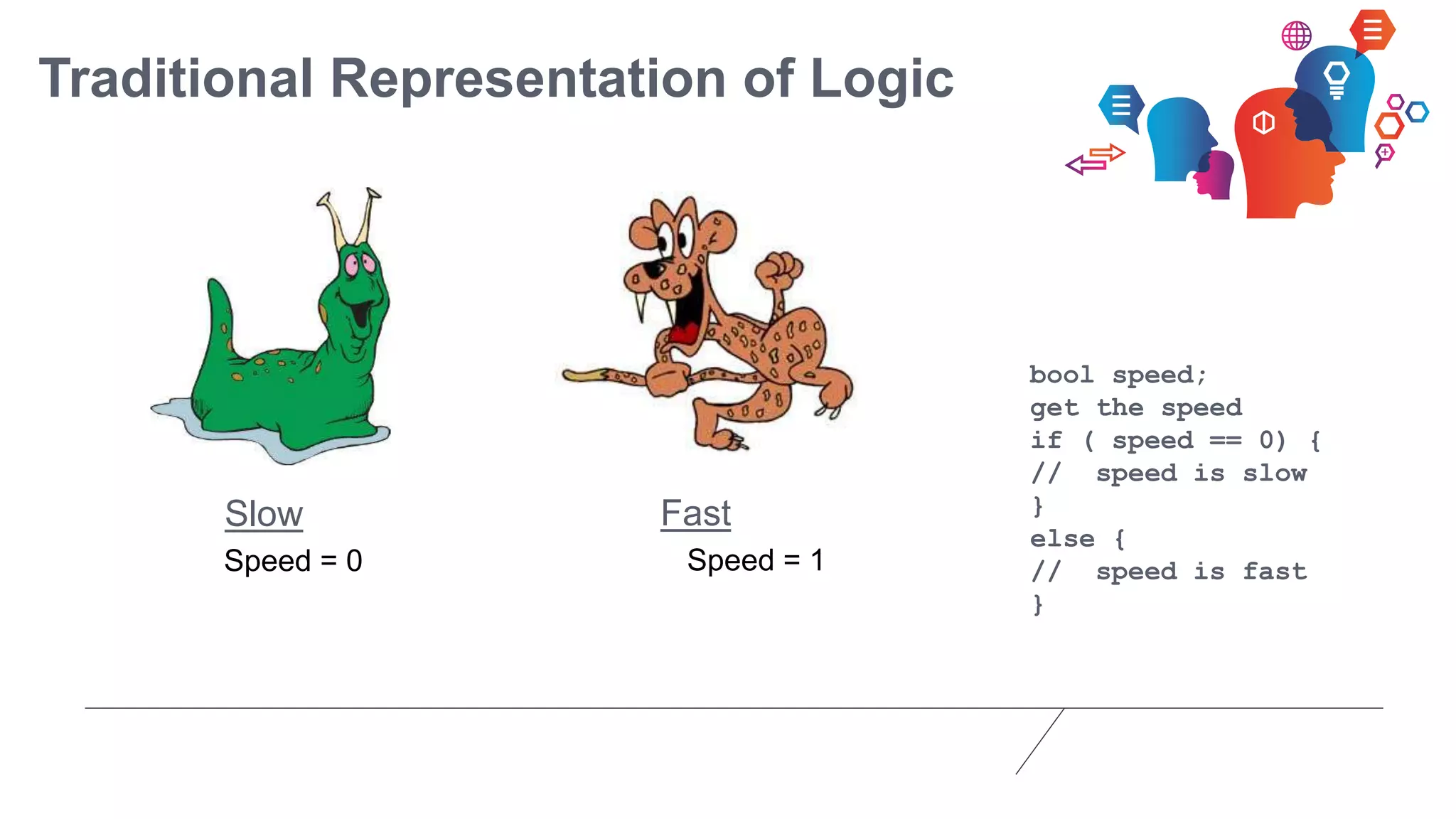
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic that helps in representing knowledge for ambiguous concepts and is closely aligned with human reasoning. Its applications range from control systems, such as anti-lock brakes and temperature controllers, to expert systems. The technique allows for approximate solutions and processes incomplete data, filling gaps left by traditional binary logic methods.



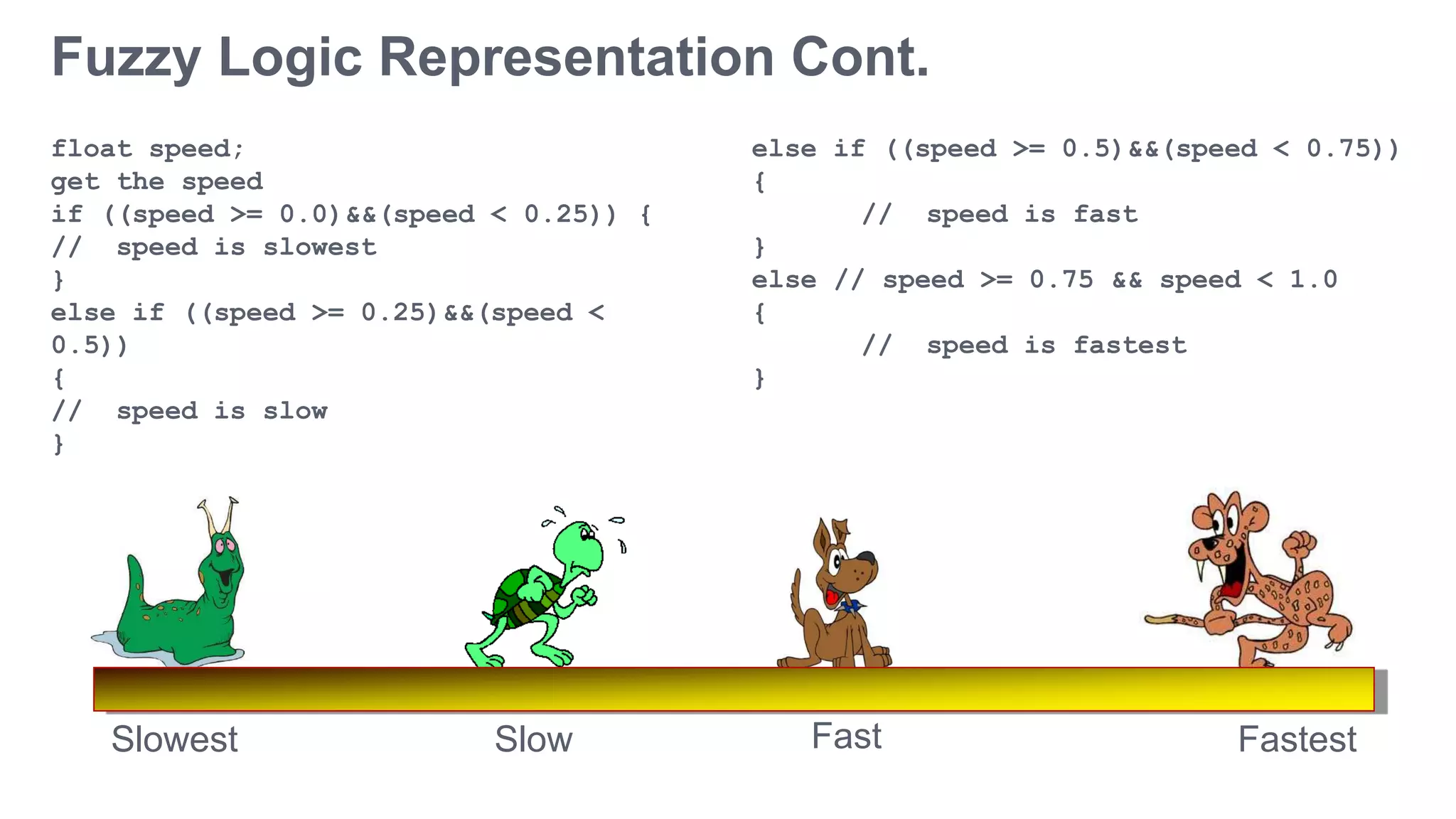
![Fuzzy Logic Representation
For every problem must represent in terms of fuzzy sets
What are fuzzy sets?
Slowest Fastes
t
Slow Fast
[ 0.0 – 0.25 ] [ 0.25 – 0.50
]
[ 0.50 – 0.75
]
[ 0.75 – 1.00
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzylogicmis-161209165736/75/Fuzzy-logic-mis-13-2048.jpg)