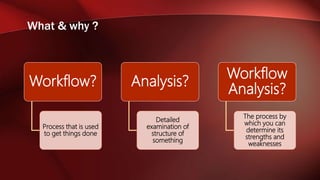
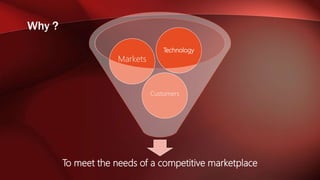
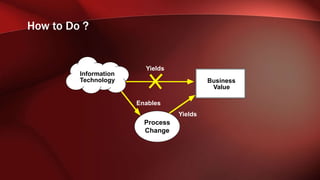
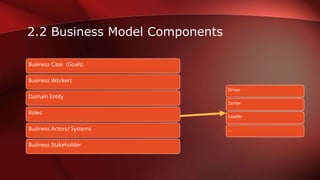
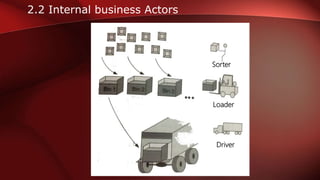
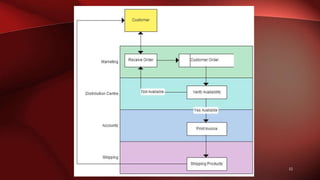
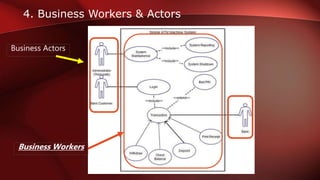
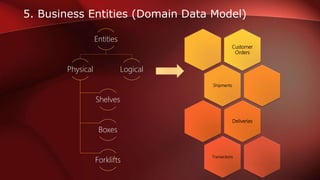
The document discusses workflow analysis for businesses. It defines workflow analysis as examining a process to determine its strengths and weaknesses. Workflow analysis is done to meet competitive needs by increasing efficiency, optimizing space utilization, improving customer satisfaction, easing regulatory compliance, and boosting employee morale. Major steps involve qualitative and quantitative process analysis. Key methods outlined are interviews, observations, process modeling, value chain analysis, and cost analysis. The document also provides templates for outlining a business model by describing the environment, workflows, actors, and key entities.