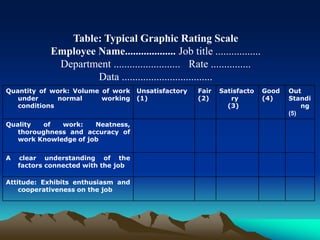
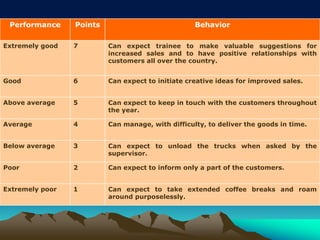
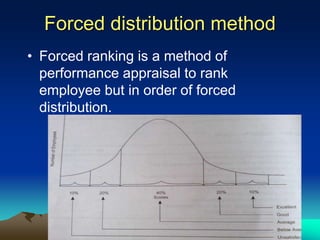
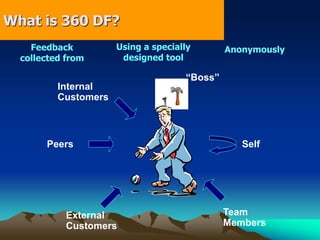
The presentation outlines performance appraisal (PA) as a method for evaluating employee behavior and performance in the workplace, covering both quantitative and qualitative aspects. It emphasizes the importance of regular performance reviews for providing feedback, identifying training needs, and aiding in career planning. Various appraisal methods are discussed, including traditional graphic rating scales, ranking techniques, and modern approaches such as 360-degree feedback, highlighting common challenges in conducting appraisals.