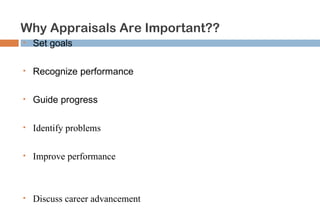
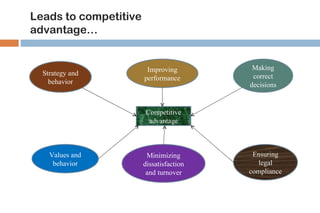
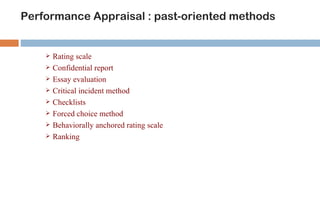
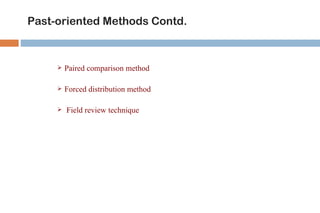
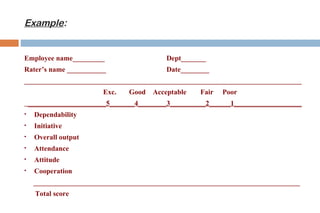
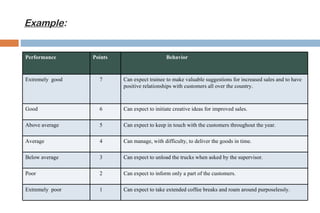
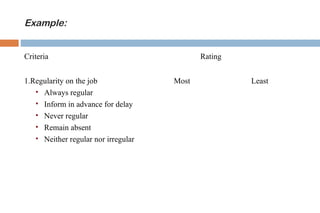
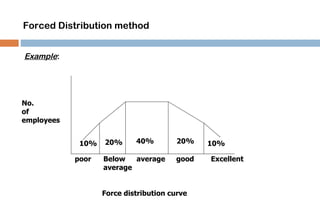
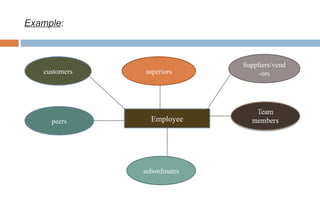
This document discusses various methods used for performance appraisal. It describes past-oriented methods like rating scales, confidential reports, essays and checklists that evaluate past performance. Future-oriented methods like management by objectives, 360-degree feedback, and psychological appraisals focus on future potential. The document emphasizes that performance appraisal is important to set goals, recognize performance, guide progress, identify problems, and improve performance. It also leads to competitive advantage by improving strategy, behavior, decision-making and ensuring legal compliance.