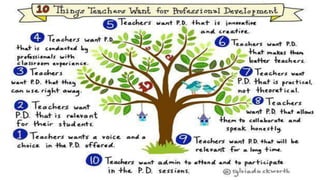
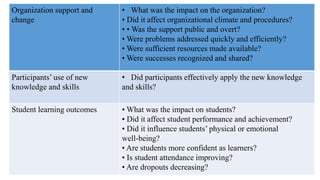
Professional development and accountability are important for teachers. It involves enhancing teachers' knowledge, skills, and practices to improve student learning. Good professional development is long-term, focused on content and skills, collaborative, and transformative by giving teachers new ideas to change their classroom practices. It is important to evaluate professional development for accountability to funders and to ensure knowledge gains are applied and improve student outcomes over time.