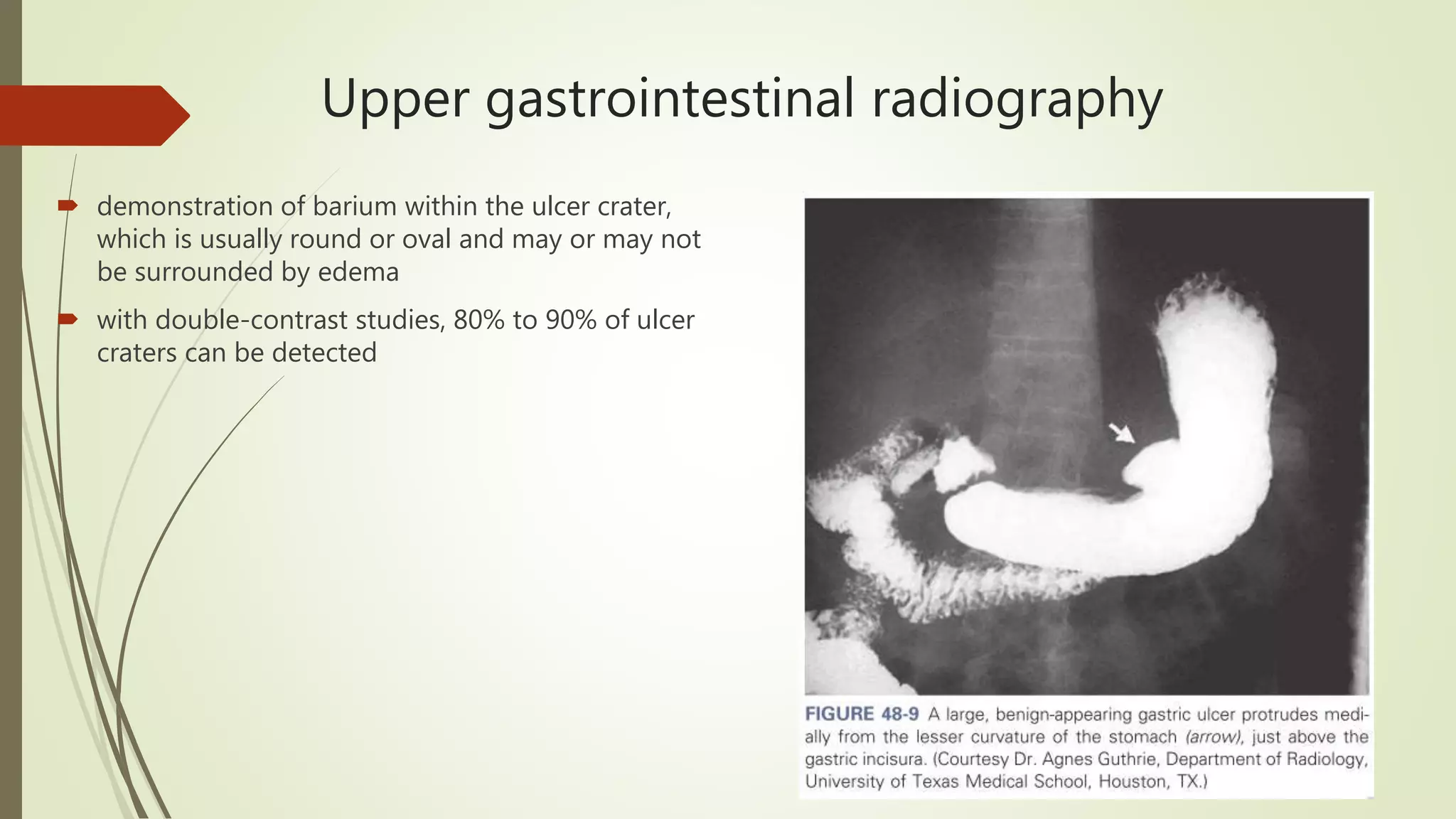
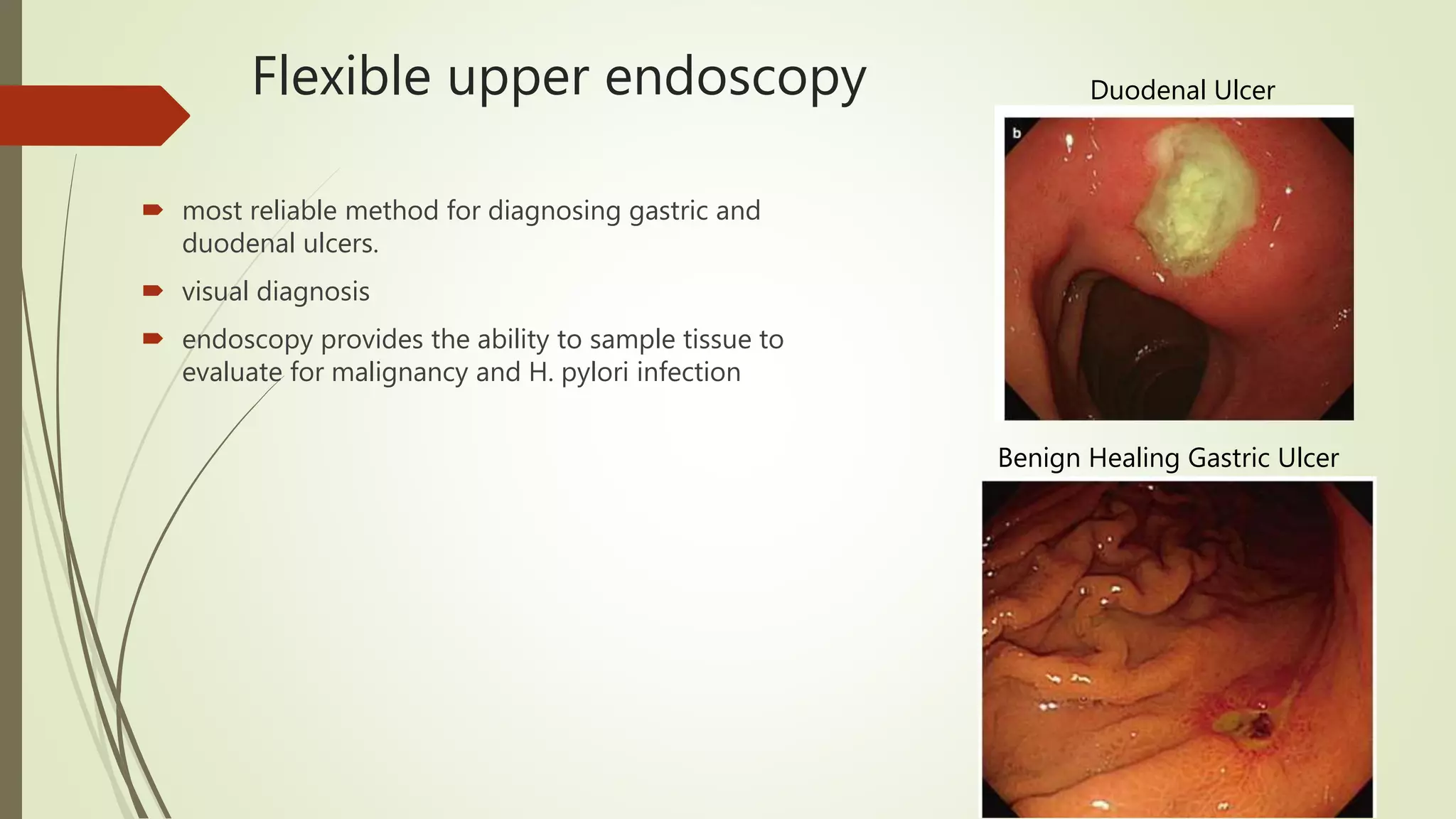
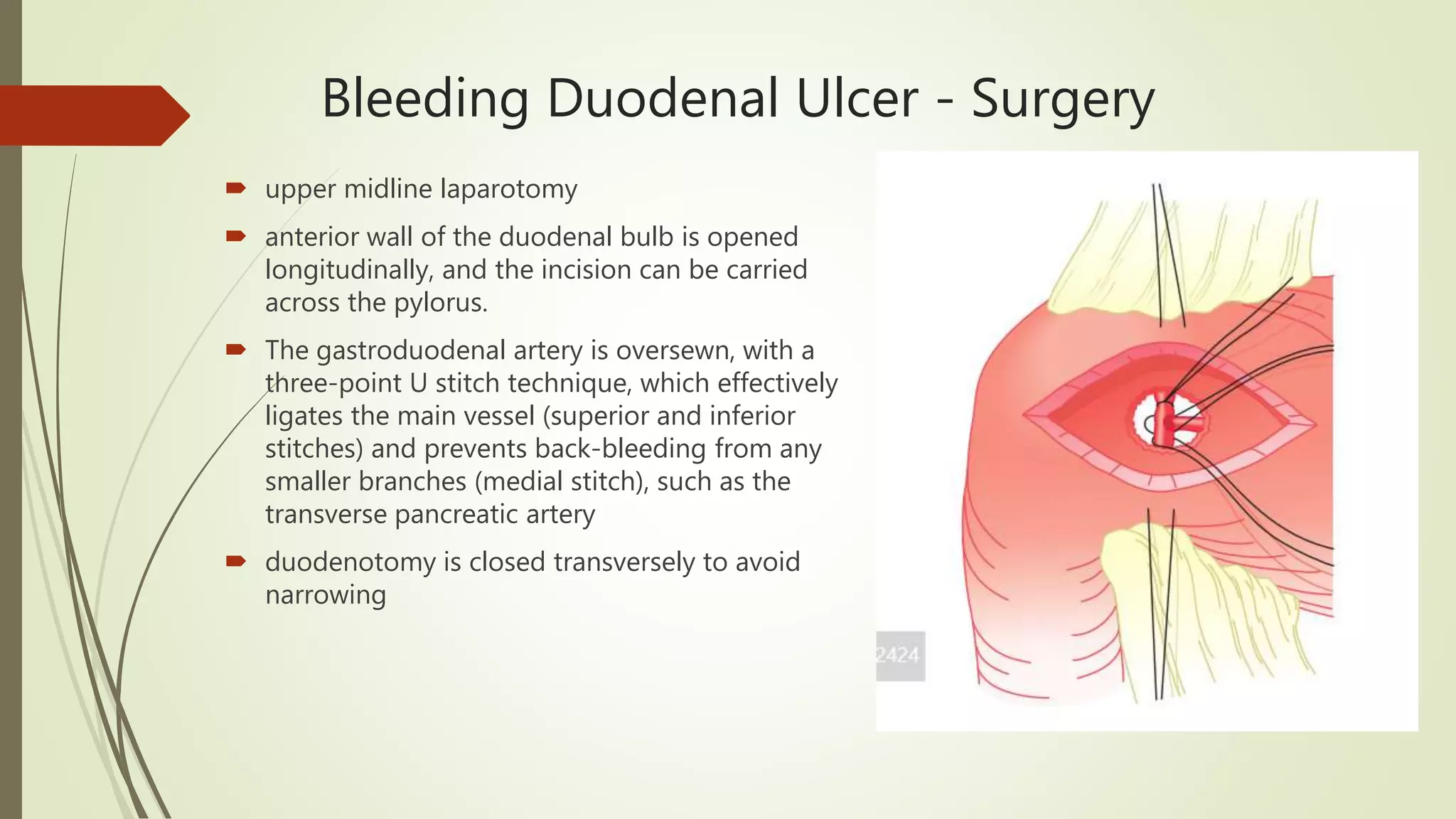
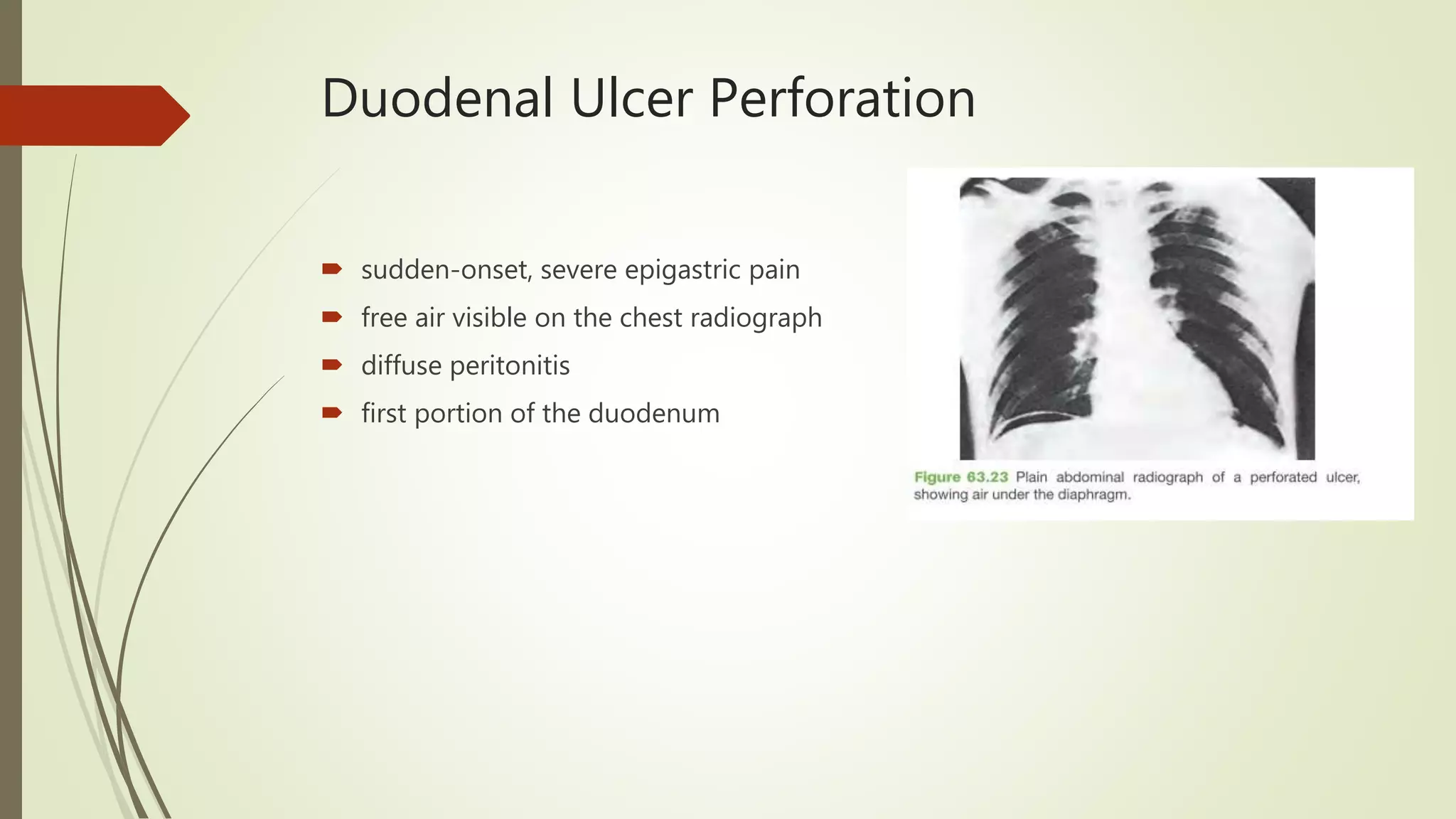
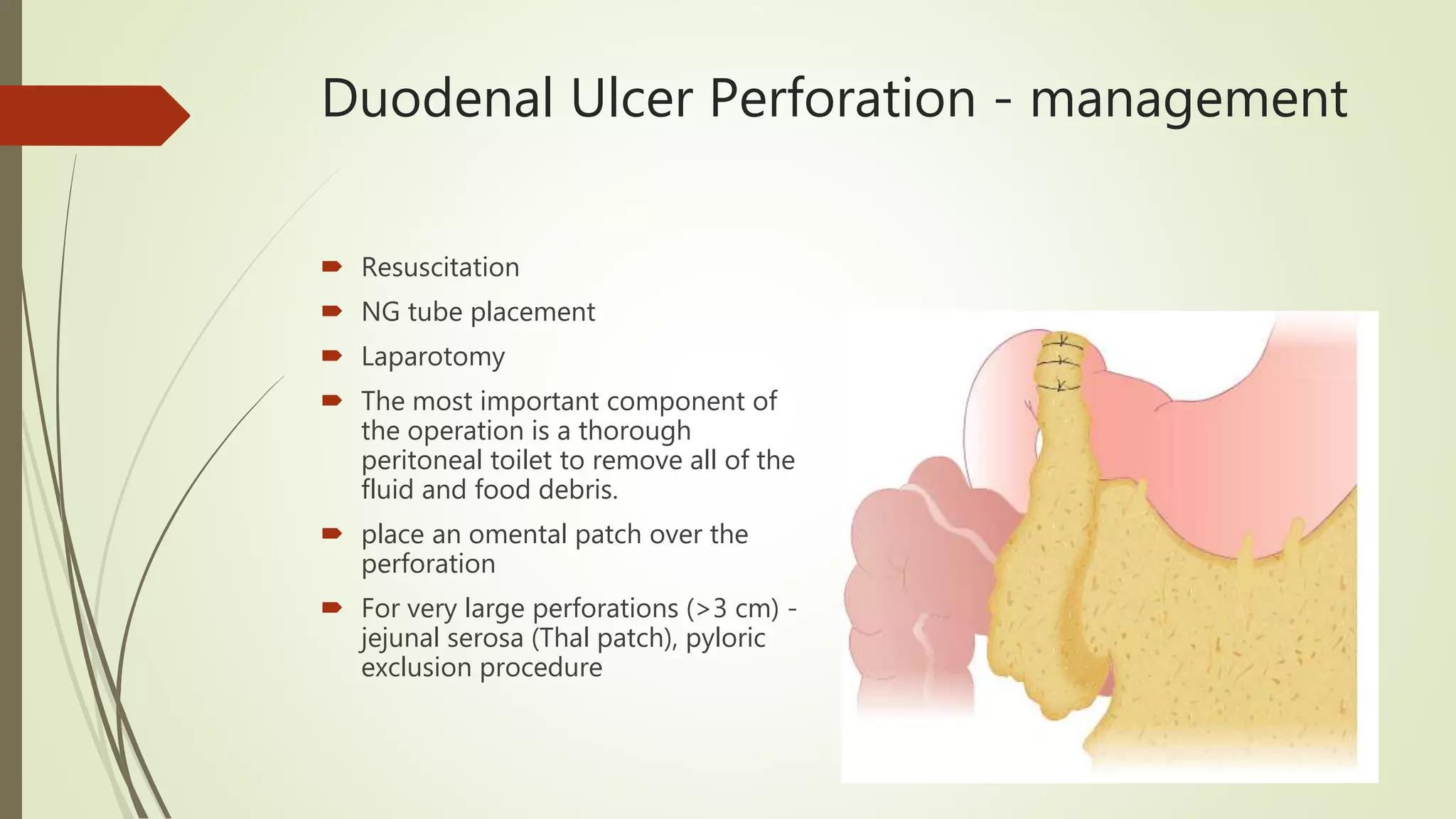
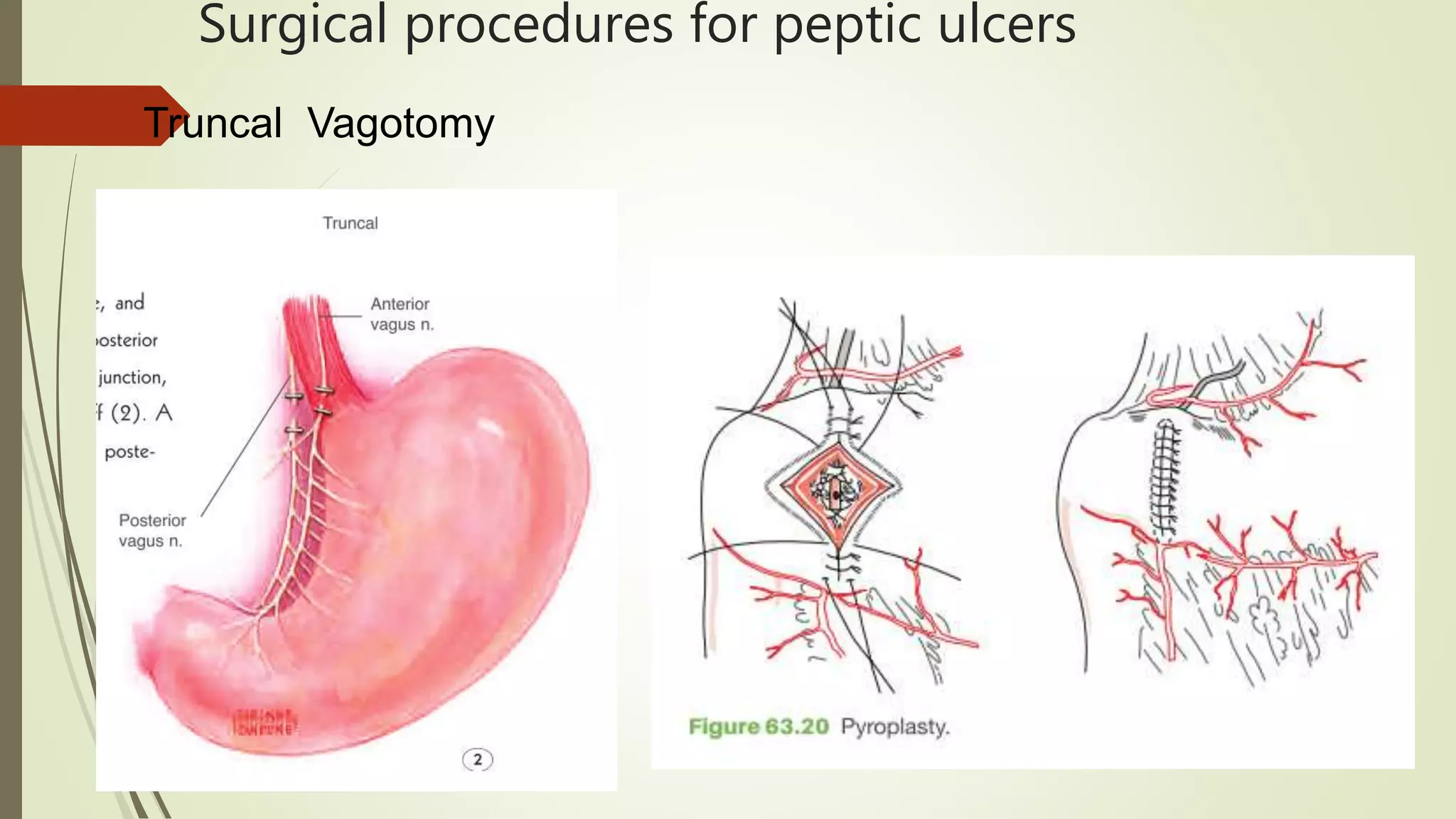
This document discusses peptic ulcer disease, focusing on duodenal ulcers. It defines peptic ulcers and describes the pathogenesis, including protective and damaging factors. Helicobacter pylori infection plays a major role in ulcer development and the mechanisms by which it causes injury are explained. Diagnosis involves endoscopy, biopsy and testing for H. pylori. Treatment involves eradicating H. pylori with antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors. Complications of duodenal ulcers like bleeding and perforation are discussed. Bleeding ulcers are classified by the Forrest system and managed initially with endoscopic methods or surgery depending on severity. Perforated ulcers require surgical repair.