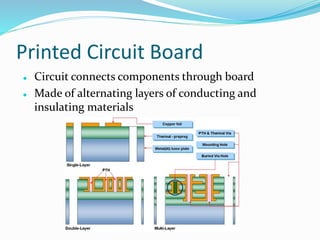
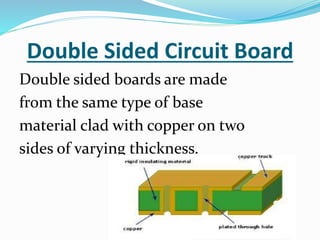
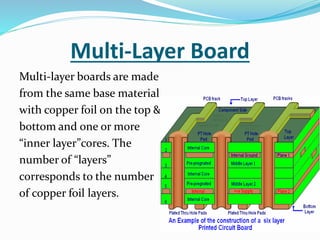
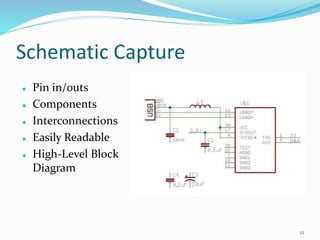
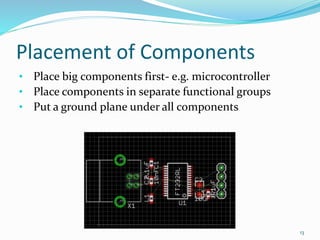
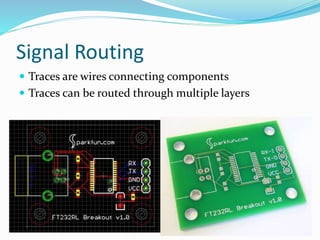
This document provides an overview of printed circuit board (PCB) design. It defines a PCB as a board that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive tracks and pads. The document describes the different types of PCBs, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. It outlines the key steps in PCB design, including designing the circuit, placing components, routing wires, and manufacturing. Common PCB design software and features like schematic capture and component placement are also summarized.