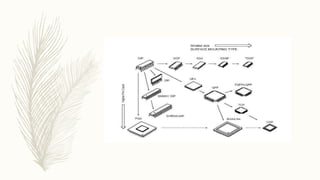
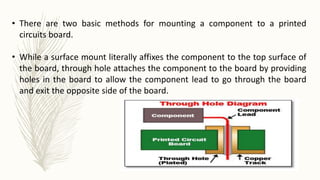
This document explains surface mount devices (SMDs) and surface mount technology (SMT), highlighting the differences between SMDs and traditional components, and detailing the assembly techniques involved. It discusses various types of passive (resistors, capacitors, inductors) and active components (diodes, transistors, integrated circuits) used in SMT, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using these technologies. Additionally, it compares SMT with through-hole technology, explaining the benefits of SMT such as smaller size and higher packaging density, as well as its challenges and cost implications.