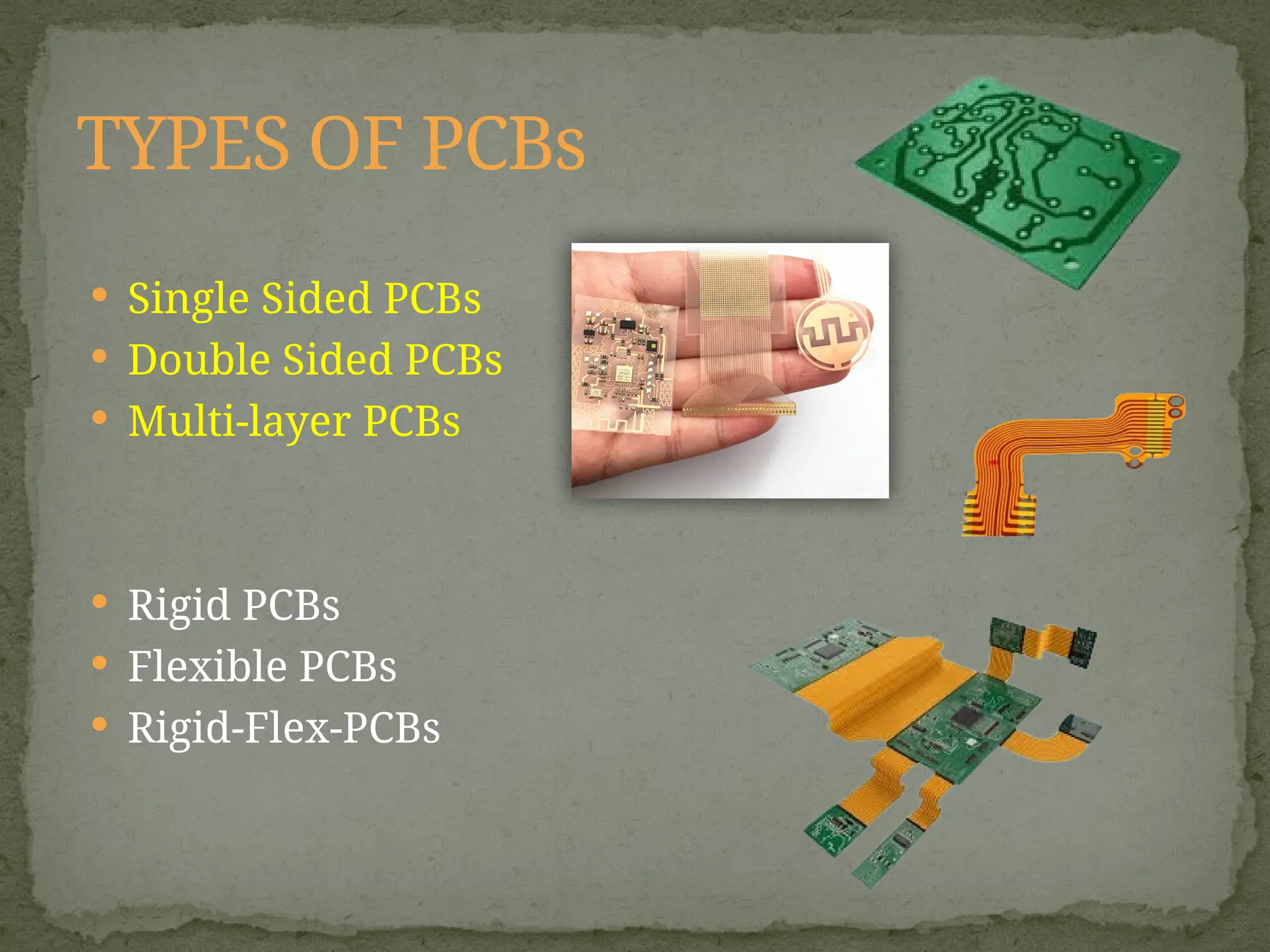
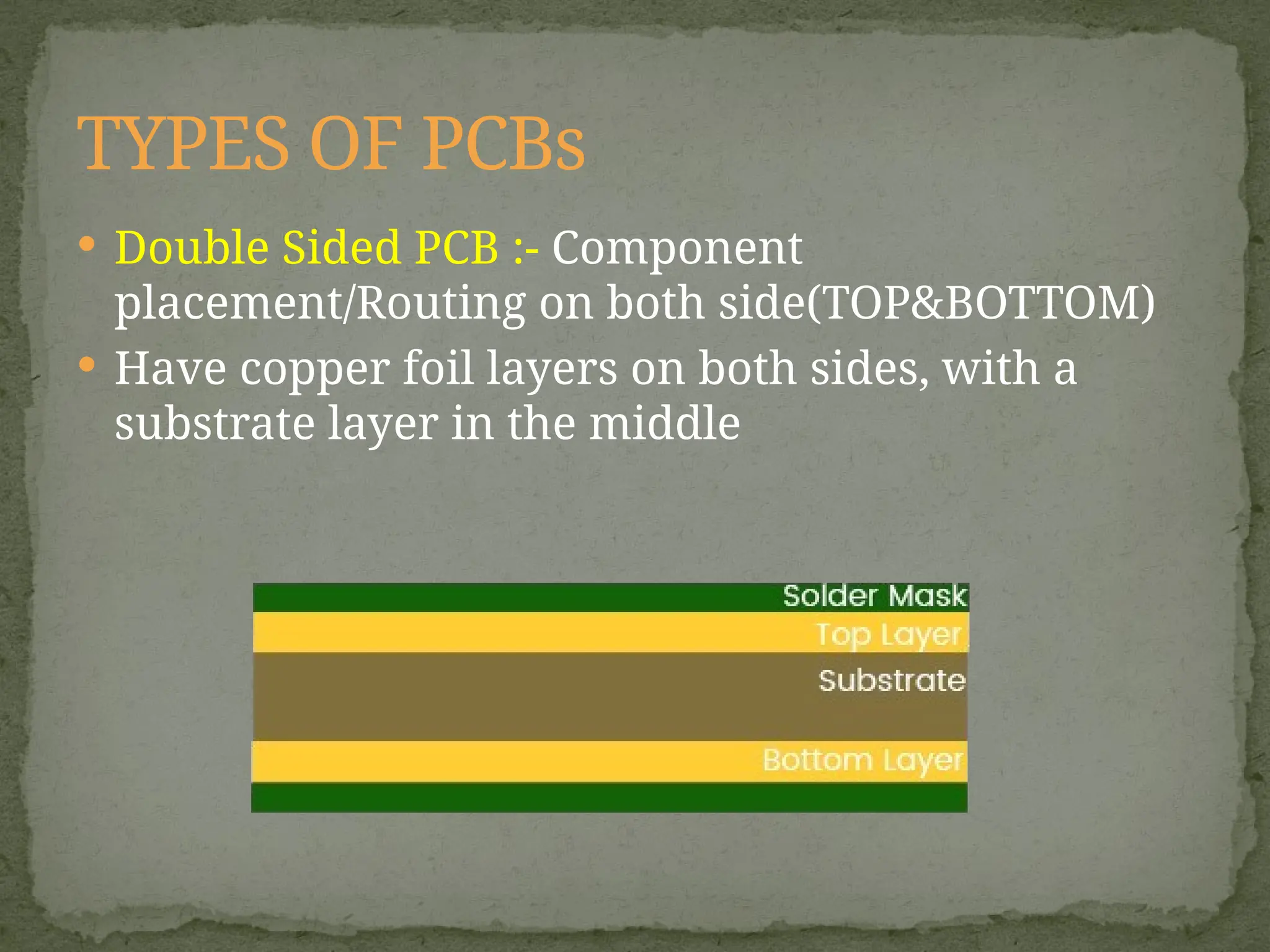
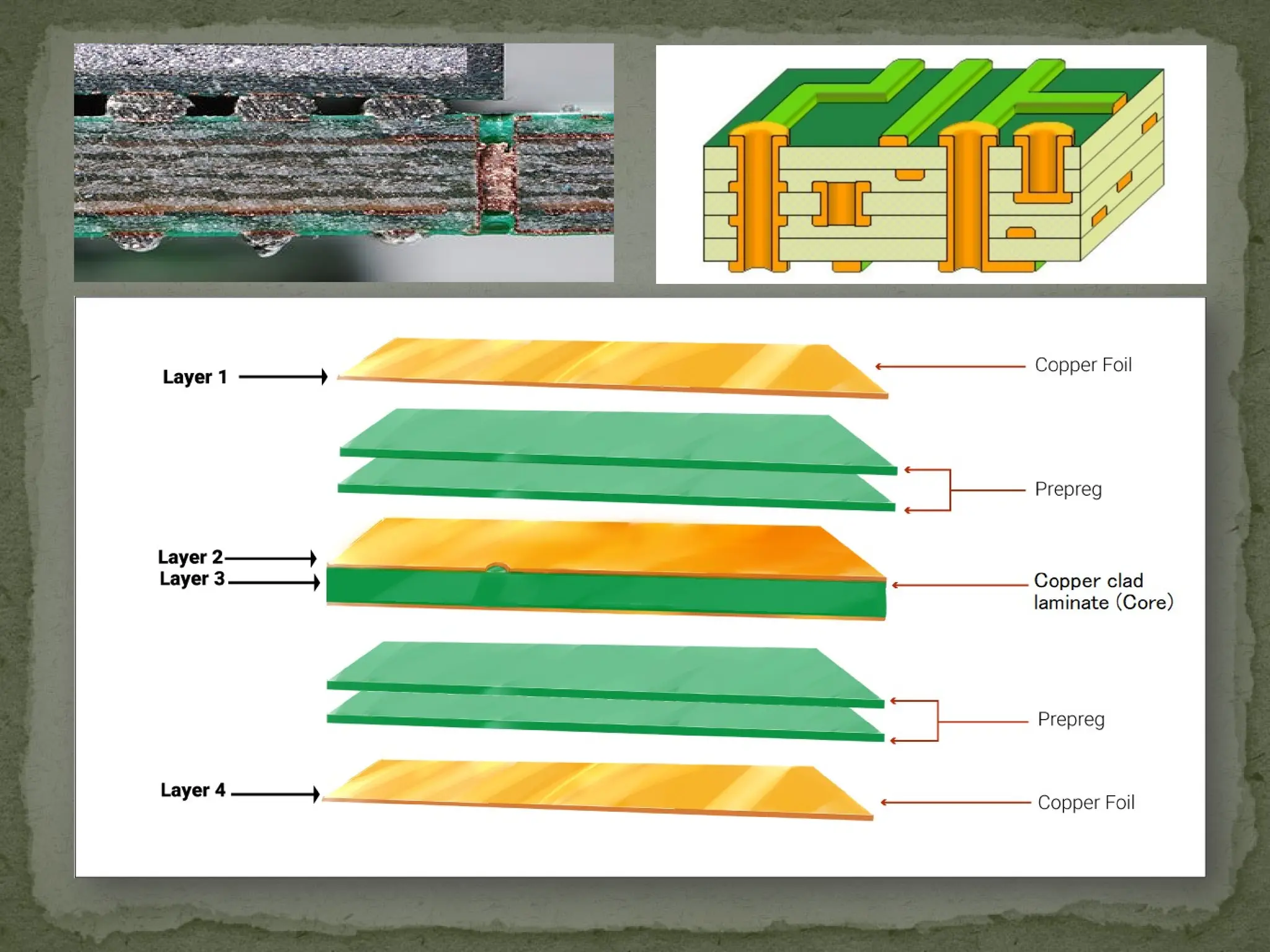
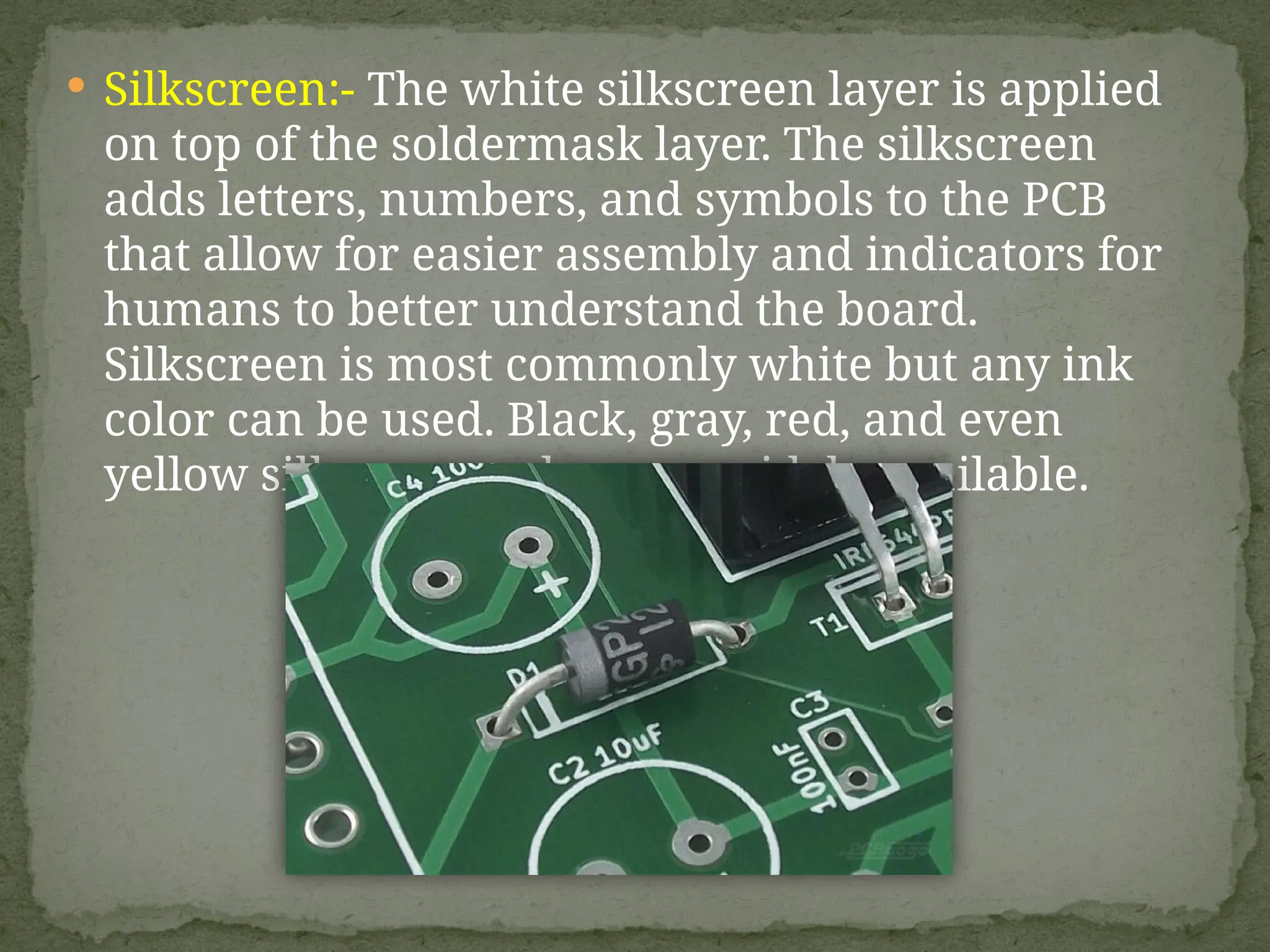
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in electronic devices, allowing the assembly of components and connections on substrates of conductive and non-conductive materials. They come in various types, including single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, rigid, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs, each tailored for specific applications and complexity levels. The manufacturing process adheres to IPC standards, categorizing quality into three classes based on reliability and inspection requirements.