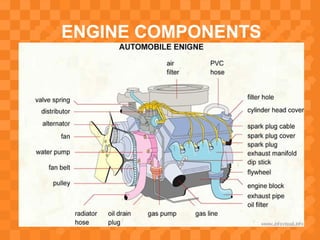
This document provides an overview of the key components of an internal combustion (IC) engine in an automobile. It lists and describes the main components, including the engine block, crankshaft, connecting rod, piston, piston rings, valves, camshaft, cylinder head, intake and exhaust manifolds, radiator, spark plugs, fuel system components, and more. The purpose is to familiarize mechanical engineering students with the basic parts of an engine and their basic functions.