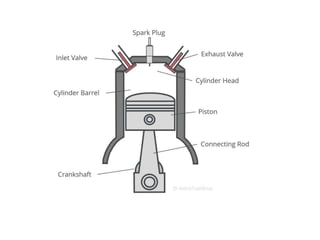
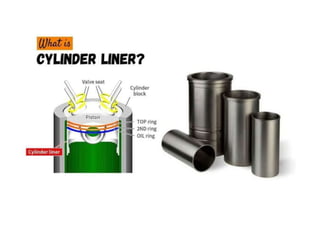
The document describes the key components of an internal combustion engine. It lists 16 components: the cylinder, cylinder block, cylinder head, cylinder liner/sleeve, piston, piston head, piston skirt, piston rings, piston pin, connecting rod, crankshaft, flywheel, crankcase, camshaft, timing gear, inlet manifold, and exhaust manifold. It provides details on the purpose and basic design of each component.