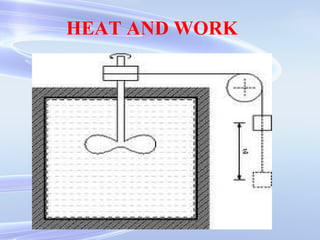
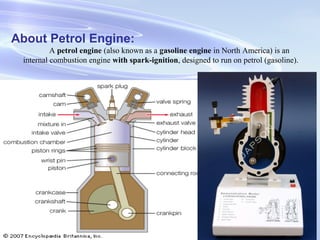
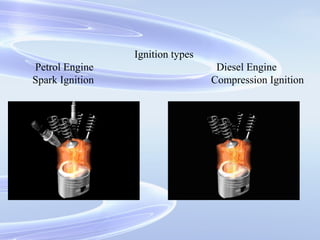
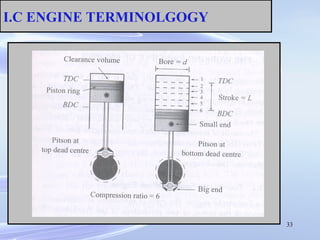
The document provides an introduction to internal combustion engines. It discusses the basic differences between internal and external combustion engines and classifications of internal combustion engines based on fuel, cycle of operation, and combustion process. It then describes the basic parts and working principles of 4-stroke petrol and diesel engines as well as 2-stroke petrol engines. Key differences between petrol and diesel engines are also highlighted. The document concludes by defining common terminology used in internal combustion engines.