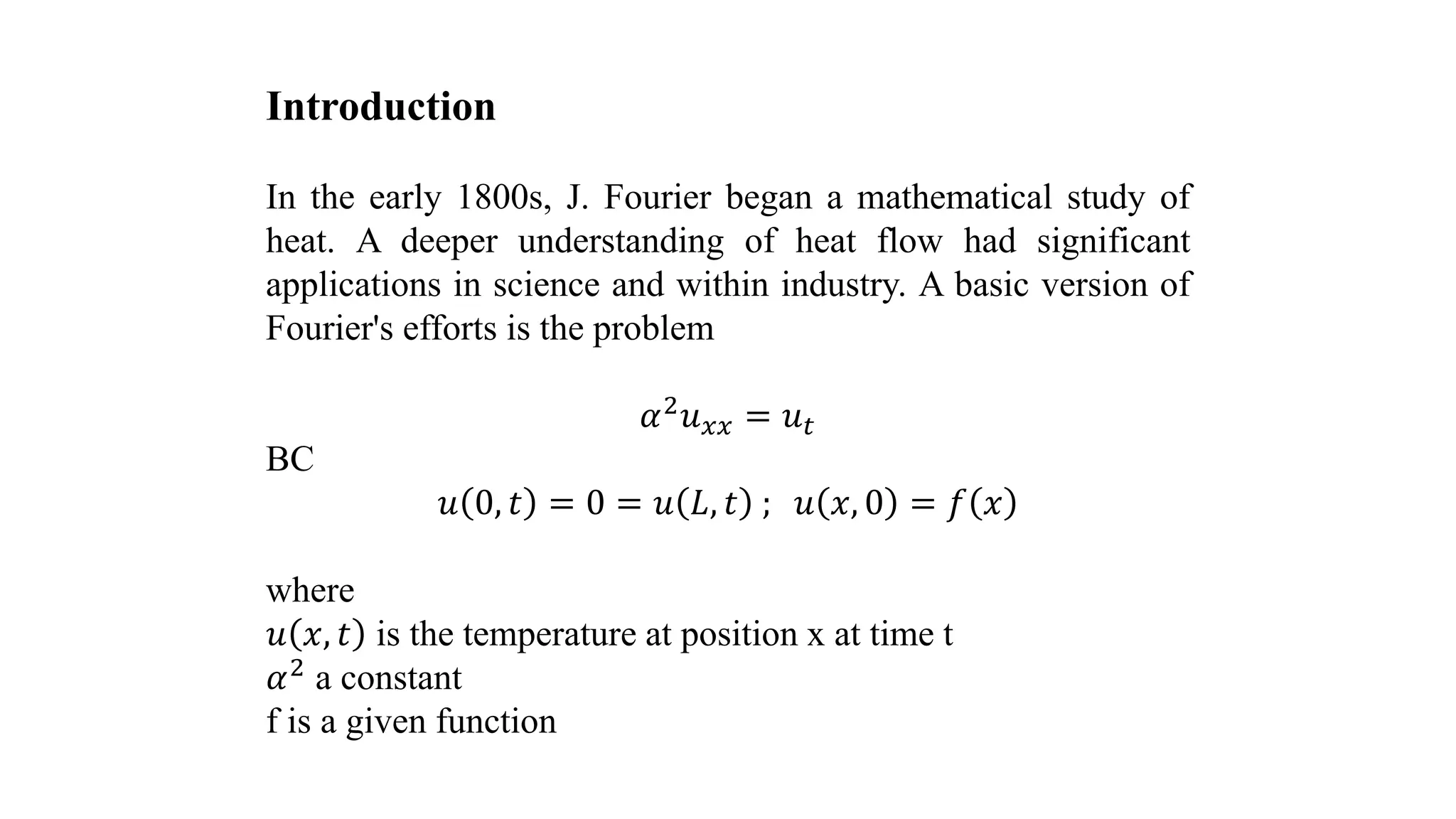
(1) The heat equation describes how heat flows over time within a material. It was first studied by Fourier in the early 1800s.
(2) The one-dimensional heat equation is derived assuming heat flows through a thin bar of homogeneous material with insulated sides. The temperature at any point depends only on position and time.
(3) Using Fourier's law of heat conduction and assumptions about the bar, an expression can be derived that relates the rate of heat transfer to the second spatial derivative of temperature - leading to the heat equation α2uxx = ut, where α is the thermal diffusivity.








![The minus sign appears in the above two terms since there will be a
positive flow of heat from left to right only if the temperature is greater
to the left of x = xo than to the right (in this case, 𝑢𝑥(𝑥0, 𝑡) will be
negative).
Now. simplifying the above and applying the fundamental theorem of
calculus we obtain
𝑑𝐻
𝑑𝑡
= k𝑢𝑥(𝑥1, 𝑡) − k𝑢𝑥(𝑥0, 𝑡)
𝑑𝐻 𝑡
𝑑𝑡
= k න
𝑥0
𝑥1
𝑢𝑥𝑥 𝑥, 𝑡 𝑑𝑥
The first fundamental theorem of calculus states that, if f is
continuous on the closed interval [a,b] and F is the indefinite
integral of f on [a,b], then
න
𝑎
𝑏
𝑓 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 = 𝐹 𝑏 − 𝐹(𝑎)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7heatequation-2-230415081449-c6e6084d/75/7-Heat-Equation-2-pdf-10-2048.jpg)







