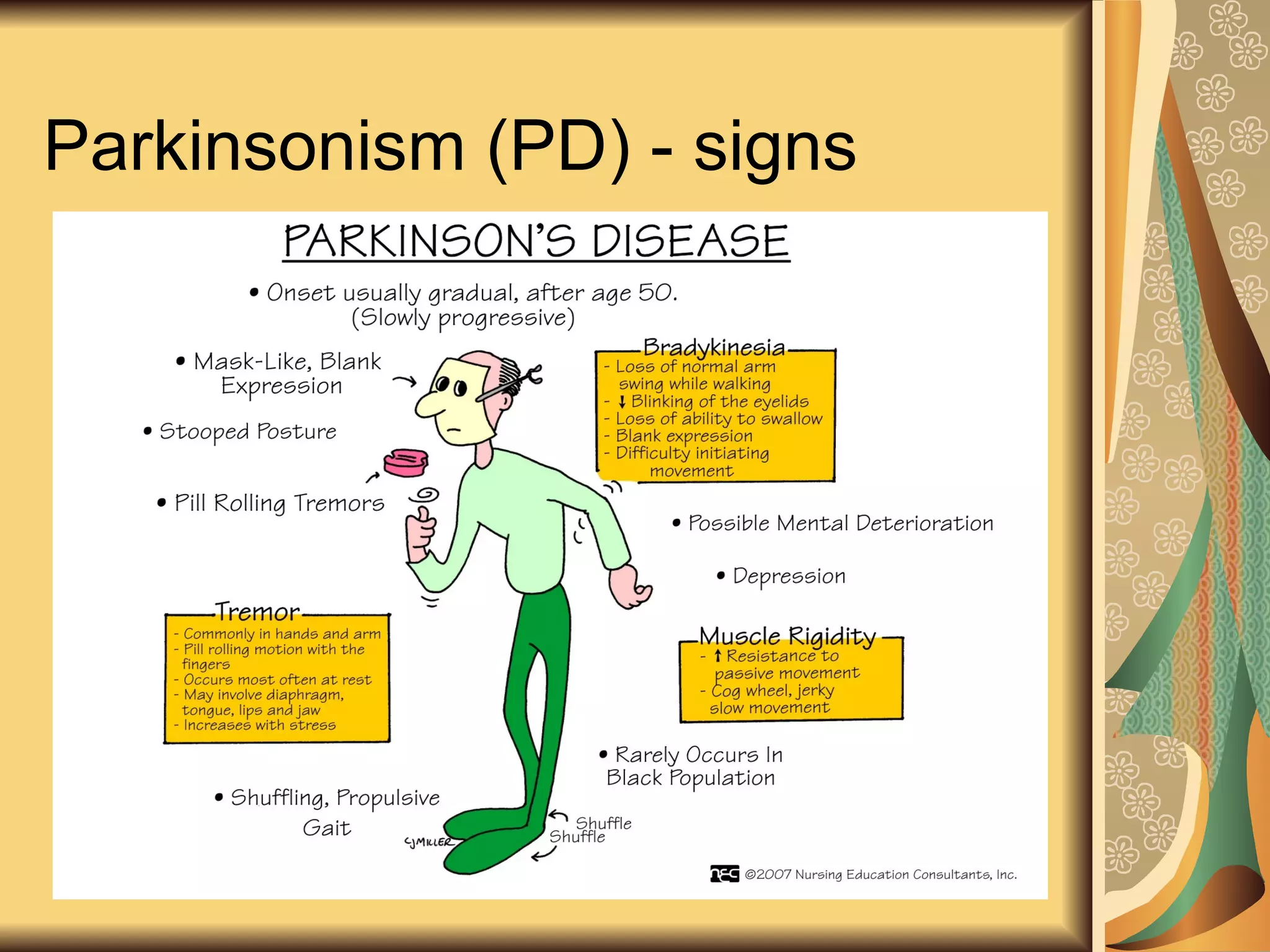
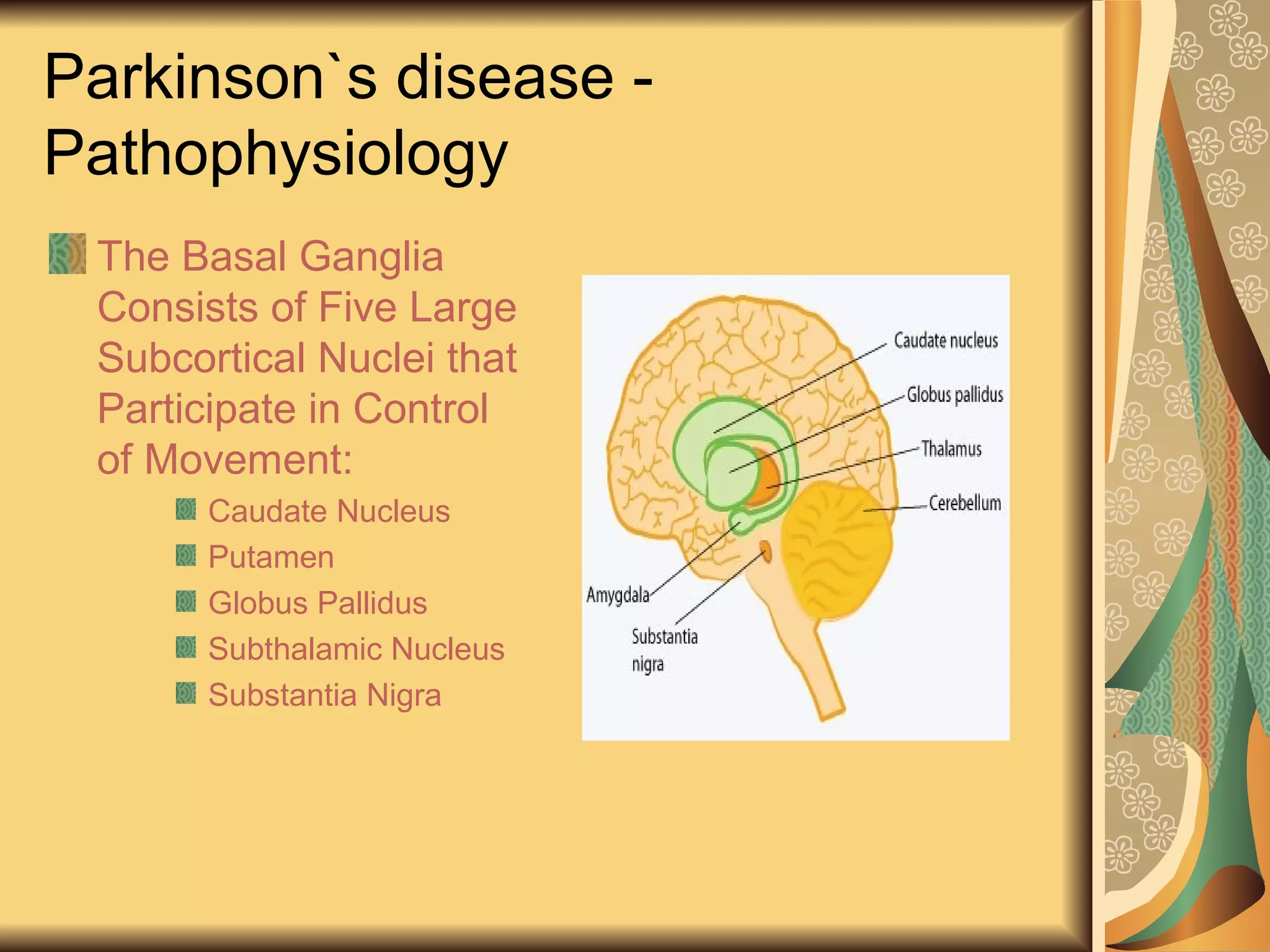
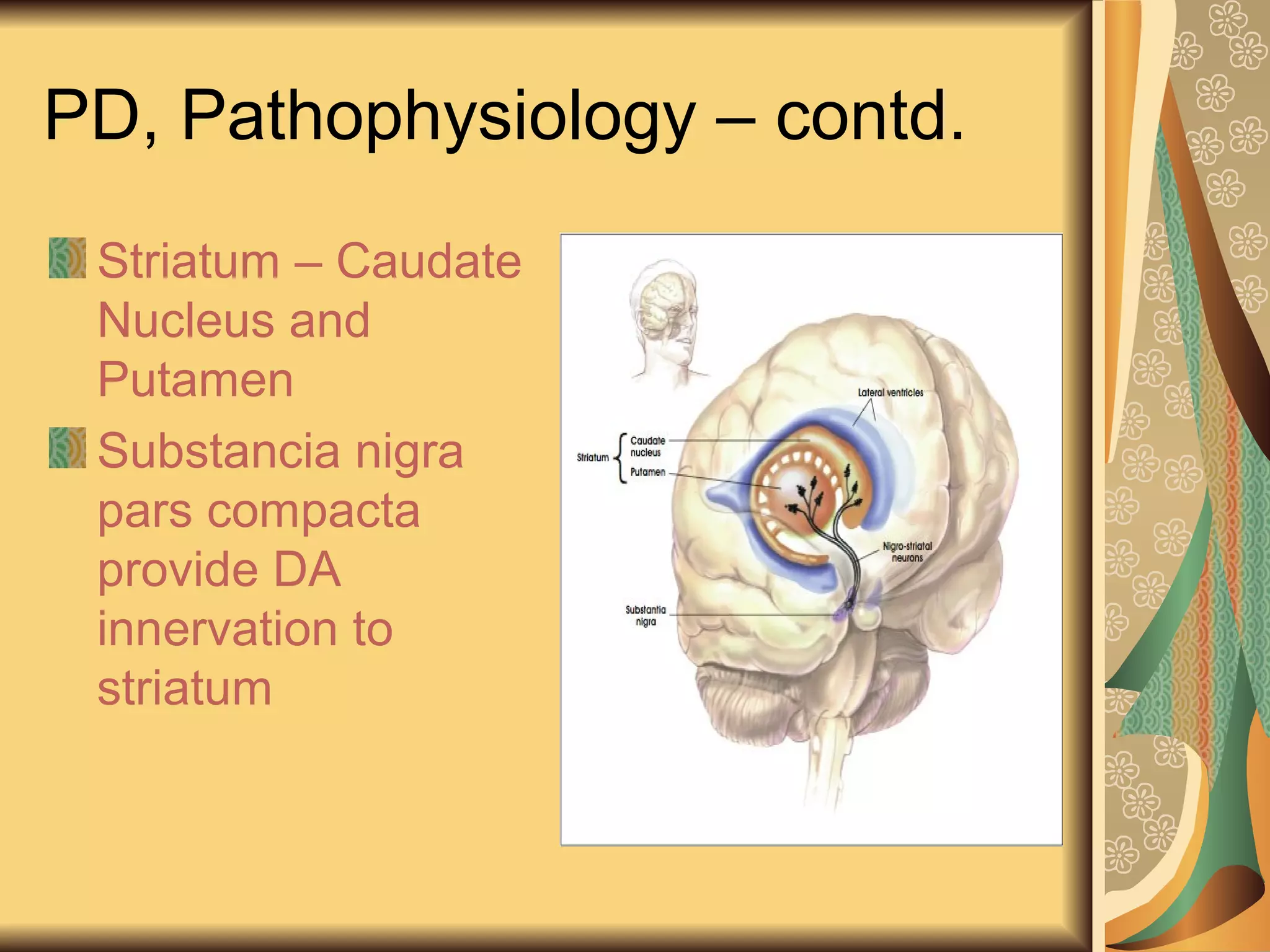
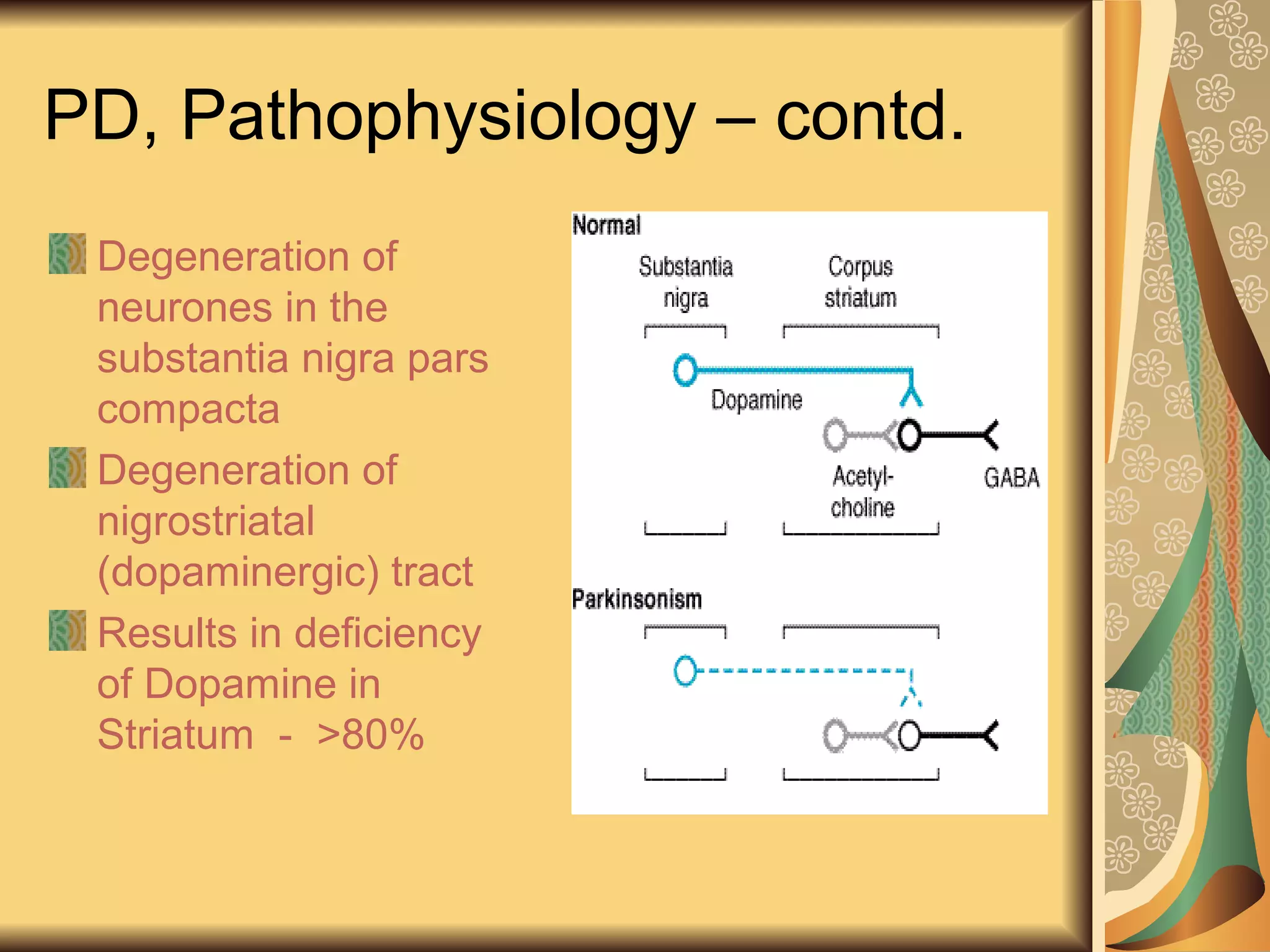
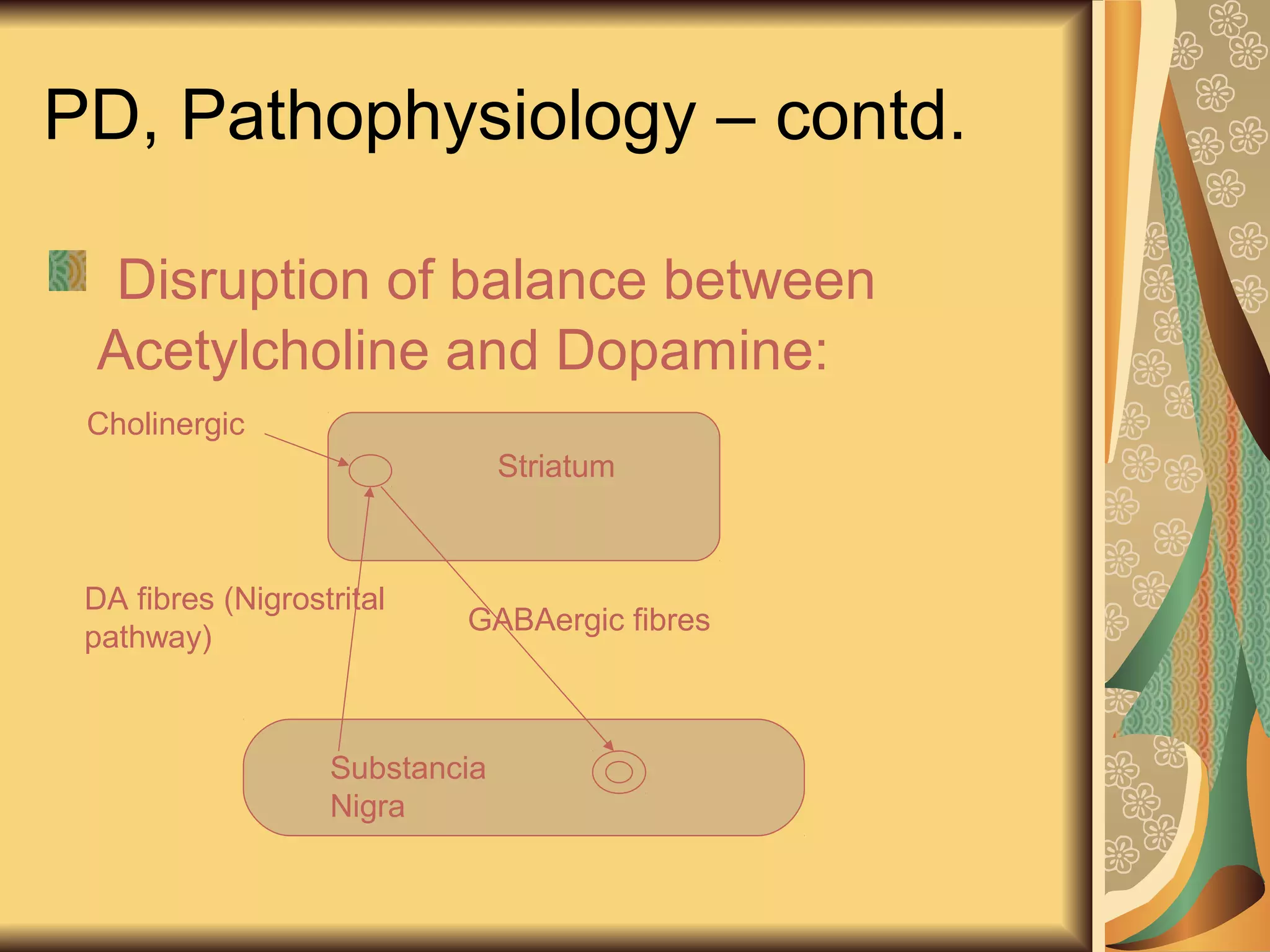
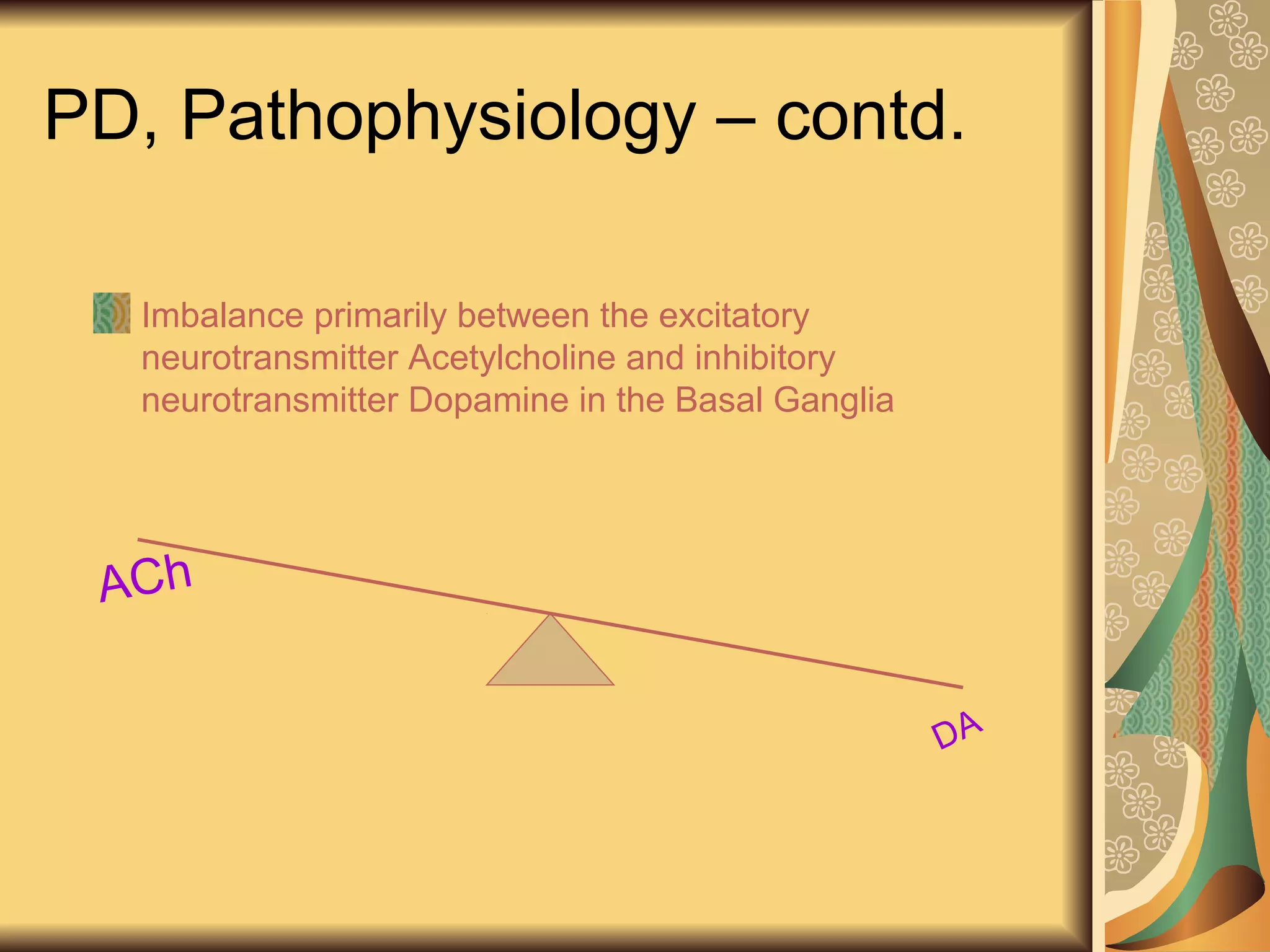
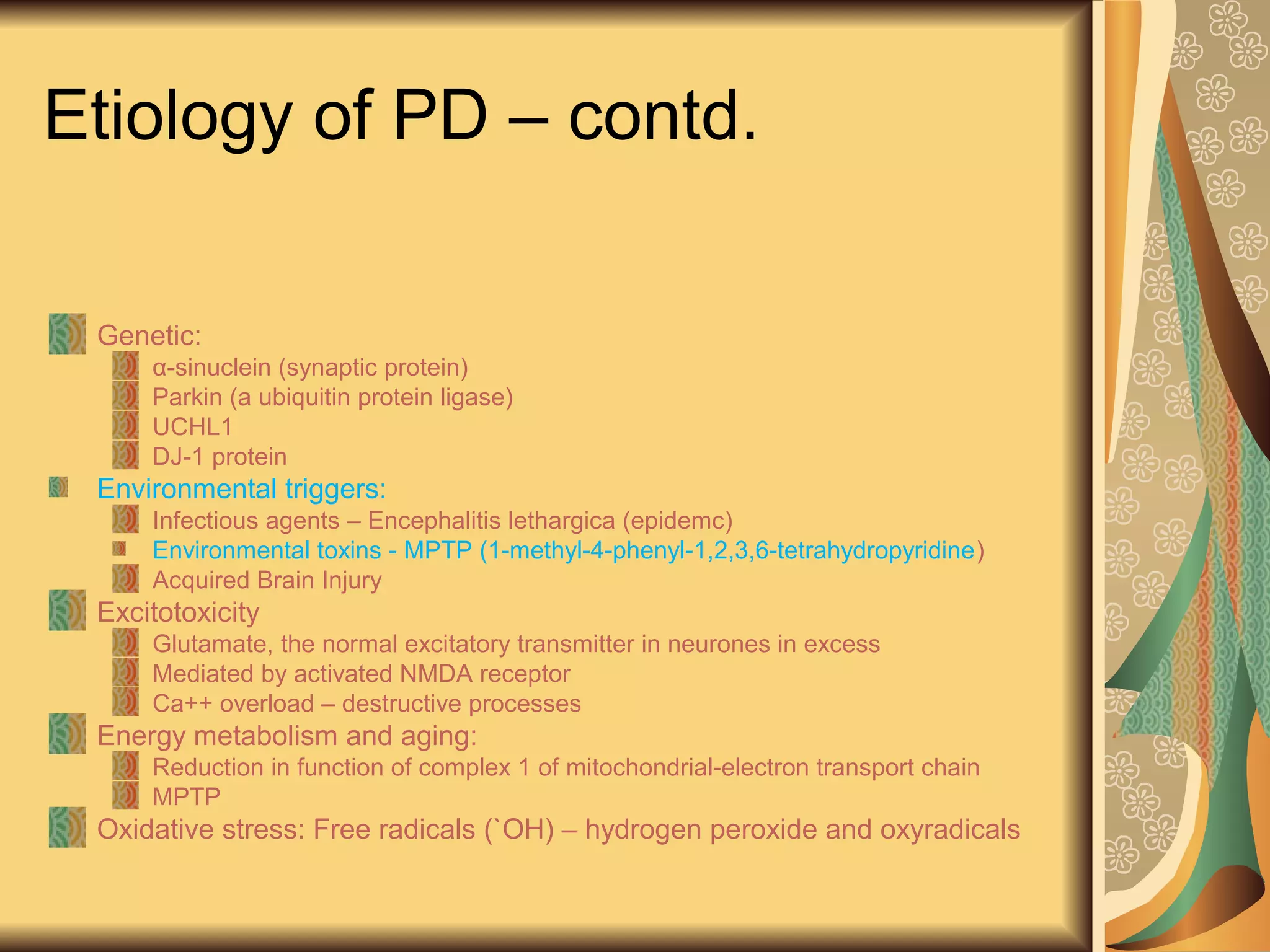
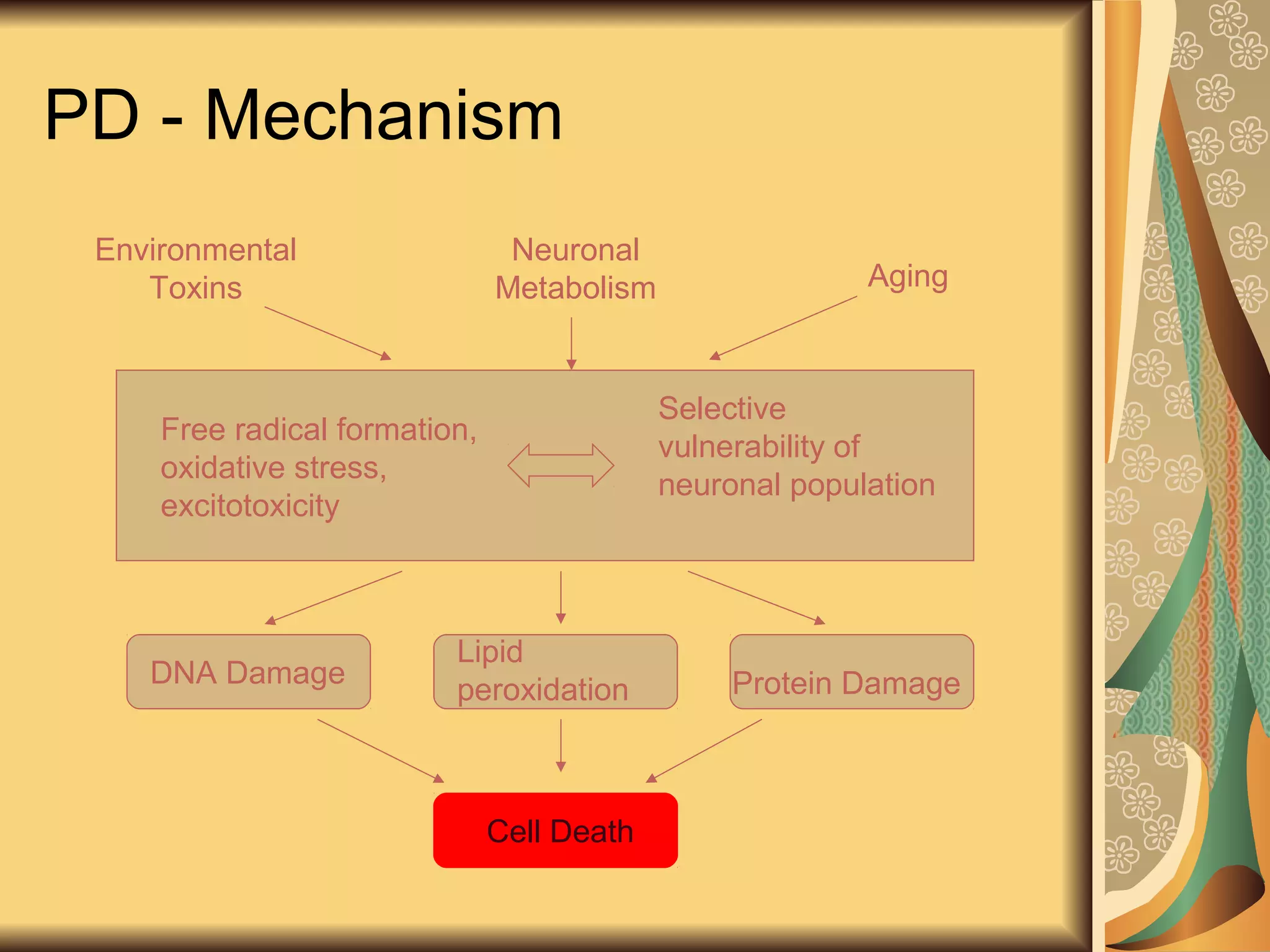
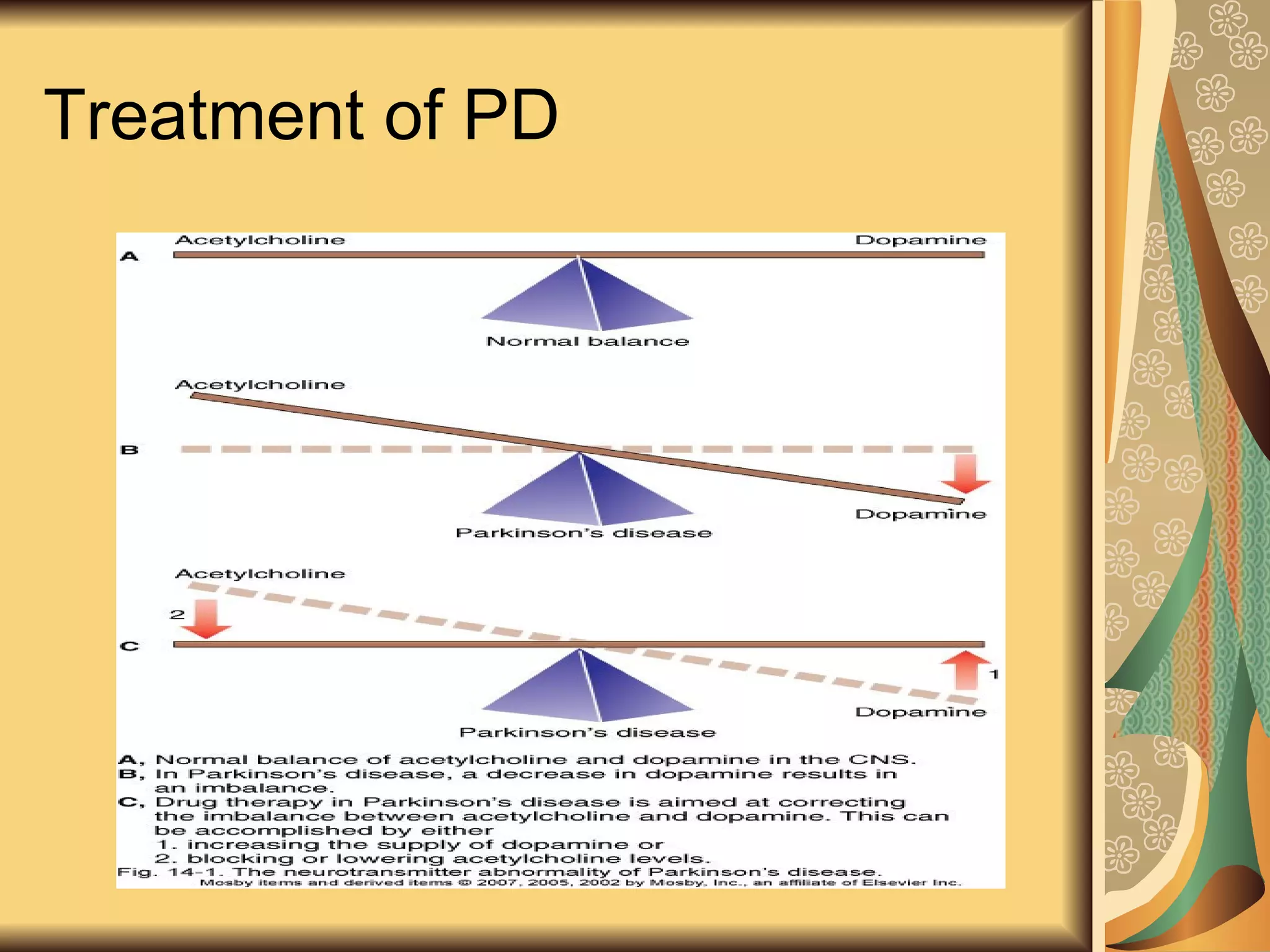
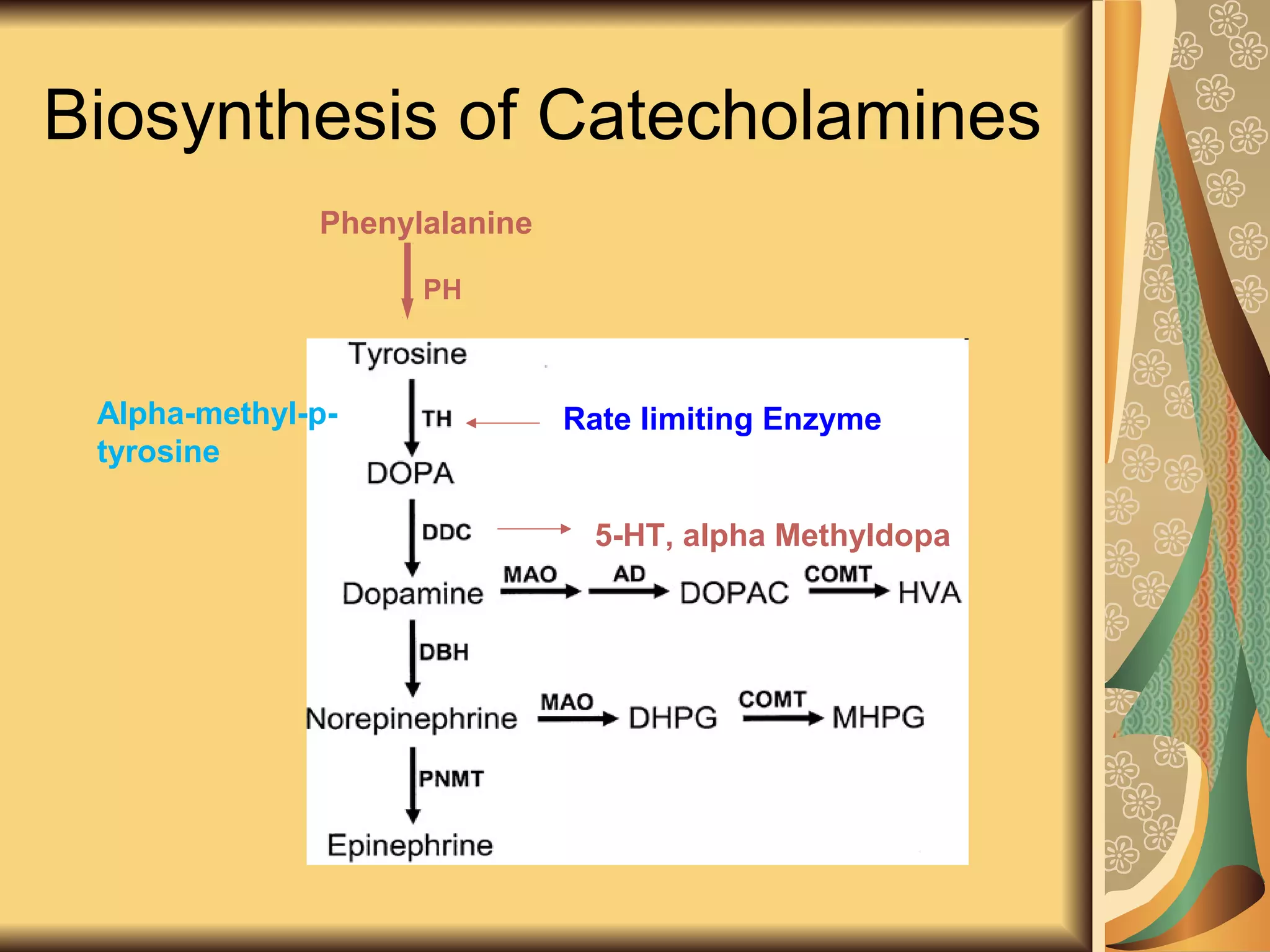
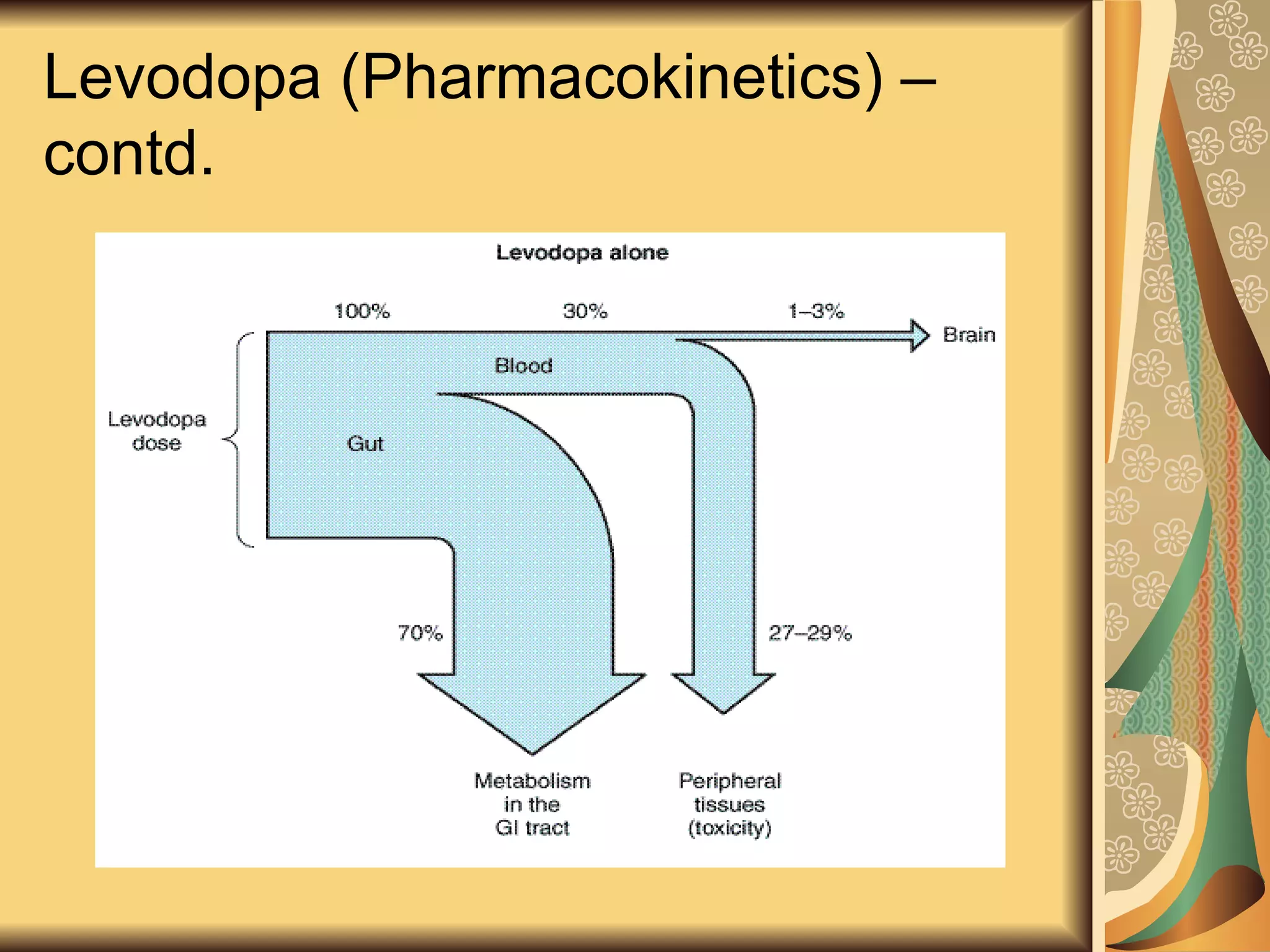
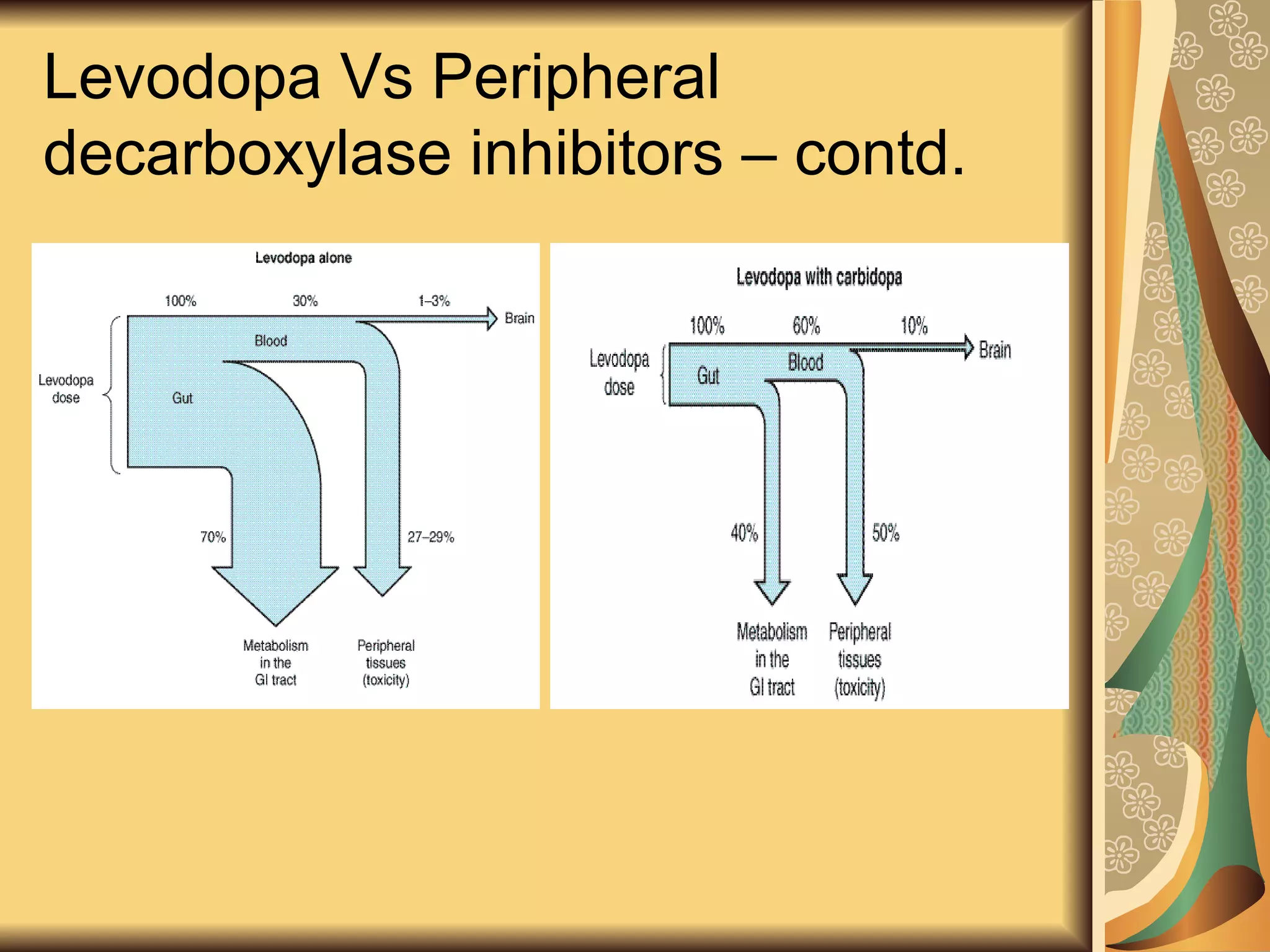
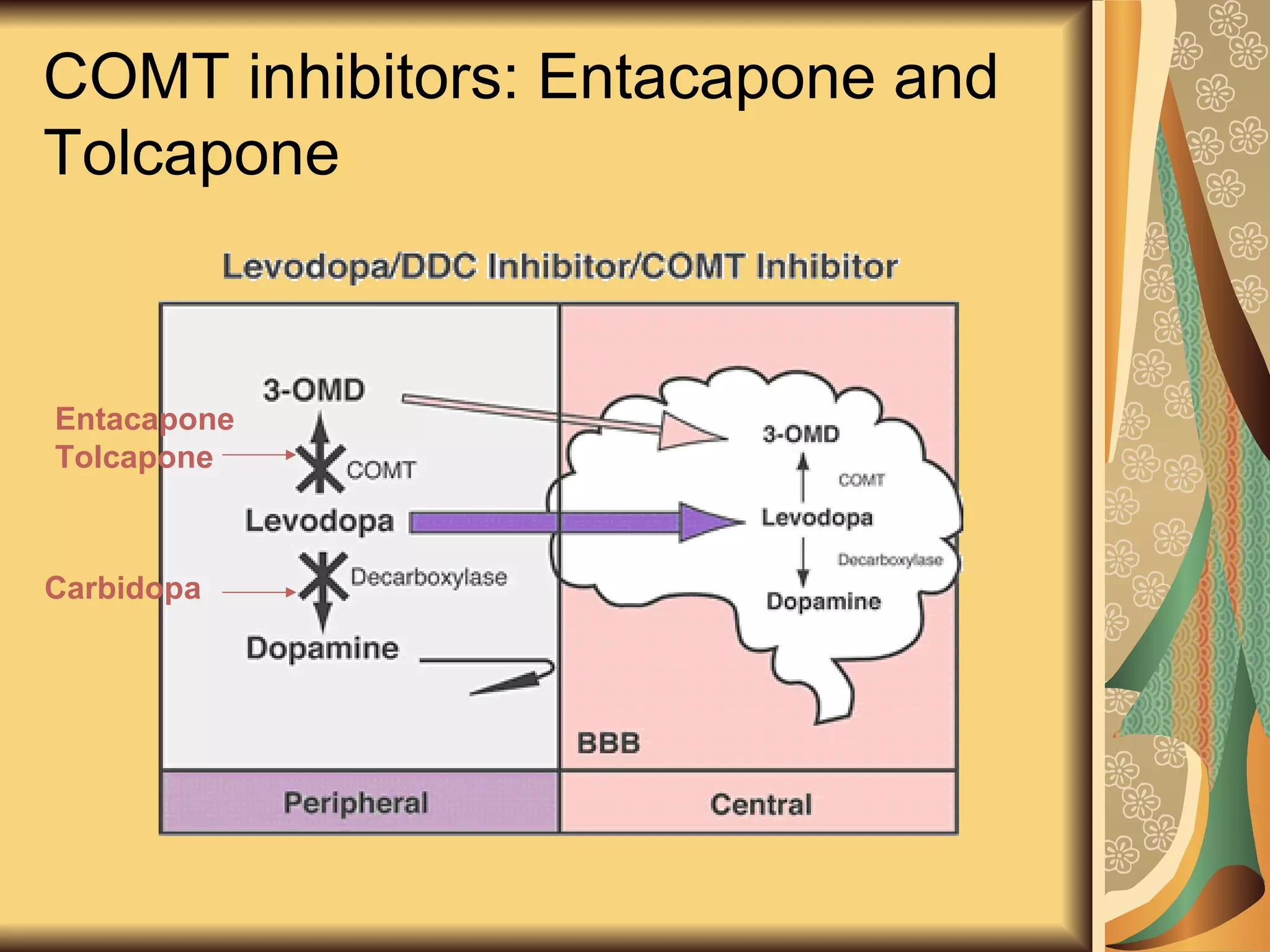
This document discusses drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease. It begins by describing the signs and symptoms of Parkinsonism including rigidity, tremor, bradykinesia, and impaired balance. It then discusses the pathophysiology involving degeneration of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra and resulting dopamine deficiency in the striatum. The document covers various drug classes used to treat Parkinson's including levodopa, dopamine agonists like bromocriptine and pramipexole, MAO-B inhibitors like selegiline, and COMT inhibitors like entacapone. It provides details on the mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, benefits and adverse effects of these antiparkinsonian drugs.