Atypical antidepressants have several advantages over traditional antidepressants:
1. They have fewer side effects like sexual dysfunction and weight gain.
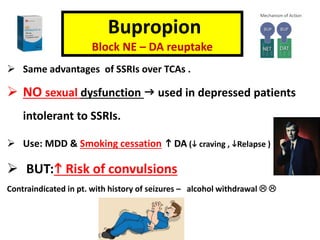
2. Bupropion is used for major depressive disorder and smoking cessation. Mirtazapine is used for depression and insomnia.
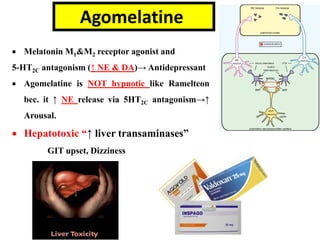
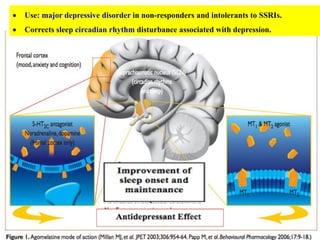
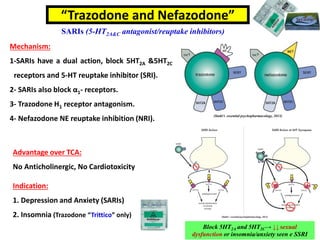
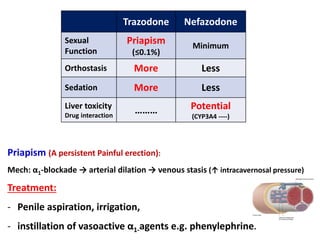
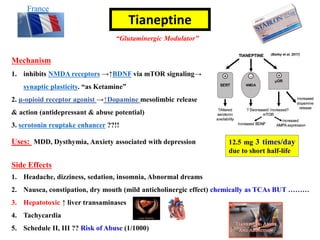
3. Other atypical antidepressants include trazodone, nefazodone, agomelatine, and vortioxetine which are used for depression and related conditions.