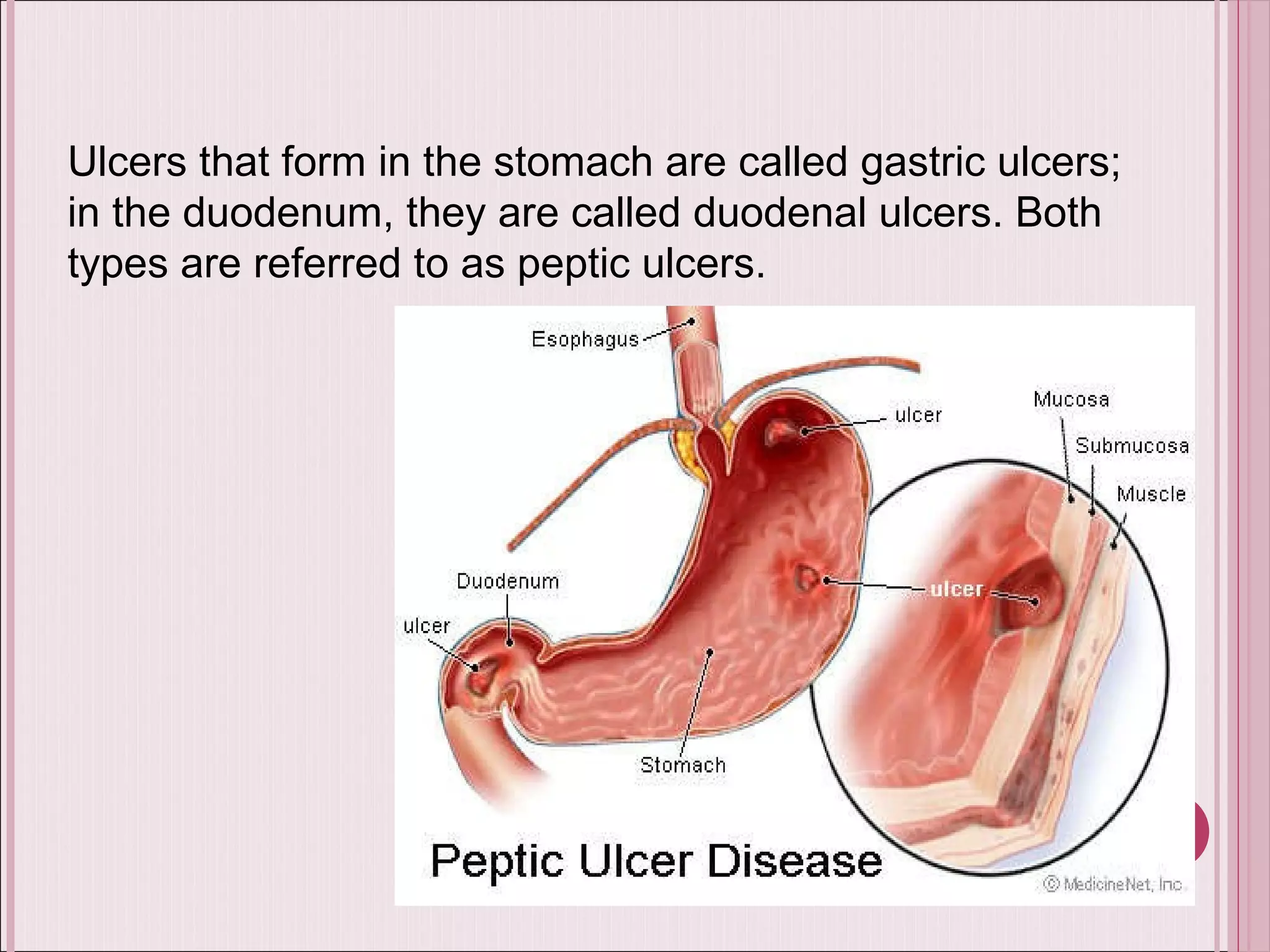
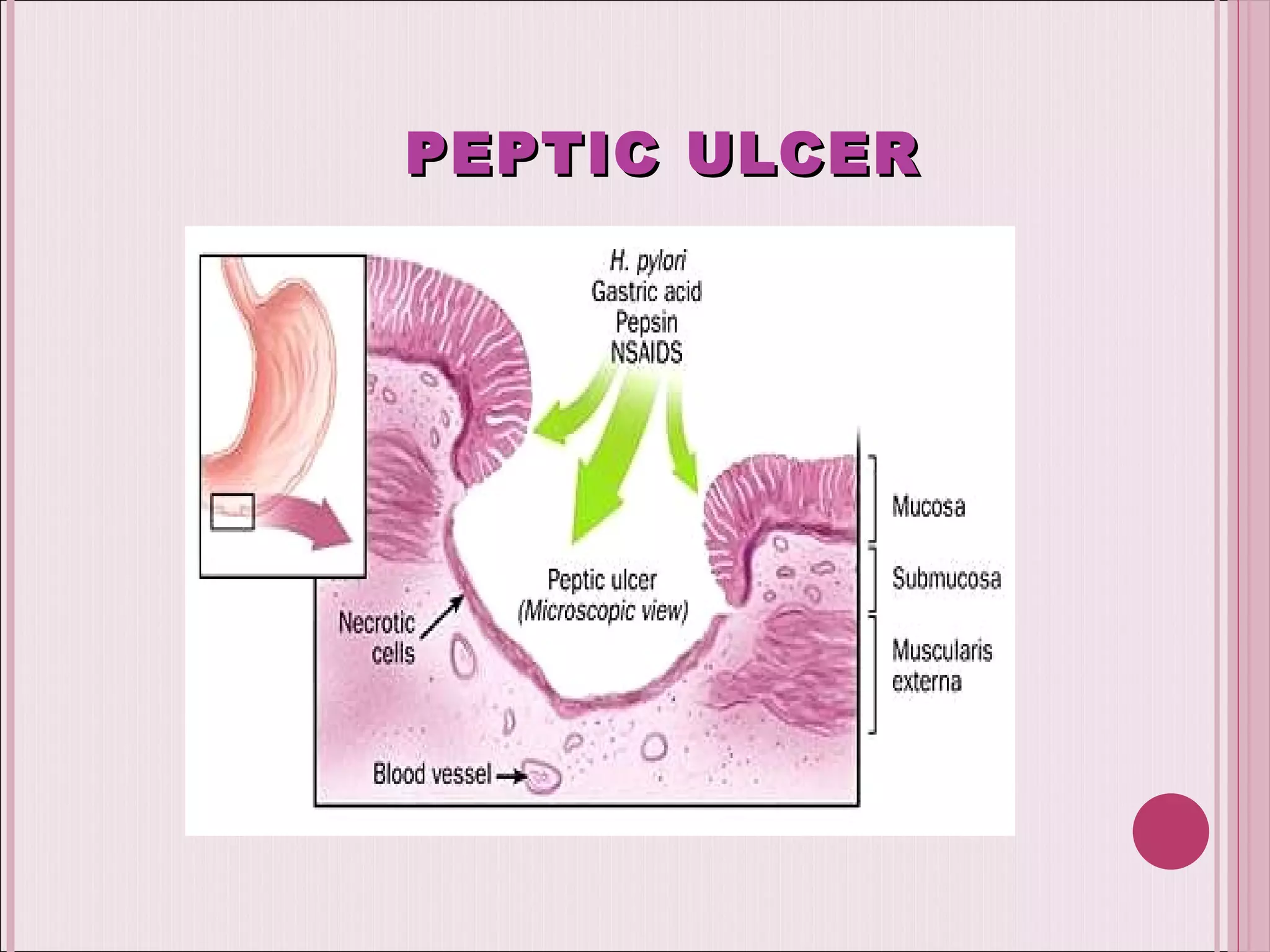
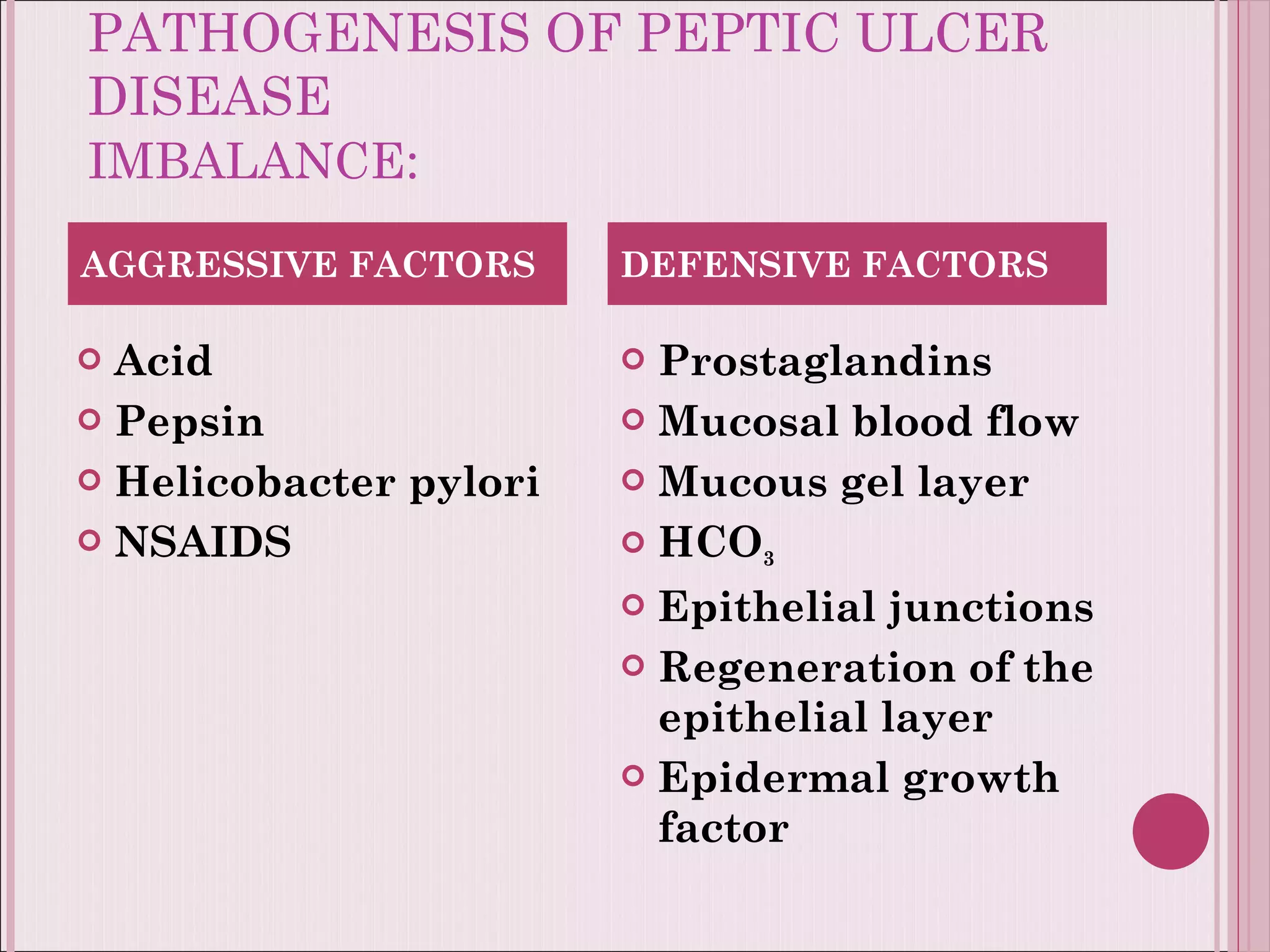
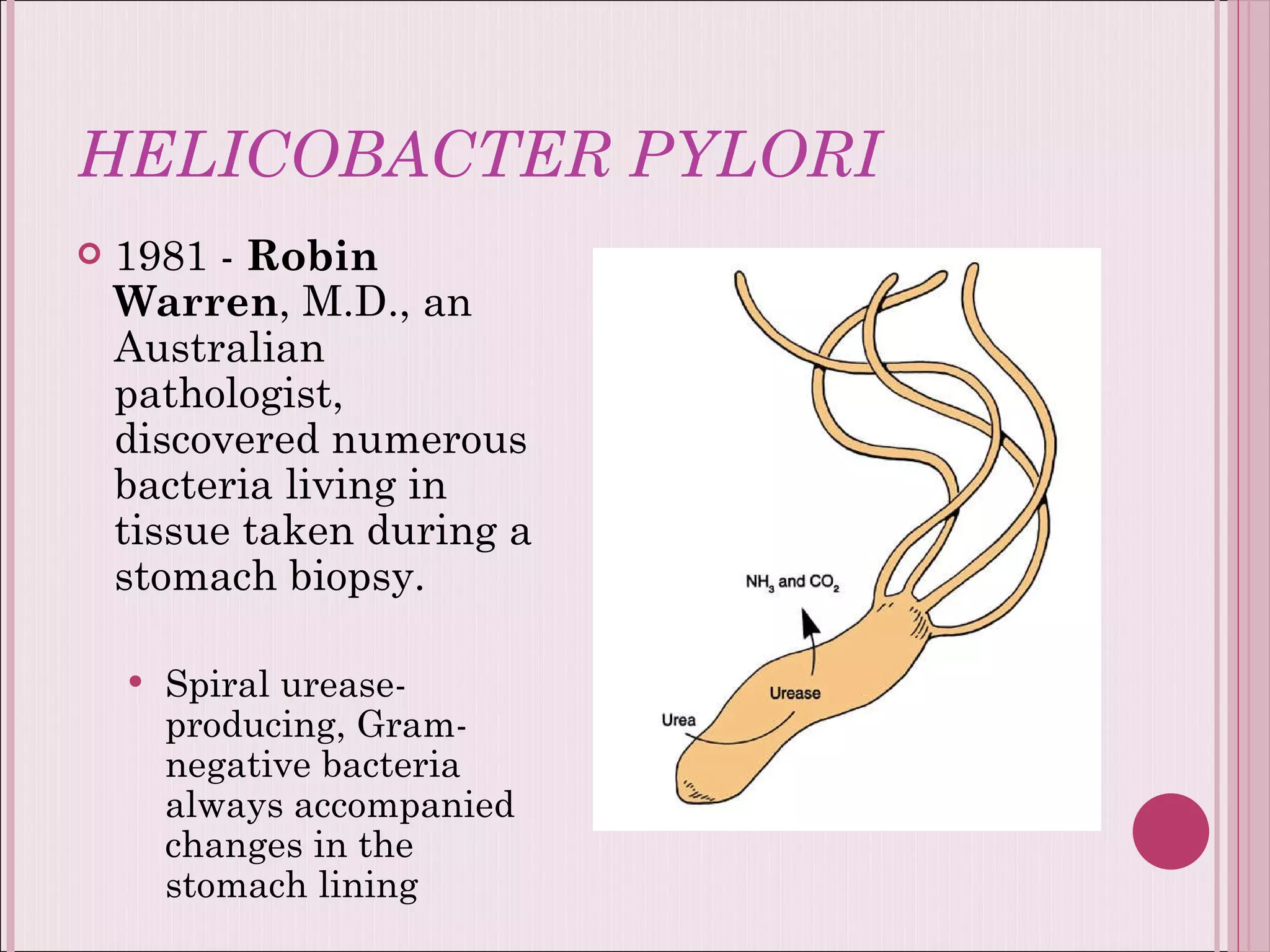
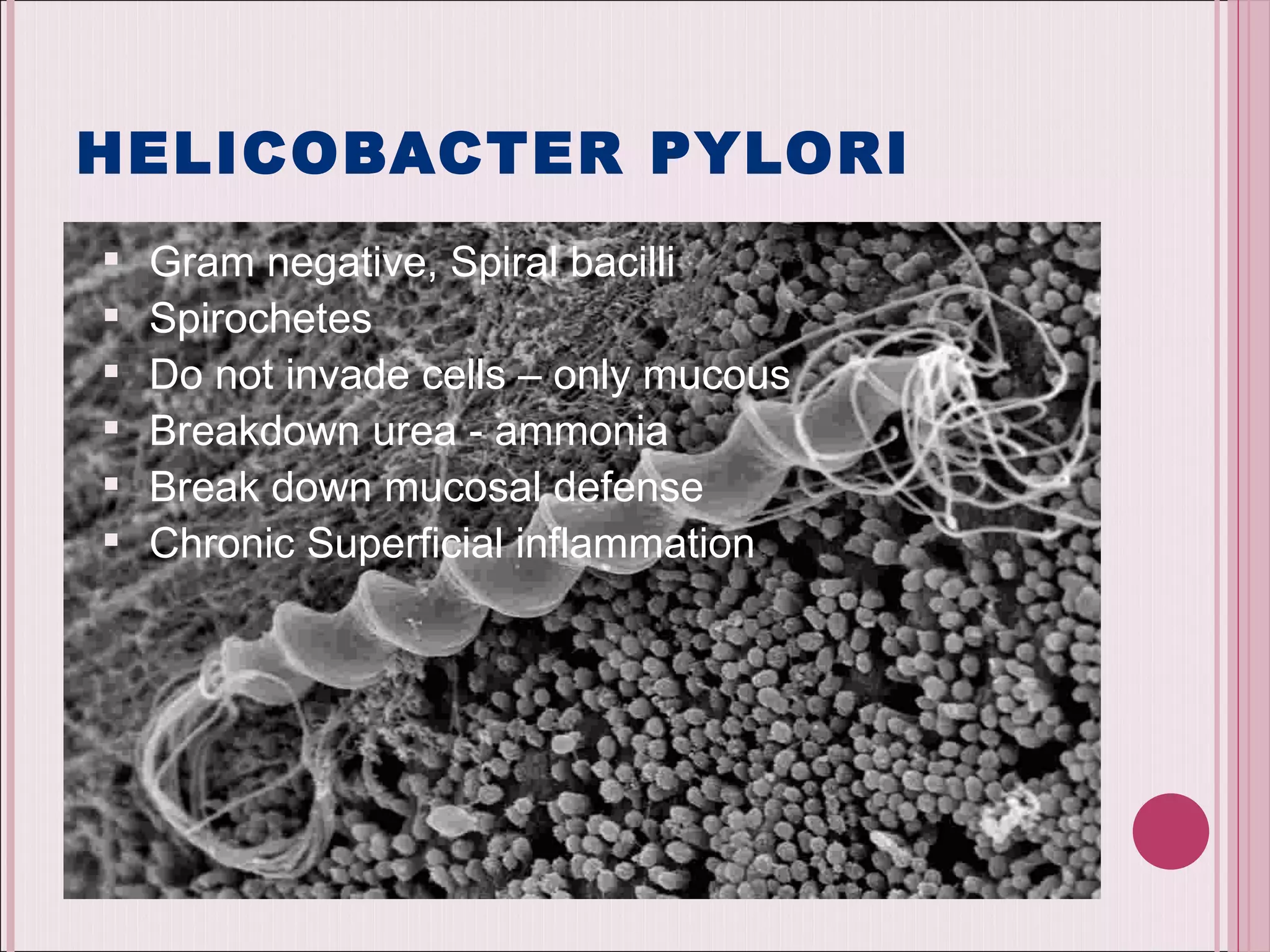
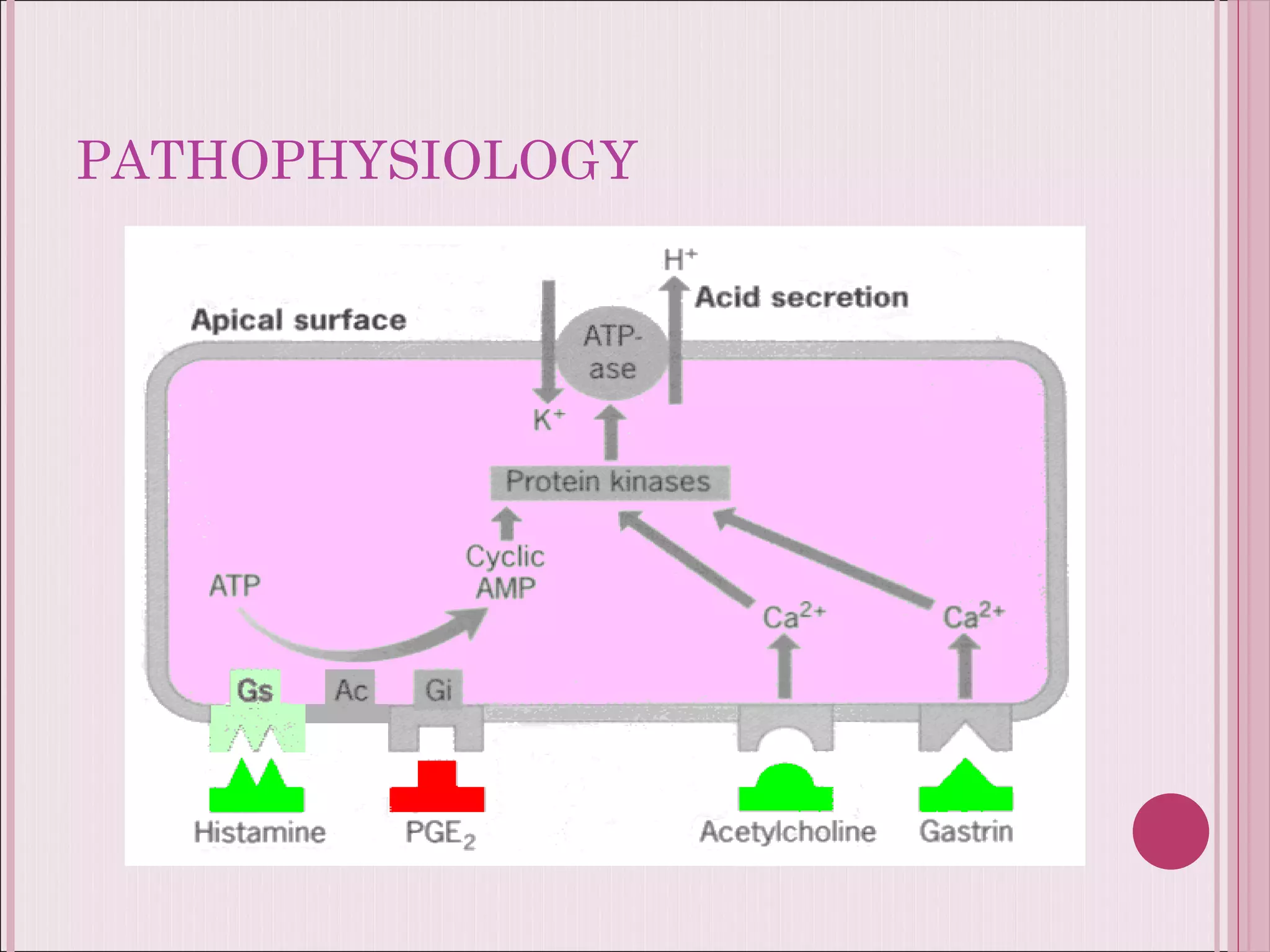
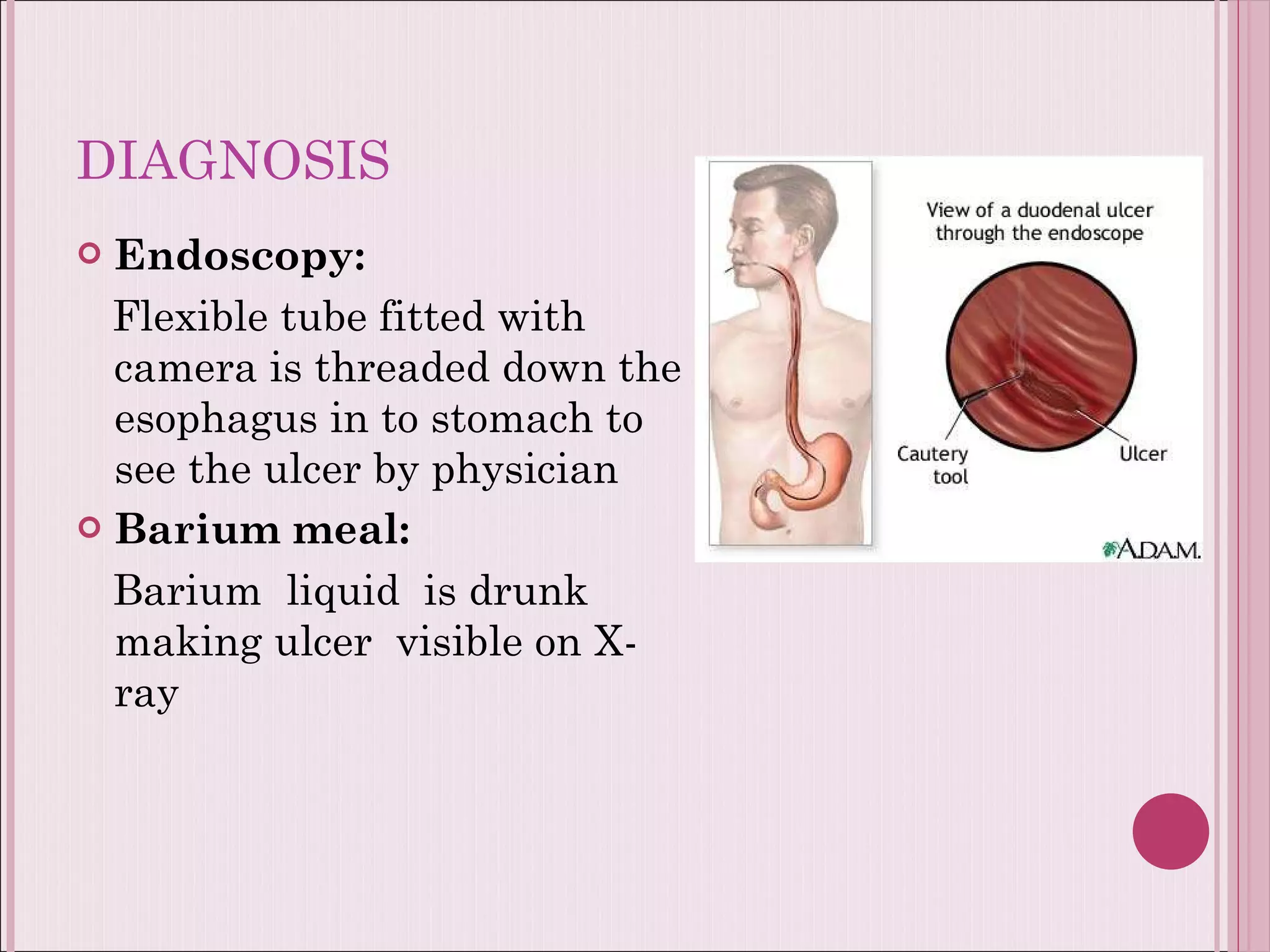
This document summarizes various drugs used to treat peptic ulcers caused by excess stomach acid and Helicobacter pylori infection. It discusses histamine antagonists like cimetidine that block acid production. Proton pump inhibitors like omeprazole irreversibly block the acid pump. Sucralfate forms a protective barrier over ulcers. Antibiotics can eliminate H. pylori infections. Lifestyle changes and antacids are also mentioned.