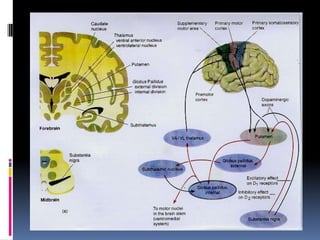
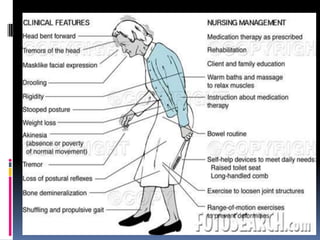
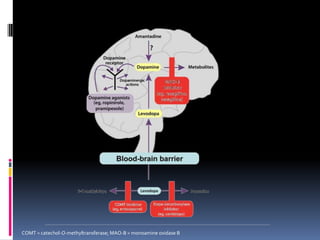
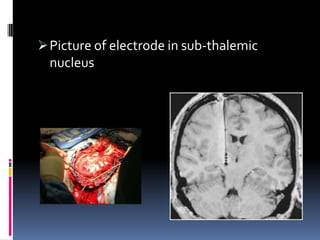
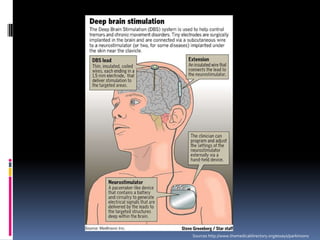
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and nonmotor dysfunction due to the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. It affects roughly 1.5 million Americans, with symptoms including tremors, bradykinesia, and impaired balance, and can be classified into three types based on age of onset. Treatment options include medications like levodopa and surgical interventions such as deep brain stimulation, with nursing management focusing on symptom relief and improving quality of life.