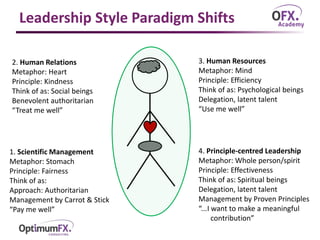
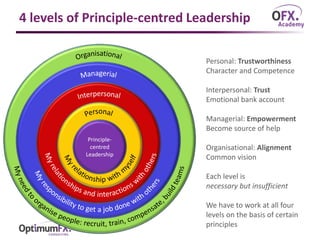
The document discusses paradigm thinking and its importance in shifting towards principle-centered leadership by challenging existing thought patterns to reveal new opportunities. It outlines what constitutes a paradigm, the effects of confirmation bias and the significance of a paradigm shift in leadership, emphasizing the need to change perspectives to foster revolutionary change. Additionally, it compares different leadership styles and highlights the four levels of principle-centered leadership, necessitating alignment and trust across personal, interpersonal, managerial, and organizational dimensions.