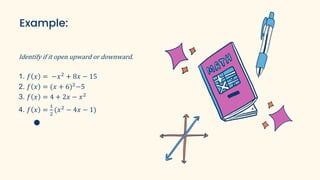
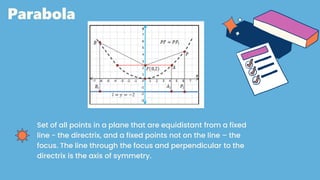
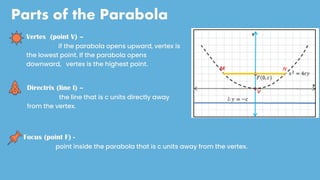
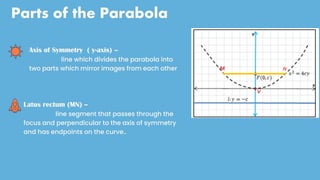
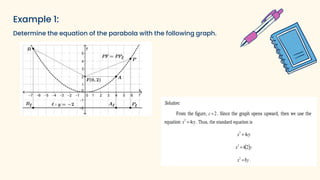
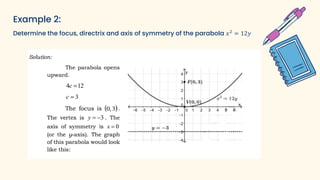
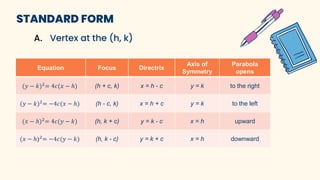
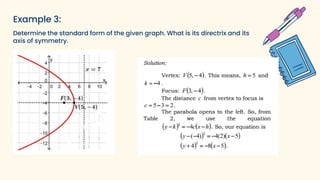
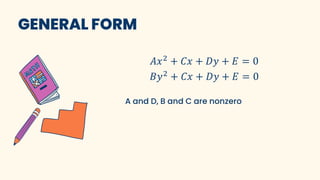
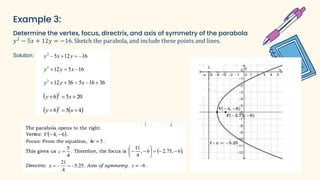
The document discusses parabolas and quadratic functions. It defines a parabola as the set of all points equidistant from a fixed line (the directrix) and a fixed point (the focus). It explains that the graph of a quadratic function f(x)=ax^2+bx+c is a parabola that opens upward if a>0 and downward if a<0. The document also identifies and describes the key parts of a parabola including the vertex, focus, directrix, and axis of symmetry. It provides the standard forms of parabolas with the vertex at the origin or a non-origin point (h,k). Several examples are worked through to identify the standard form,