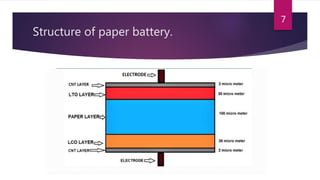
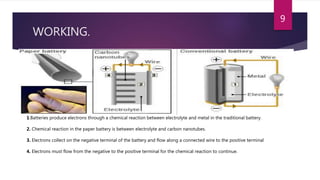
Paper batteries offer a flexible and lightweight alternative to traditional batteries. They are formed by combining carbon nanotubes with cellulose-based paper. This allows the battery to act as both an energy battery and supercapacitor, providing both steady and burst power. Paper batteries can be cut or folded without efficiency loss. They provide power from solutions like blood, sweat or urine, making them potentially suitable for medical devices. However, widespread commercial use will require more affordable manufacturing techniques and addressing current cost disadvantages compared to other batteries.