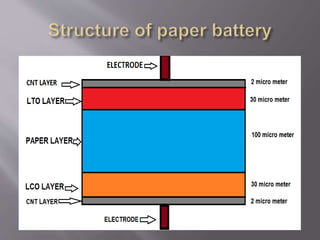
The document summarizes a paper battery, which is an ultra-thin, flexible energy storage device formed by combining carbon nanotubes with conventional paper. It works by a chemical reaction between the electrolyte and carbon nanotubes, causing electrons to flow from the negative to positive terminal. Paper batteries can power small electronics, are lightweight and flexible, produce 1.5 volts of electricity from a postage stamp sized sample, and don't lose efficiency from cutting or folding. However, carbon nanotubes are expensive and paper production may damage the environment.