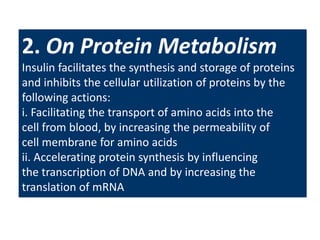
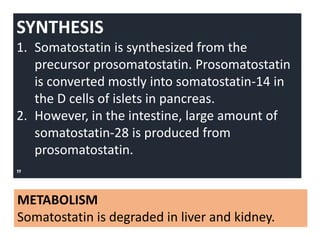
The document summarizes key information about the pancreas and pancreatic hormones. It describes the pancreas' exocrine and endocrine functions. The endocrine function is performed by islets of Langerhans, which contain alpha, beta, delta, and PP cells that secrete glucagon, insulin, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide respectively. It then provides details on the synthesis, actions, regulation and disorders related to insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin. Diabetes mellitus is discussed as resulting from insulin deficiency or excess of other hormones.