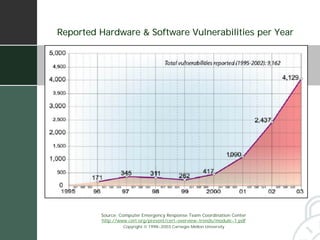
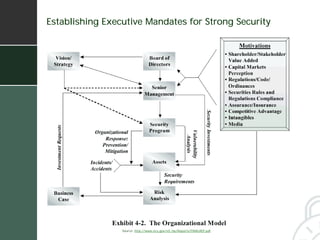
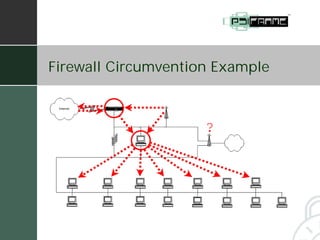
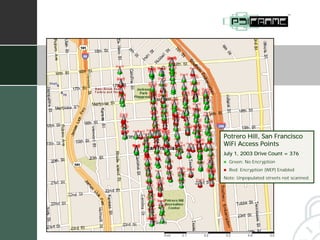
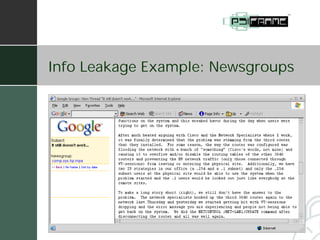
The document summarizes a presentation given by Fred Holborn of Psiframe, Inc. on data security for intellectual property managers. It discusses how theft of proprietary information caused the greatest financial losses for many organizations in 2003. It also outlines Psiframe's security assessment services which identify vulnerabilities from an attacker's perspective in order to recommend best practices for protecting information assets and networks. The document provides examples of common vulnerabilities and techniques attackers use, such as exploiting wireless networks and information leakage. It emphasizes the importance of regularly assessing security risks and implementing appropriate safeguards and regulatory compliance.