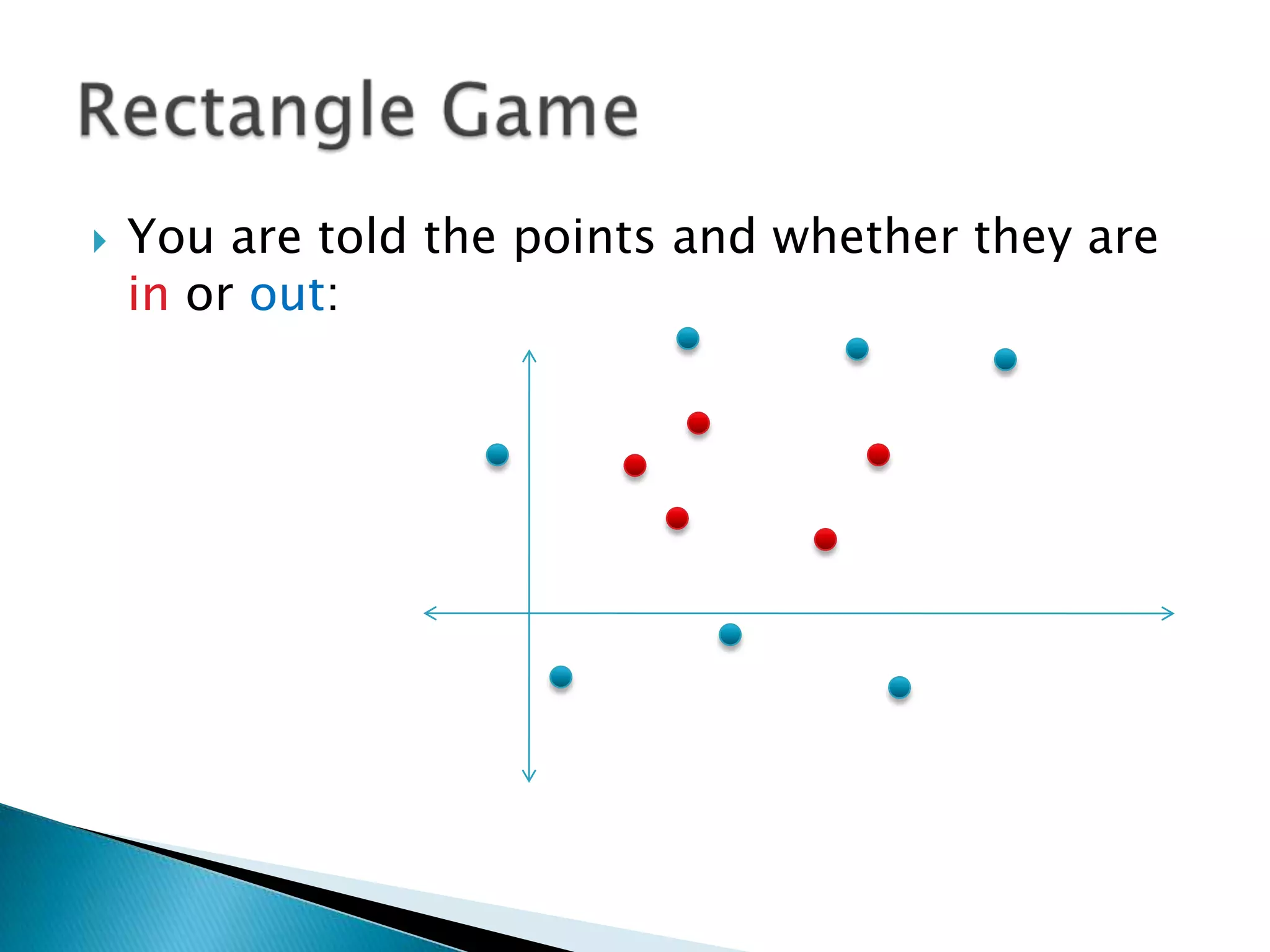
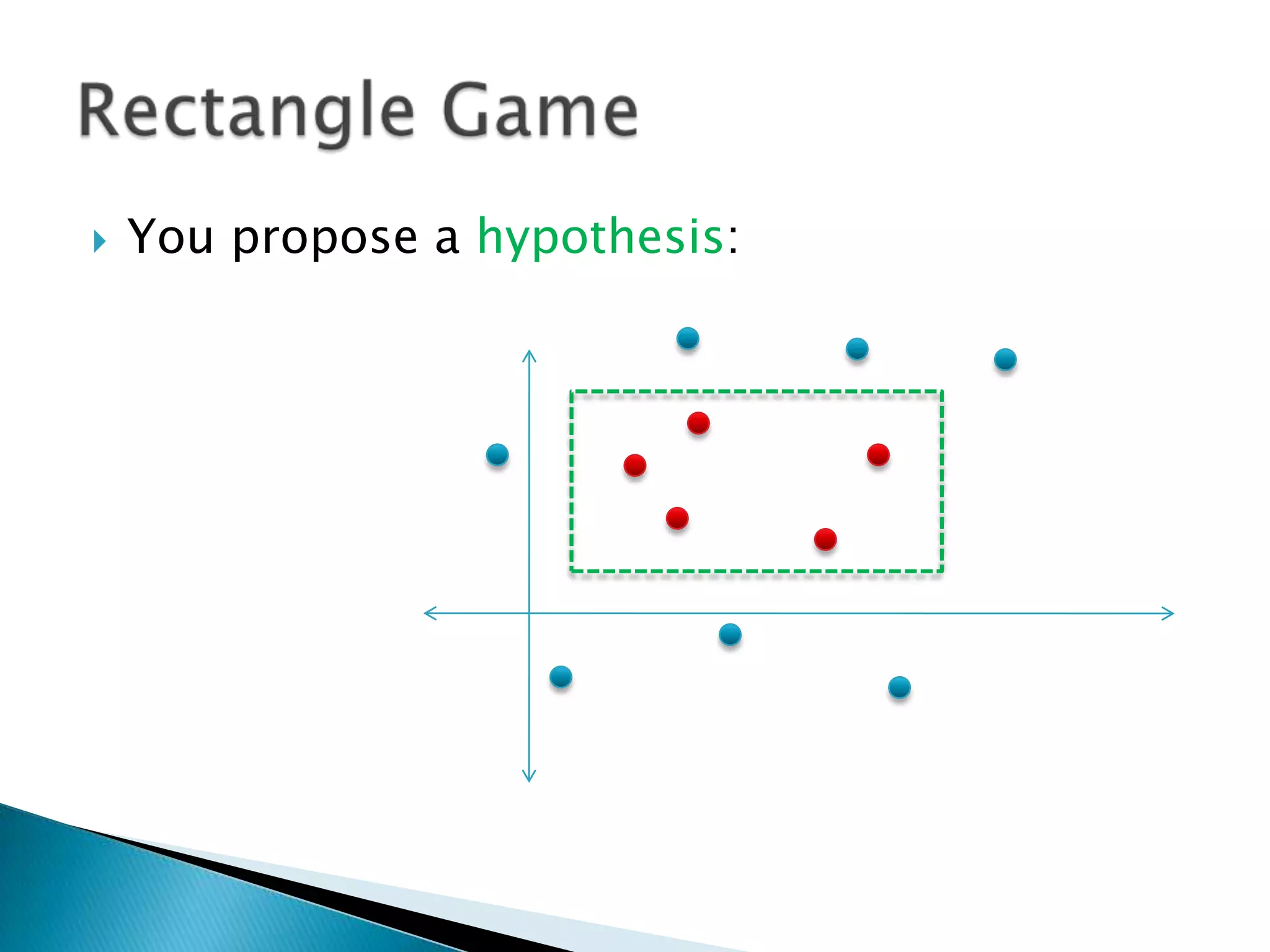
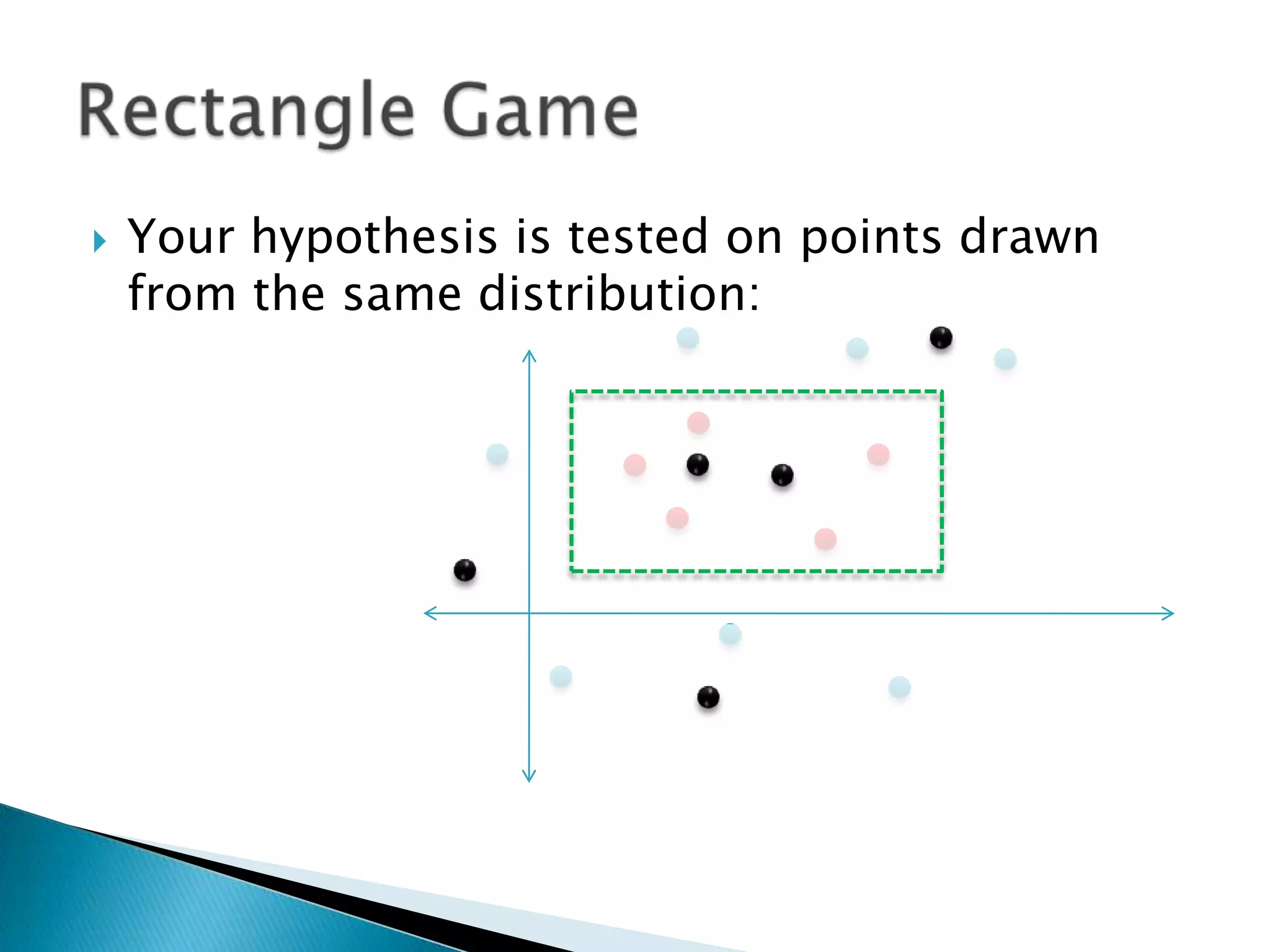
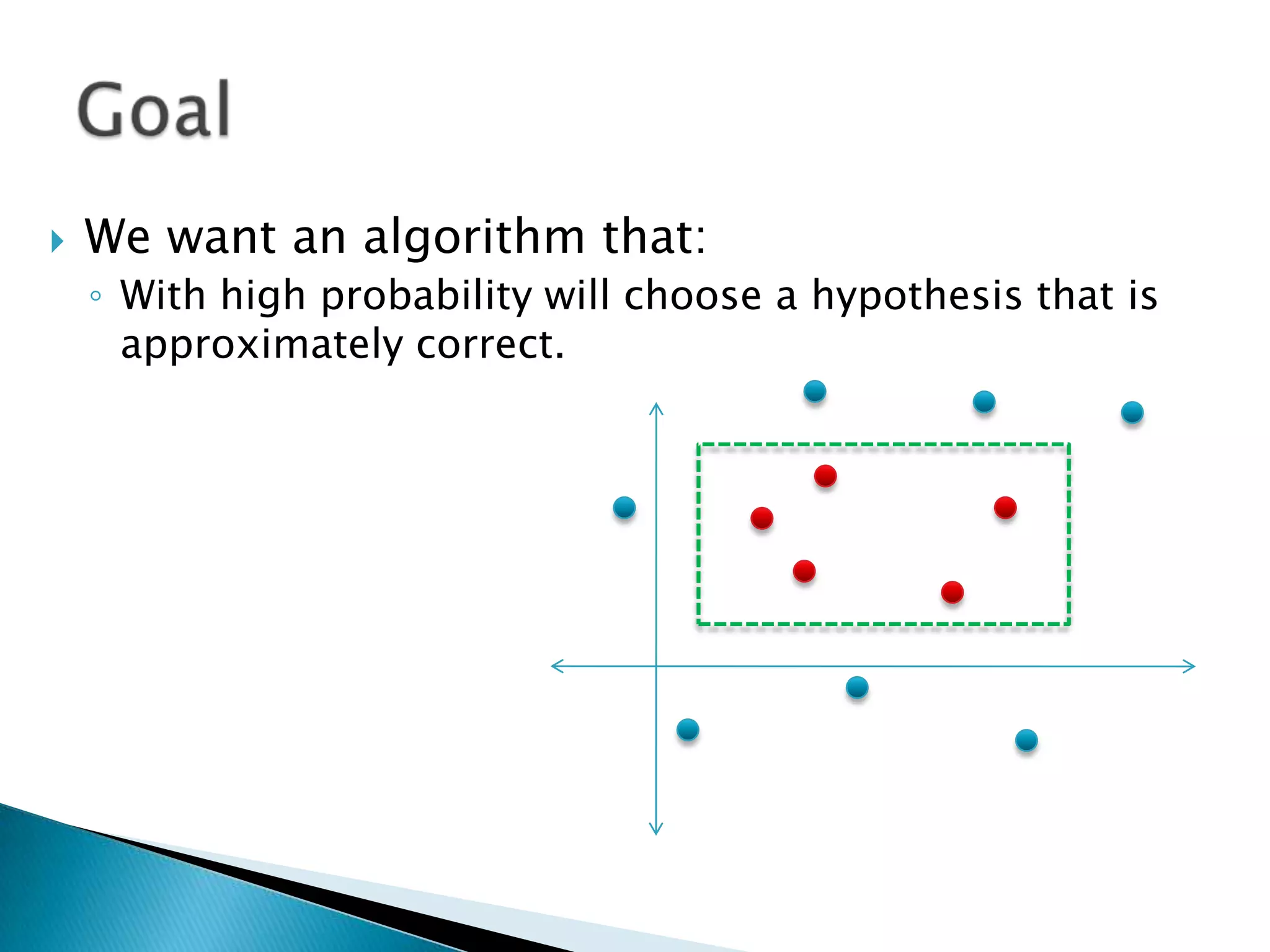
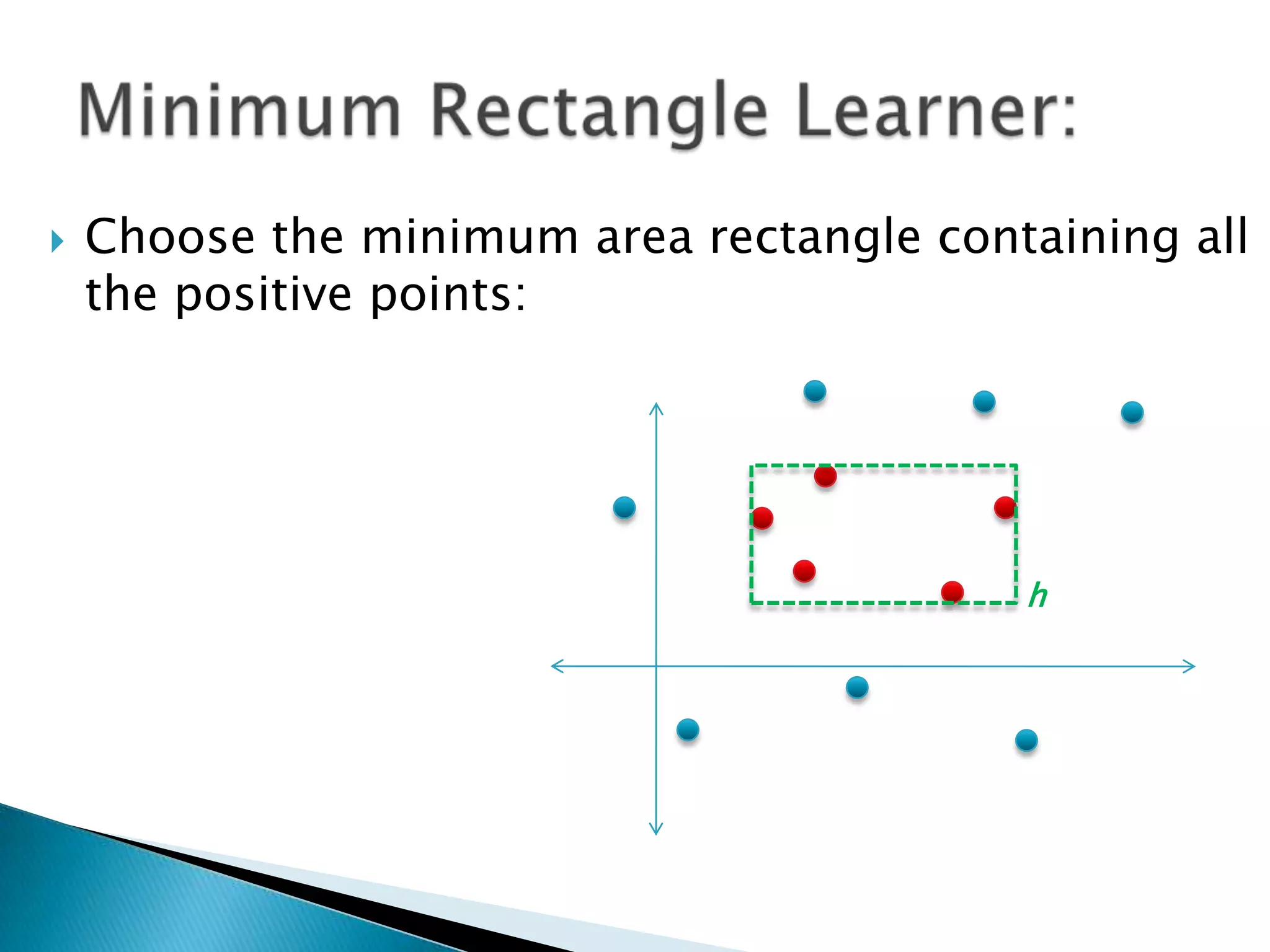
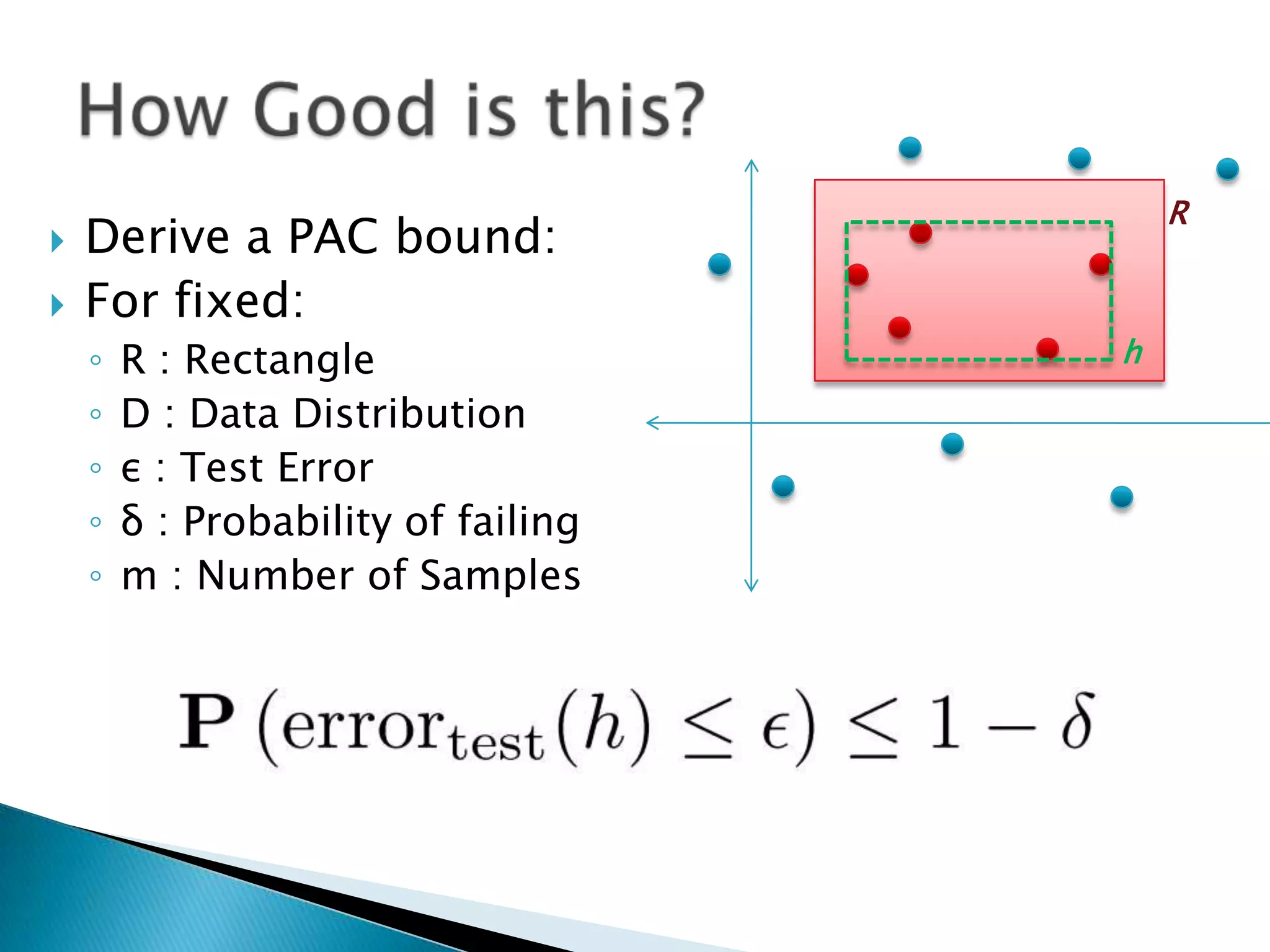
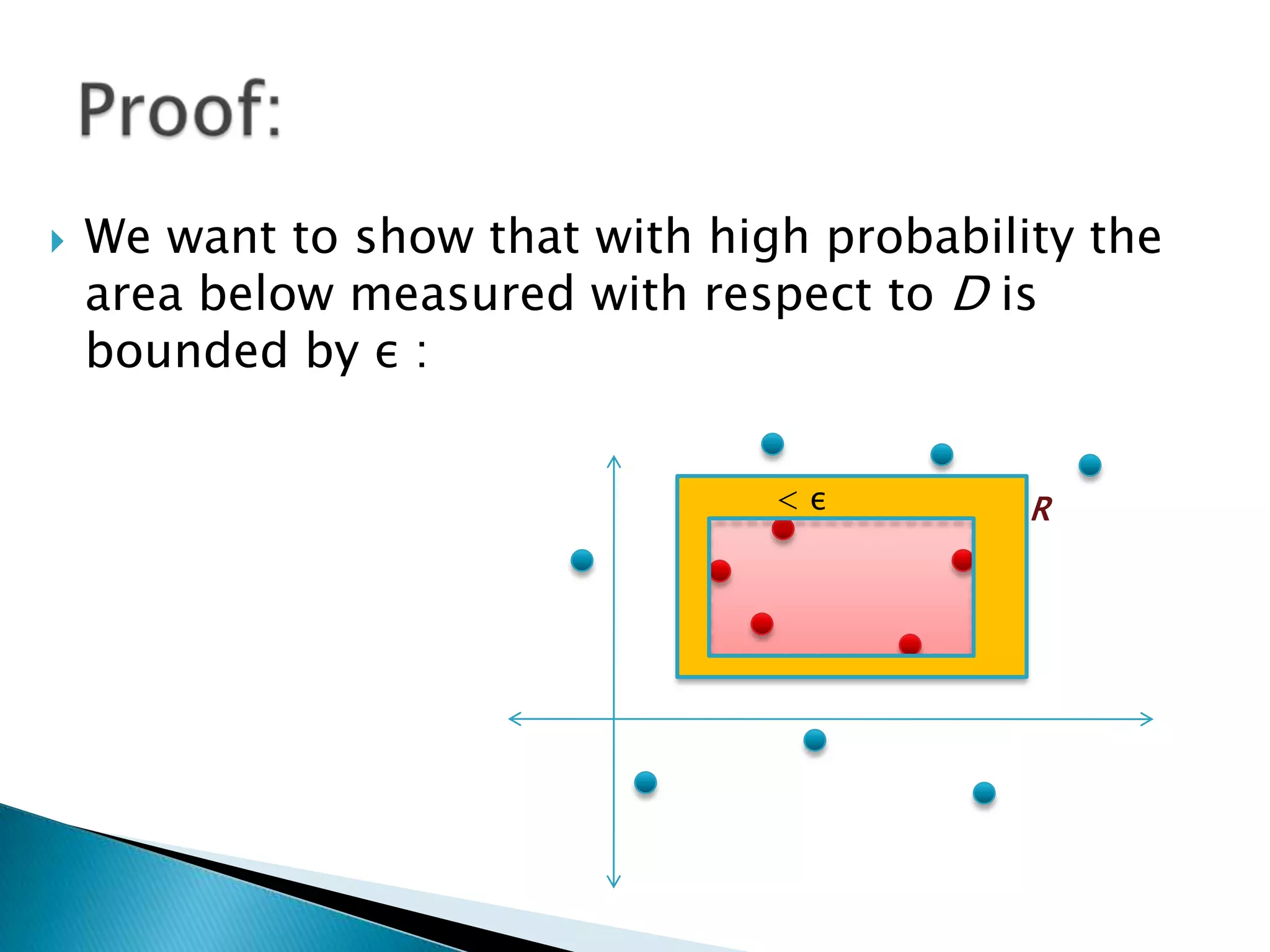
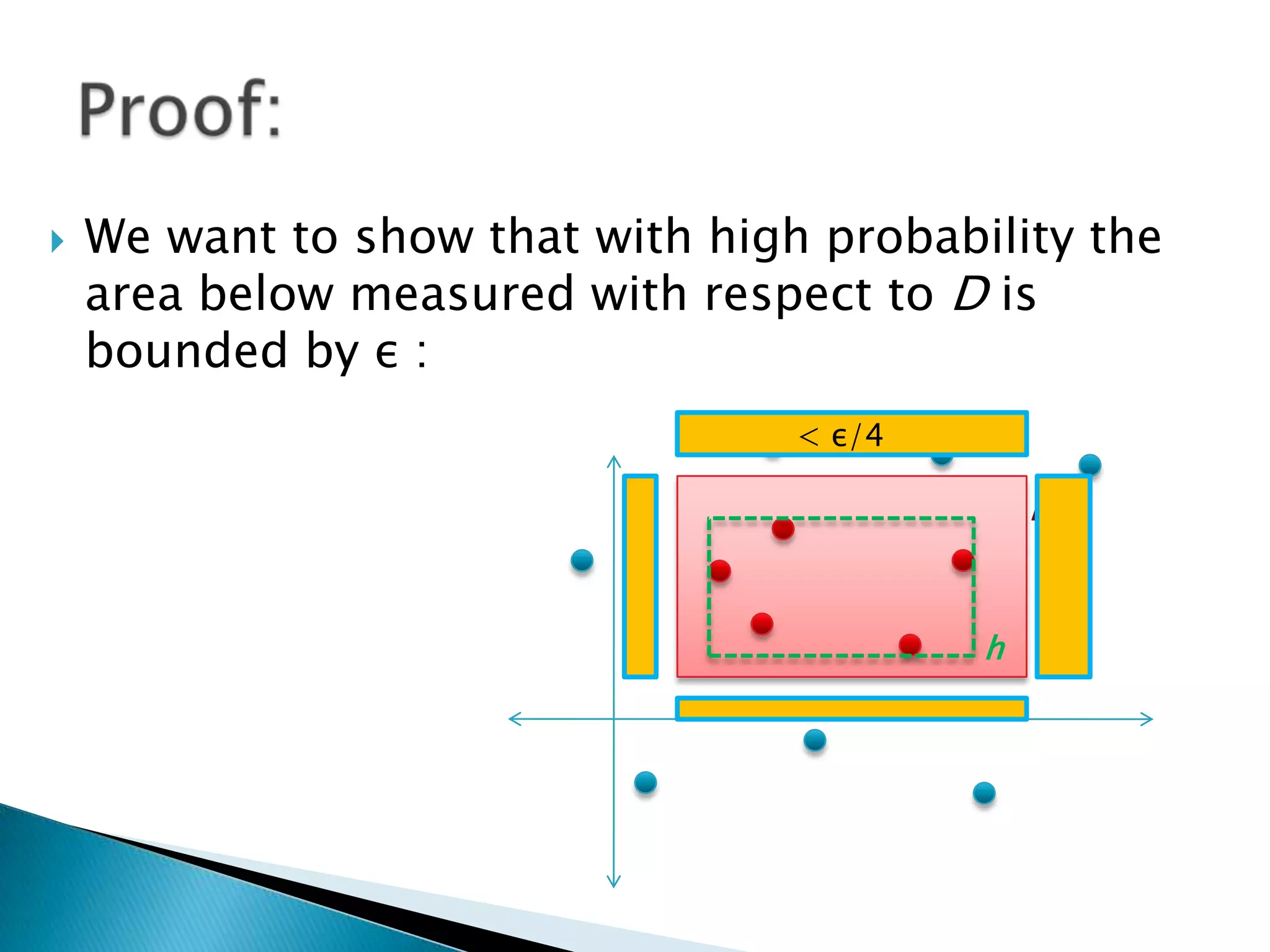
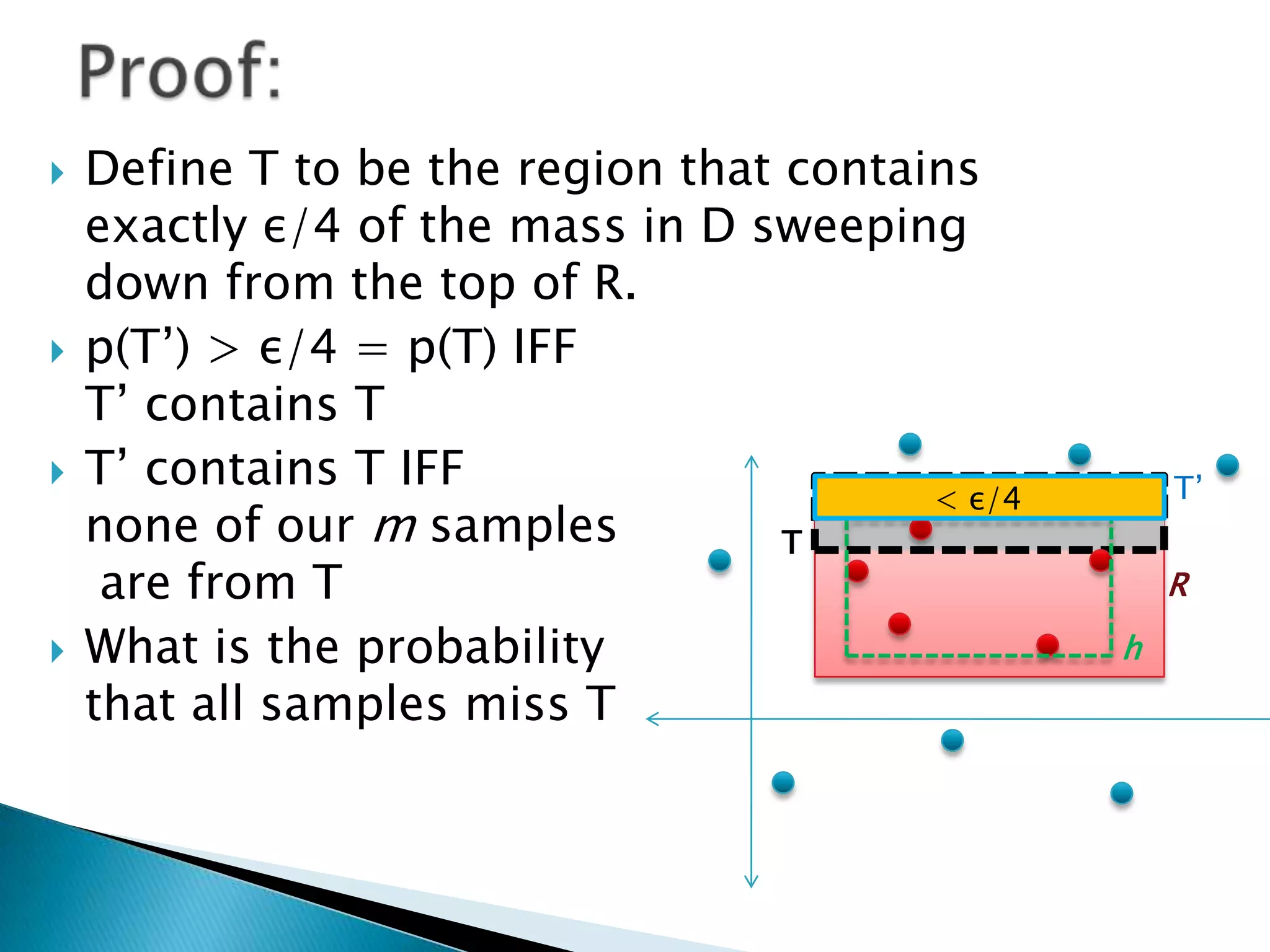
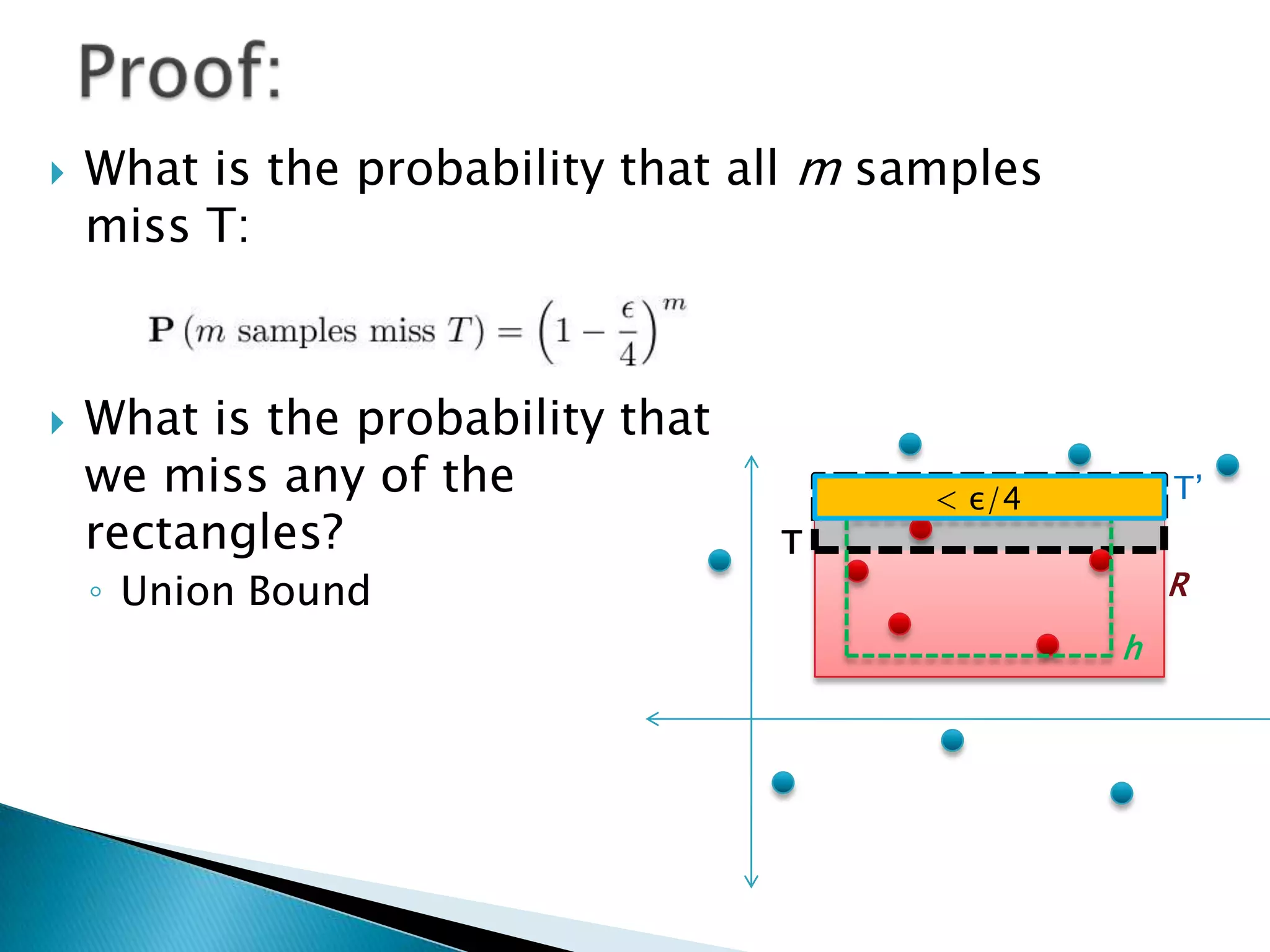
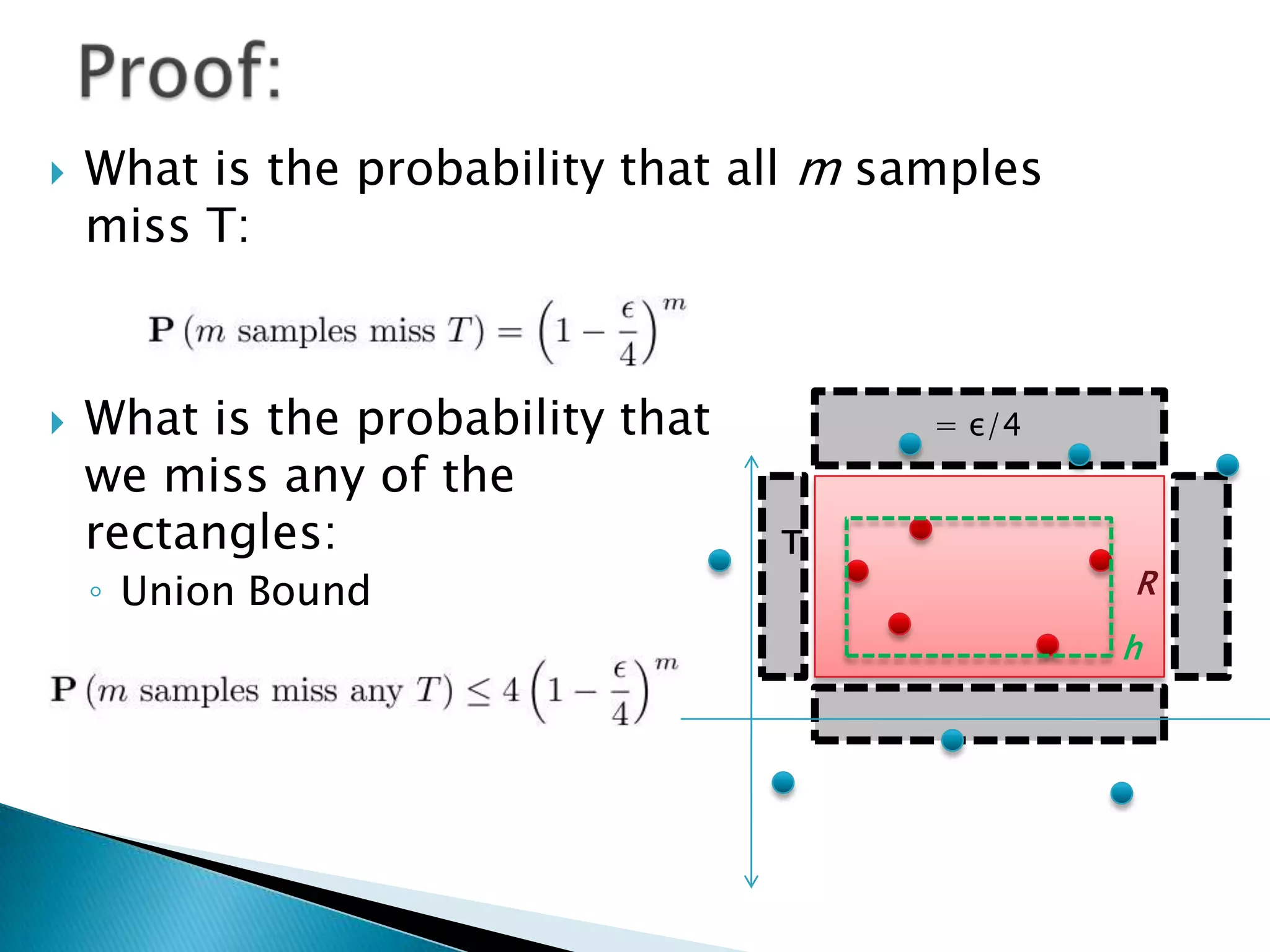
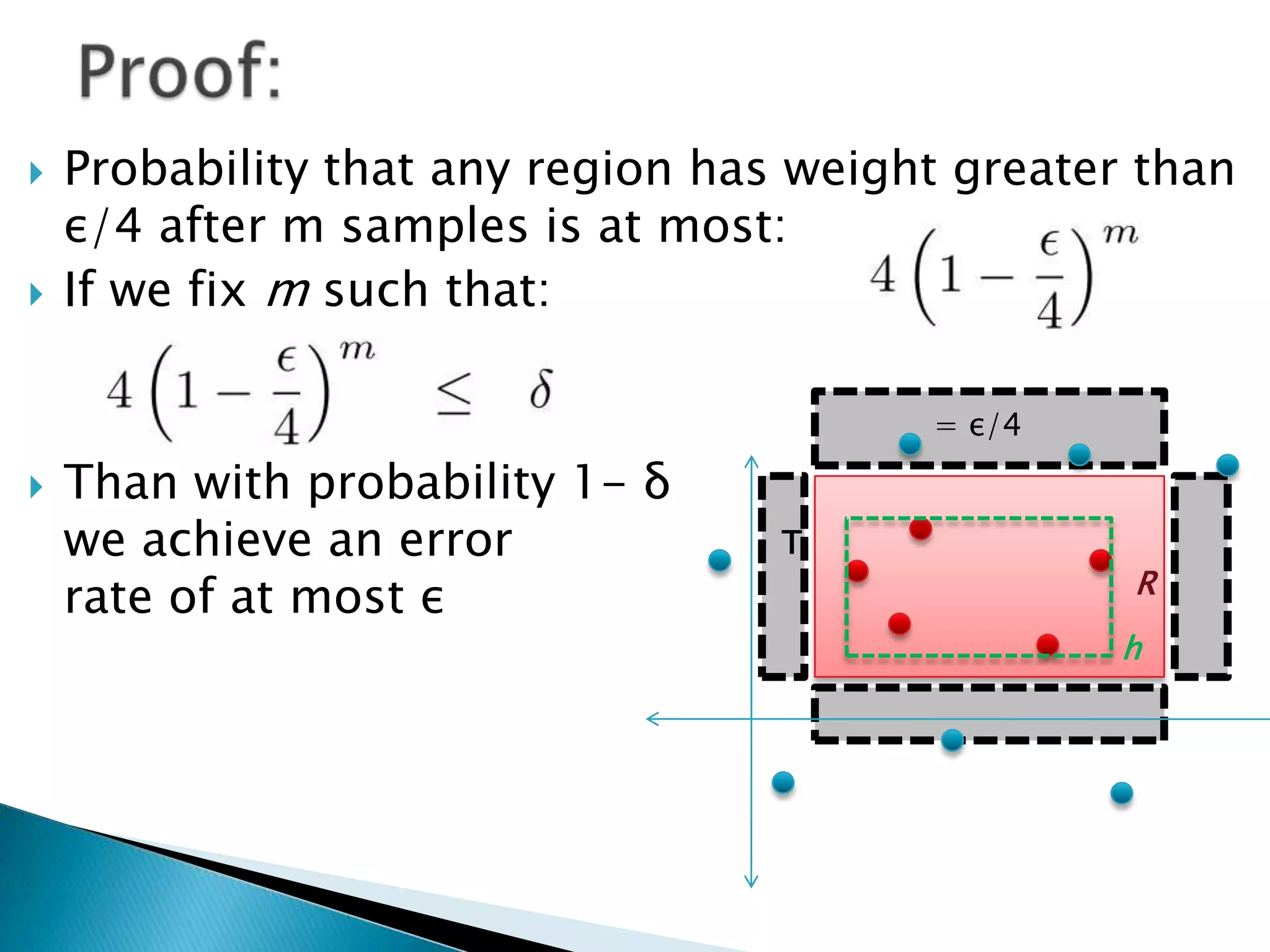
1) The document discusses PAC (probably approximately correct) learning and the VC (Vapnik-Chervonenkis) dimension.
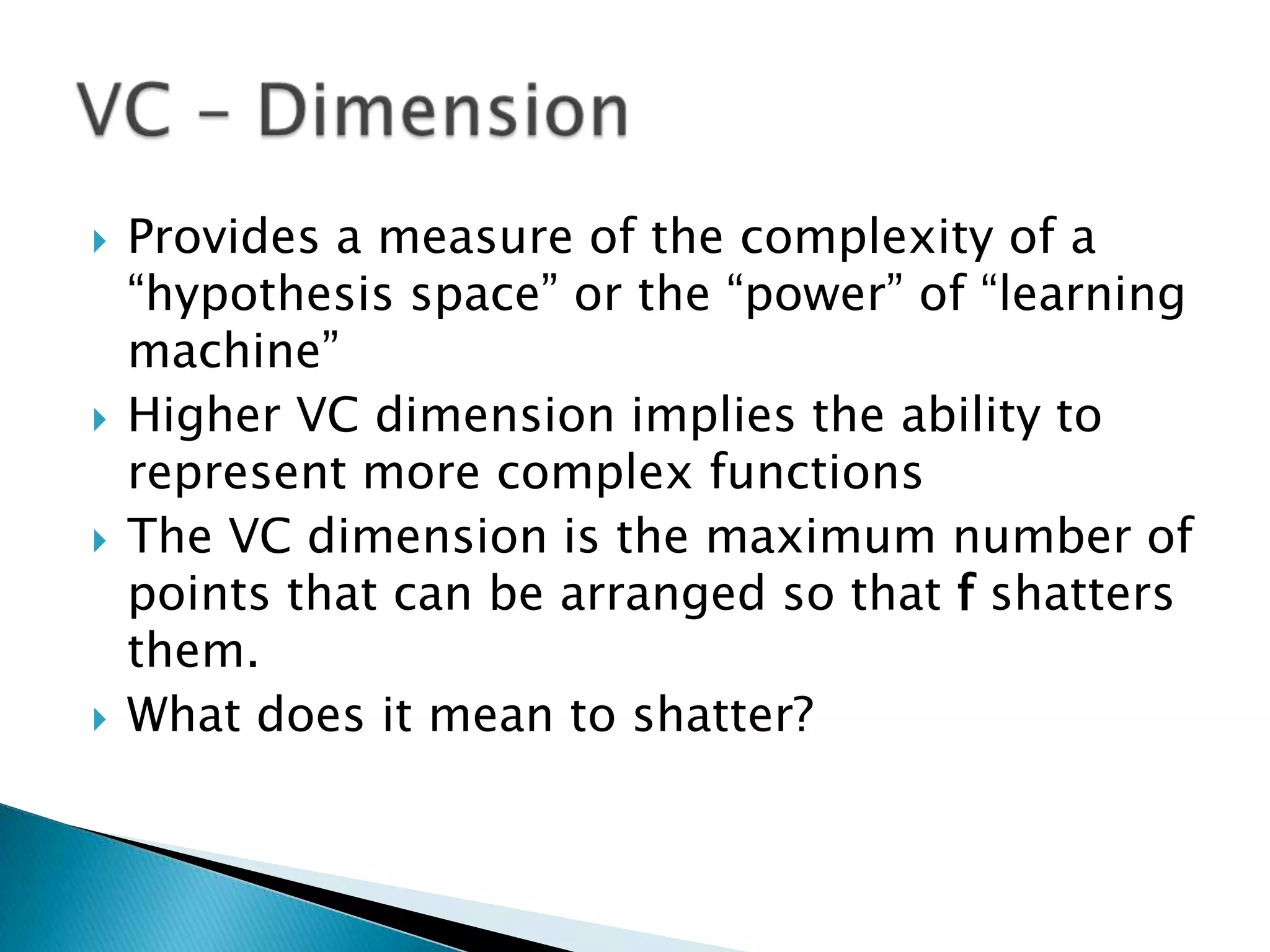
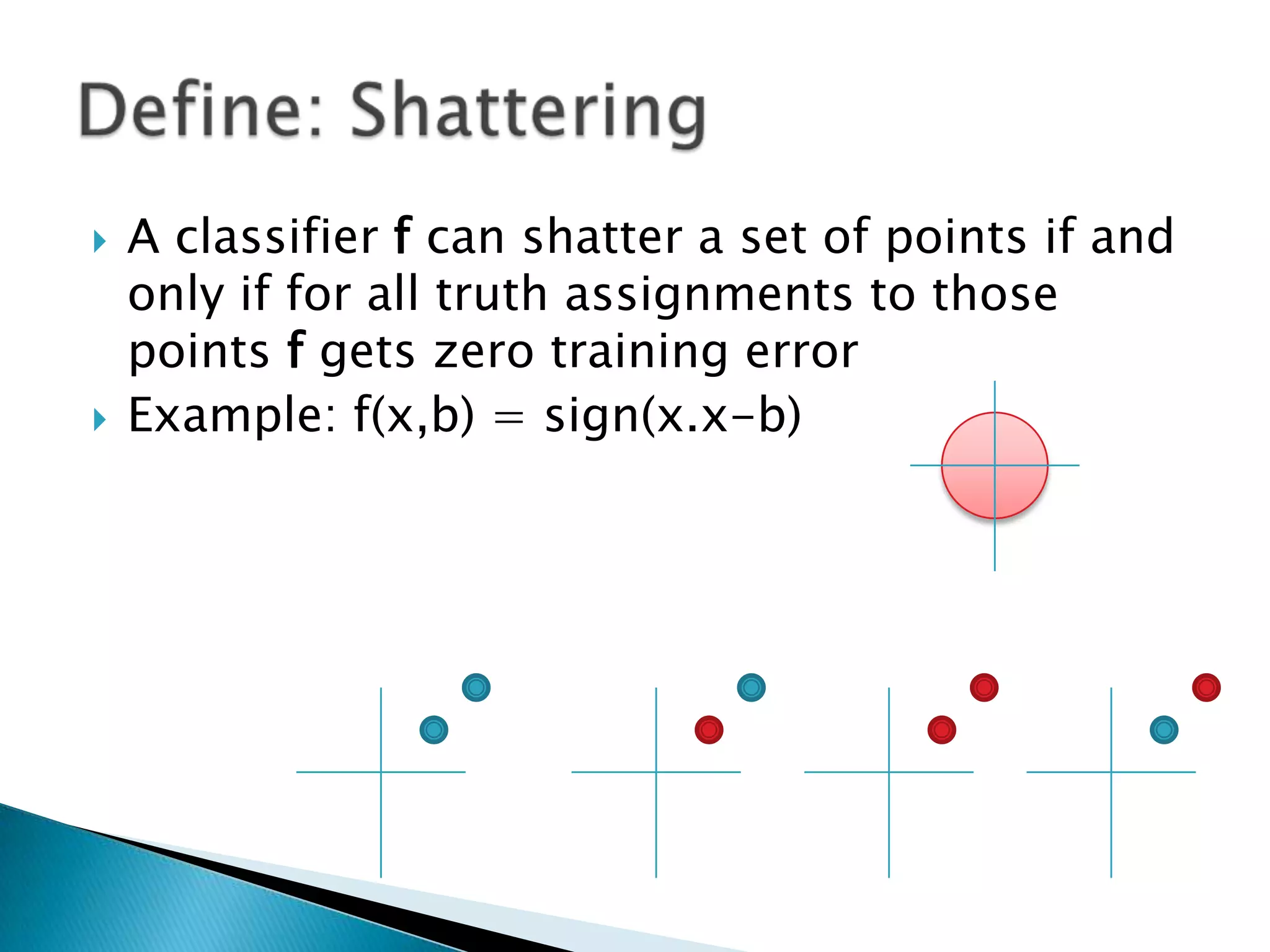
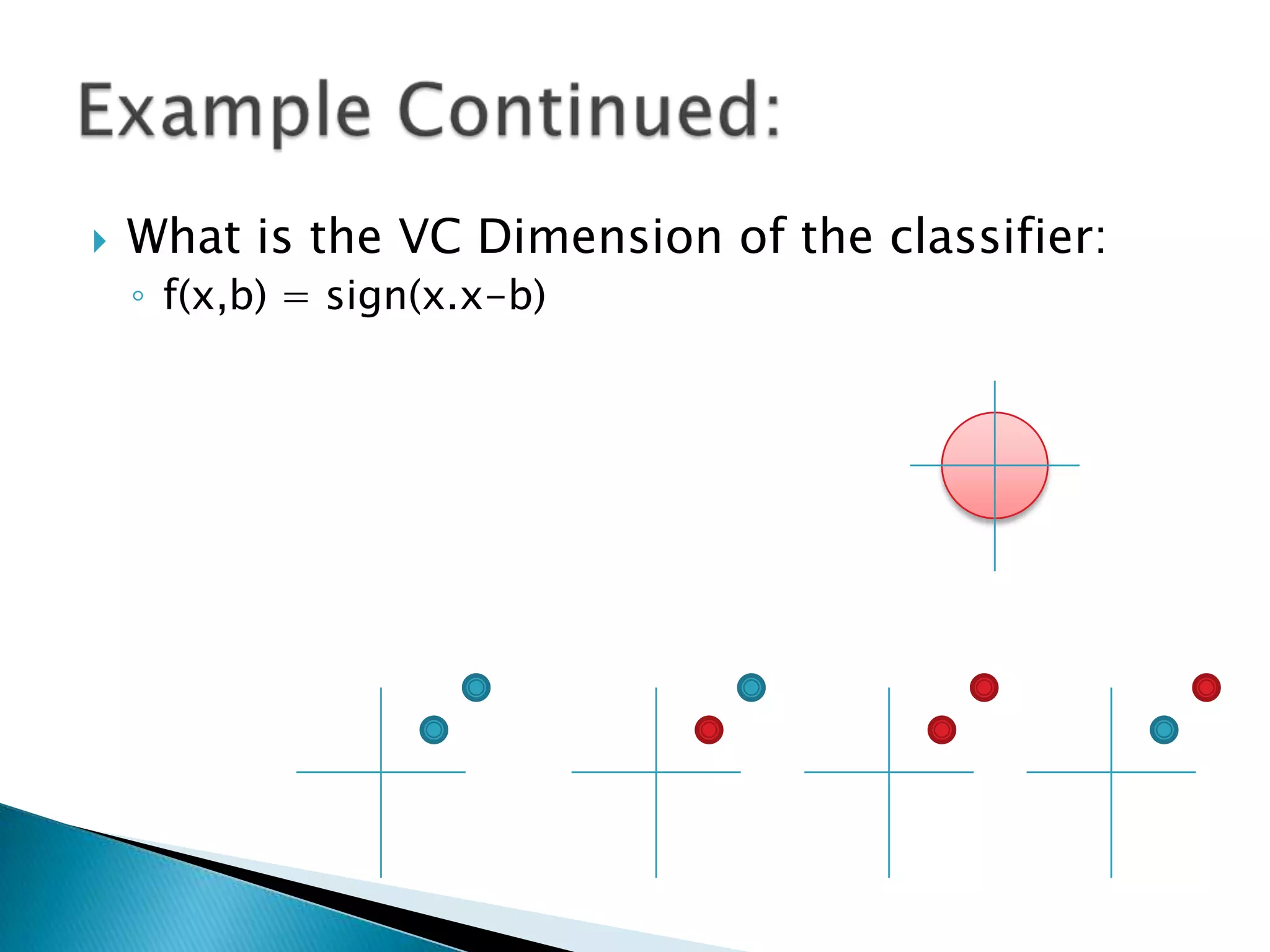
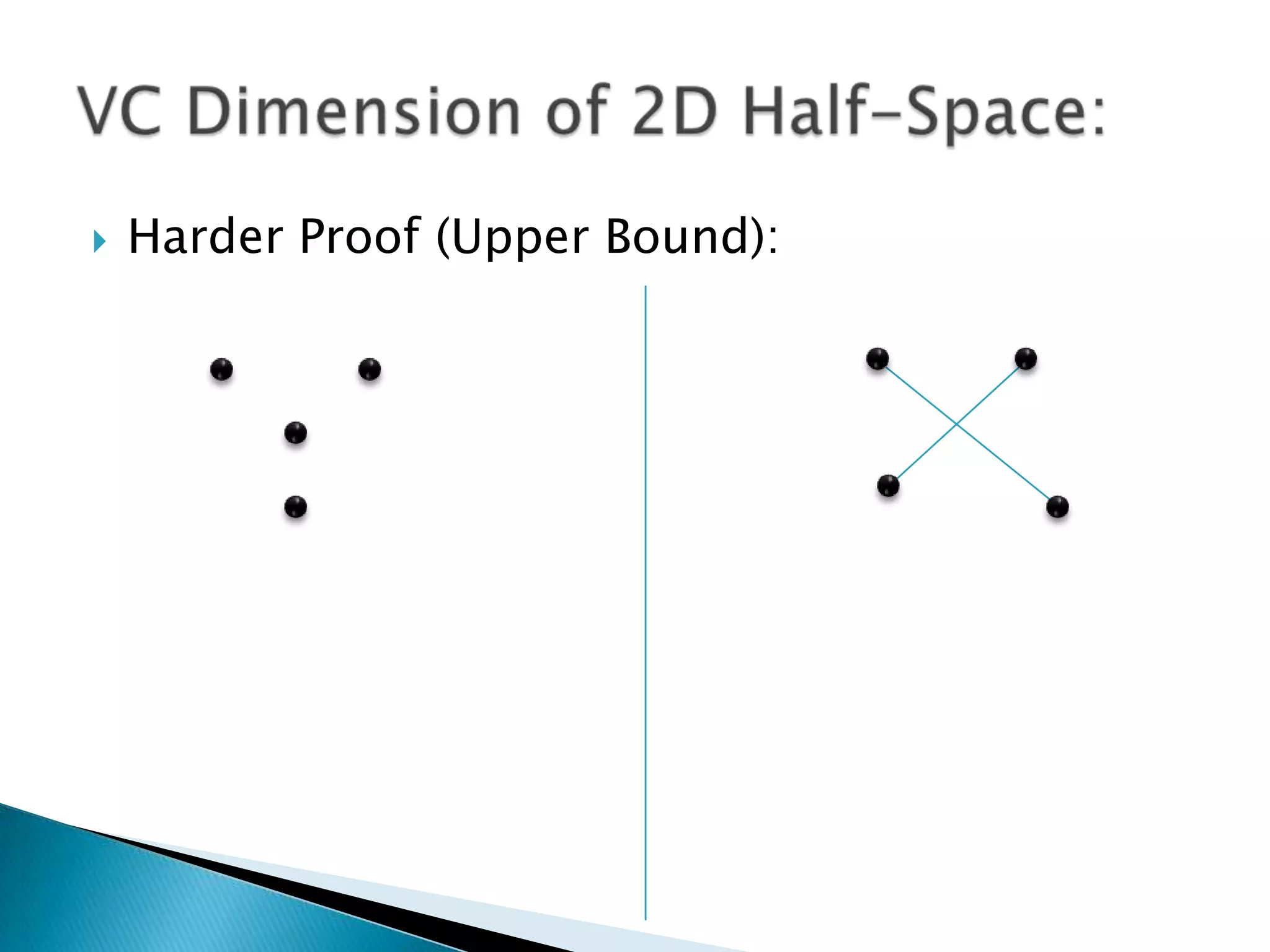
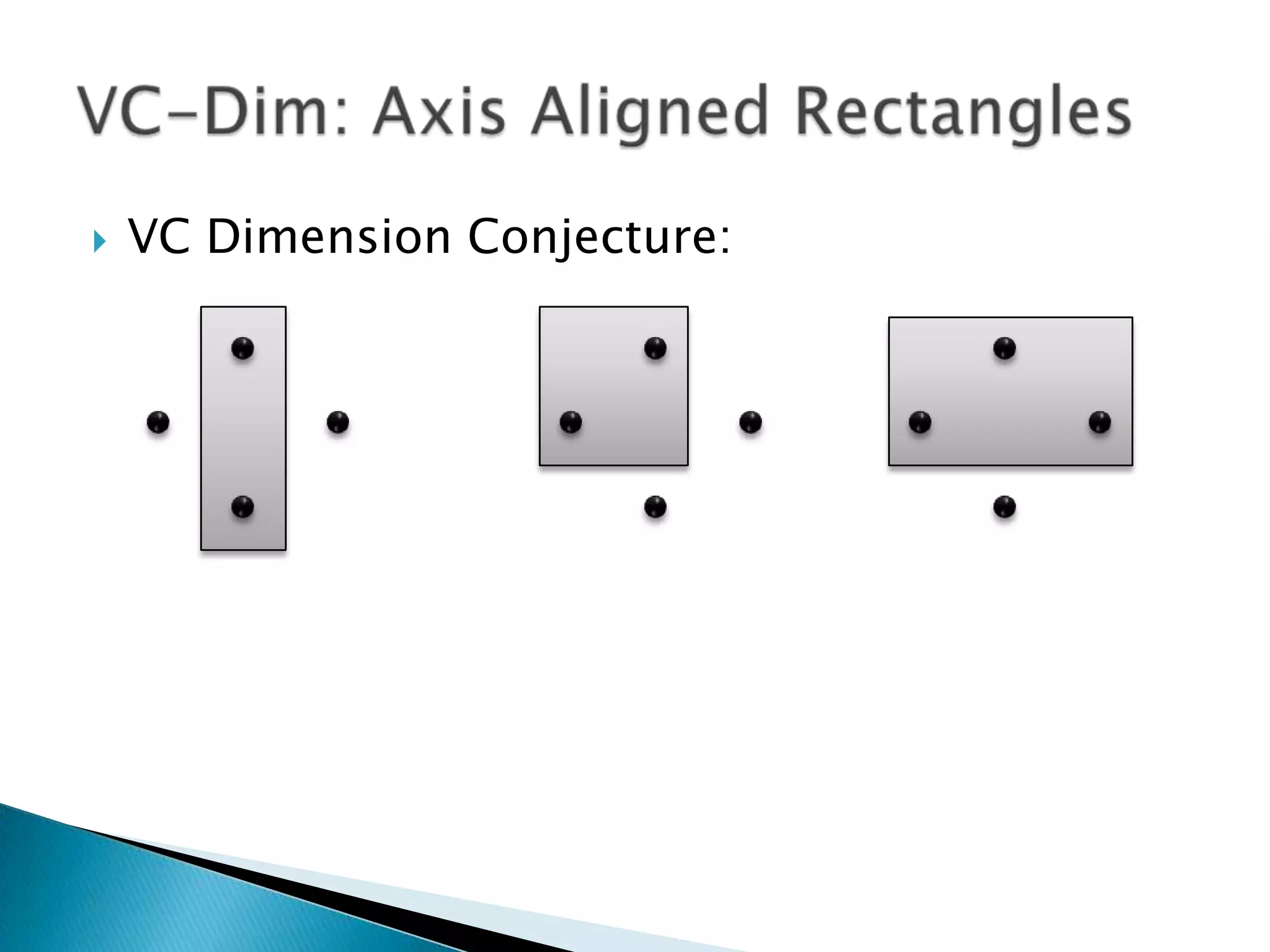
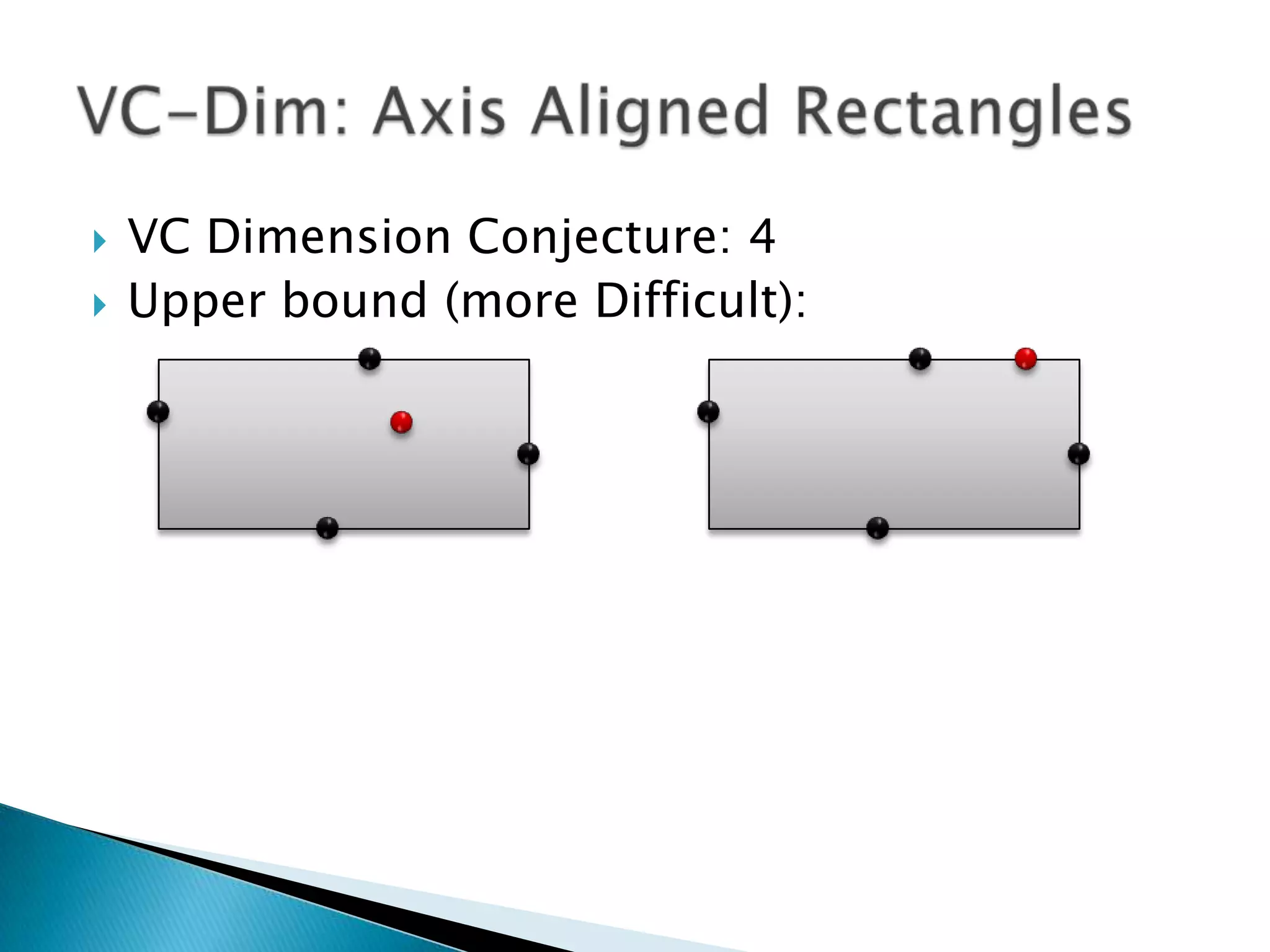
2) The VC dimension measures the complexity of a hypothesis space or learning machine. It is defined as the maximum number of points that can be arranged so that the hypotheses shatter them, meaning every possible labeling of the points is represented by some hypothesis.
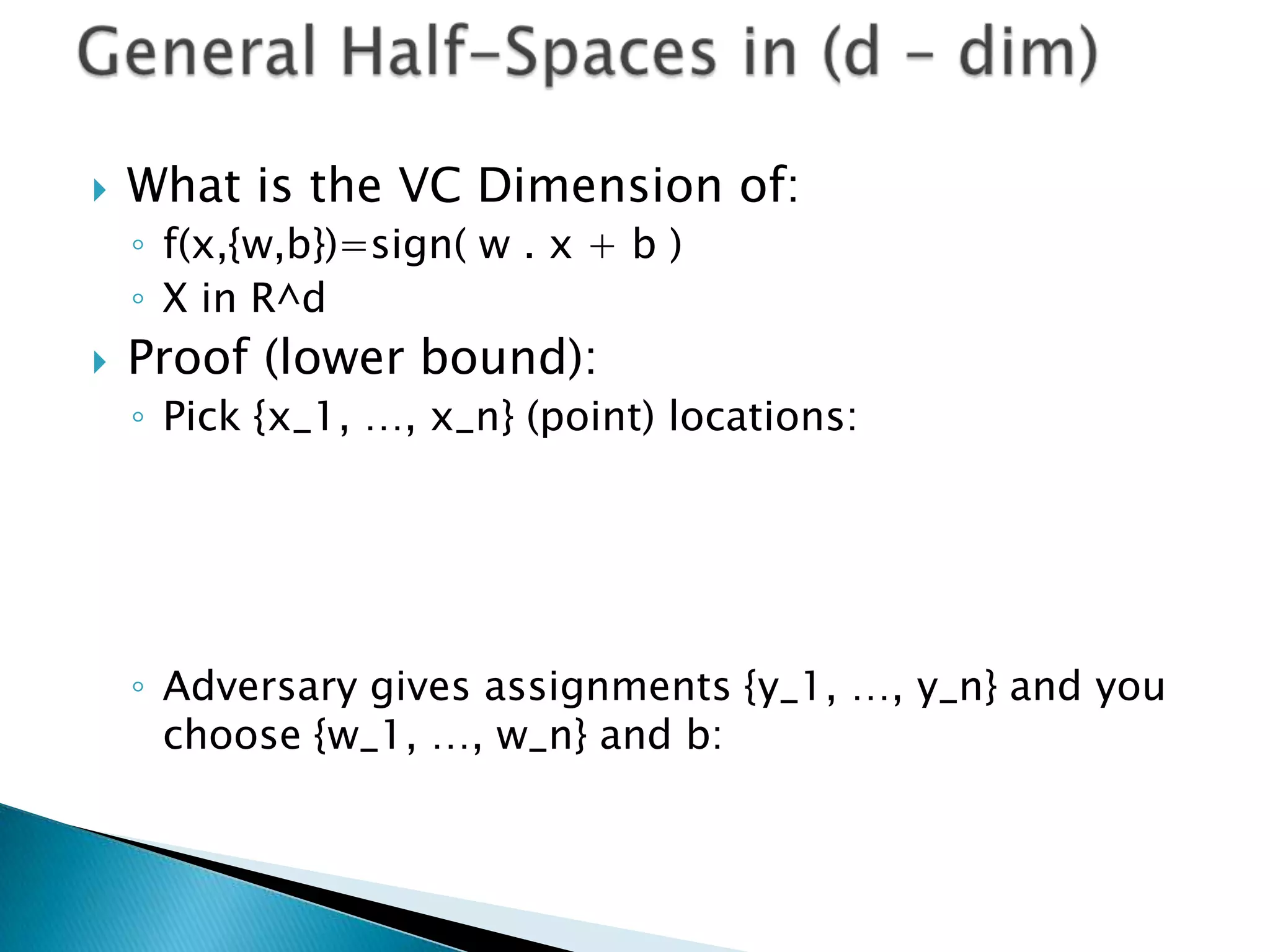
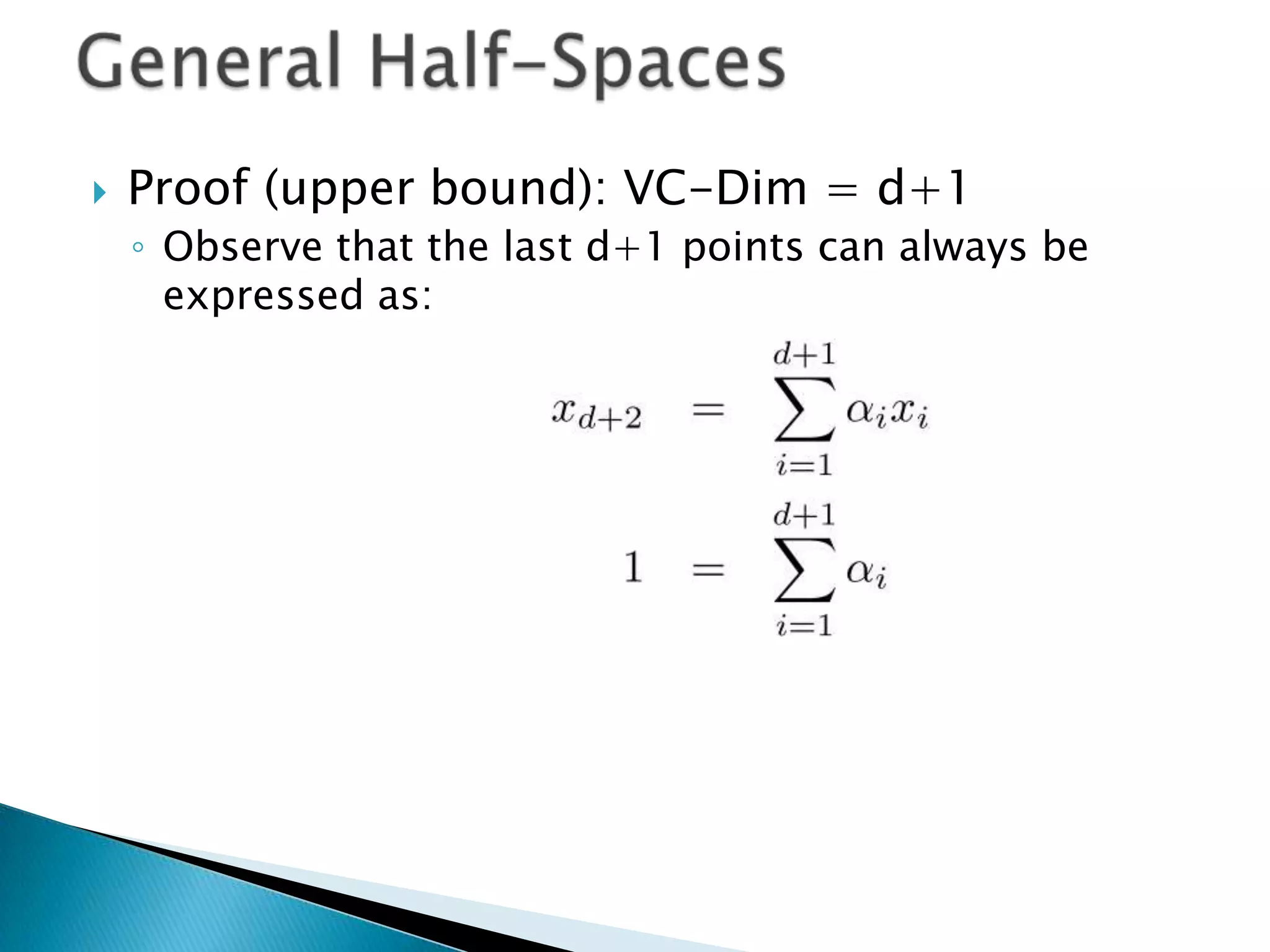
3) For linear classifiers of the form f(x) = sign(w·x + b) in R^d, the VC dimension is d+1. This provides an upper bound on the complexity of the hypothesis space.