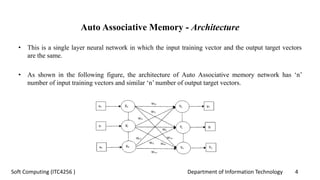
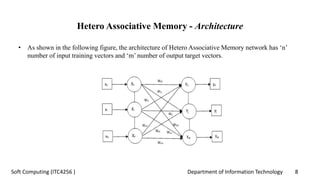
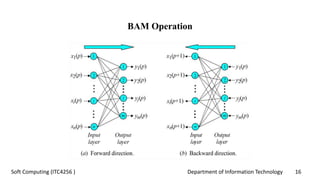
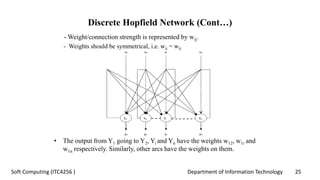
The document discusses associative memory networks, detailing their types such as auto-associative and hetero-associative networks, including their architectures and training/testing algorithms. It also covers iterative auto associative networks and bidirectional associative memories, emphasizing their operations and stability. Additionally, it introduces Hopfield networks and their discrete and continuous variants along with energy function evaluations.





















![Department of Information Technology 26Soft Computing (ITC4256 )
Discrete Hopfield Network – Training Algorithm
• During training of discrete Hopfield network, weights will be updated.
• As we know that we can have the binary input vectors as well as bipolar
input vectors.
• Hence, in both the cases, weight updates can be done with the following
relation:
Case 1 − Binary input patterns
For a set of binary patterns s p, p = 1 to P
Here, s p = s1 p, s2 p,..., si p,..., sn p
Weight Matrix is given by
P
wij = ∑ [2si(p)−1][2sj(p)−1] for i ≠ j
p=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200809090807/85/Associative-memory-network-26-320.jpg)
![Department of Information Technology 27Soft Computing (ITC4256 )
Discrete Hopfield Network – Training Algorithm
Case 2 − Bipolar input patterns
For a set of binary patterns s p, p = 1 to P
Here, s p = s1 p, s2 p,..., si p,..., sn p
Weight Matrix is given by
P
wij = ∑ [si(p)][sj(p)] for i ≠ j
p=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200809090807/85/Associative-memory-network-27-320.jpg)





