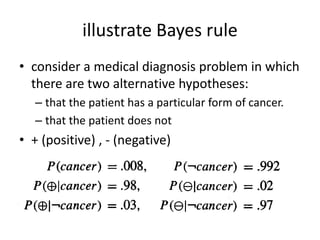
This document discusses Bayesian learning and the Bayes theorem. Some key points:
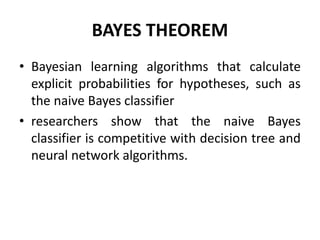
- Bayesian learning uses probabilities to calculate the likelihood of hypotheses given observed data and prior probabilities. The naive Bayes classifier is an example.
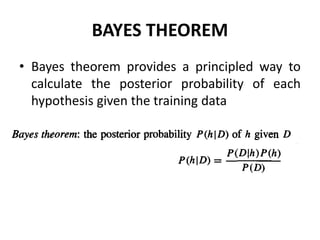
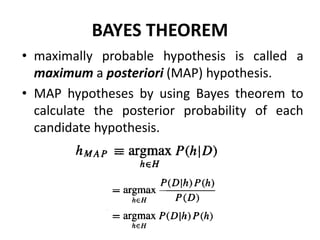
- The Bayes theorem provides a way to calculate the posterior probability of a hypothesis given observed training data by considering the prior probability and likelihood of the data under the hypothesis.
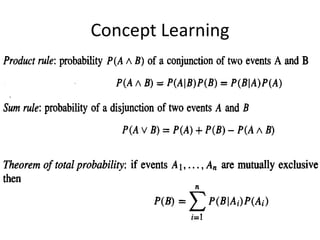
- Bayesian methods can incorporate prior knowledge and probabilistic predictions, and classify new instances by combining predictions from multiple hypotheses weighted by their probabilities.