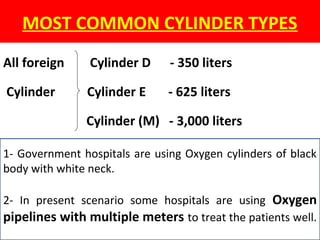
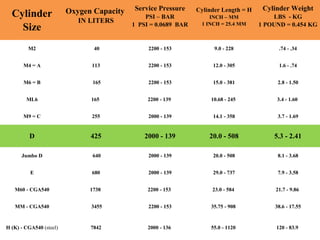
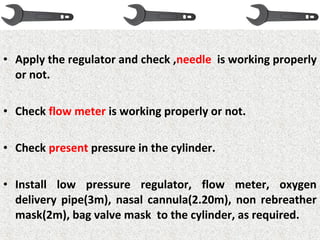
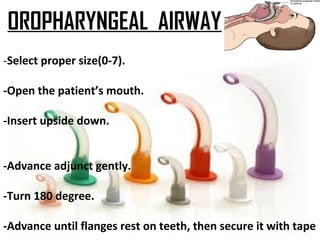
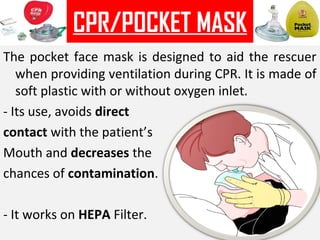
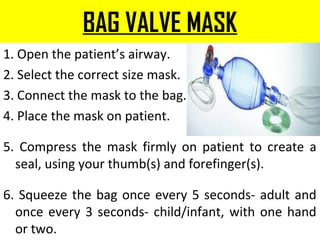
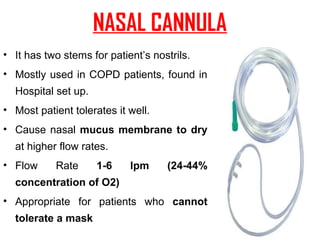
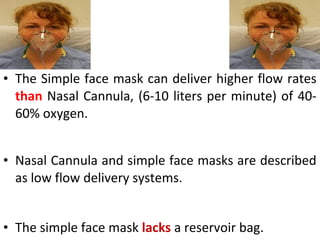
This document provides an overview of oxygen therapy, including key information about its discovery, importance, delivery methods, and equipment. It discusses five situations where oxygen is needed, describes common delivery devices like nasal cannulas and masks, and explains key oxygen system components like cylinders, regulators, flow meters, and humidifiers. The document also covers suction equipment and its role in oxygen therapy.