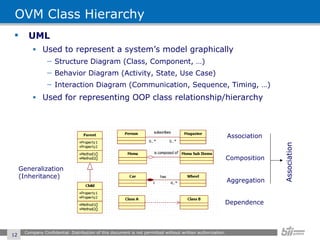
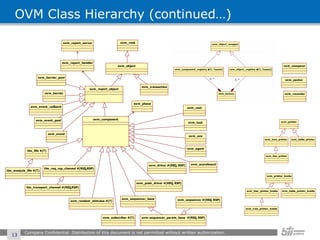
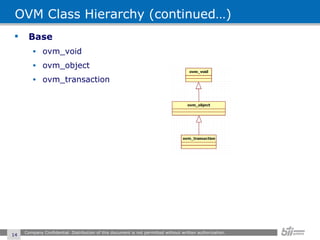
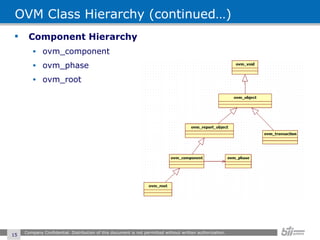
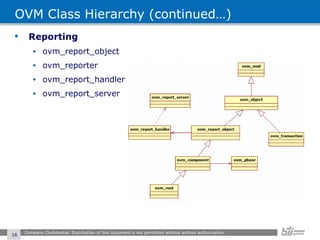
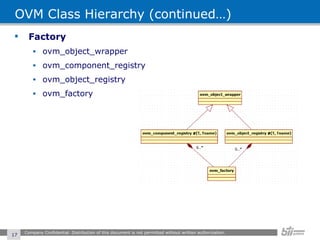
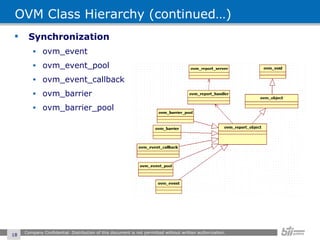
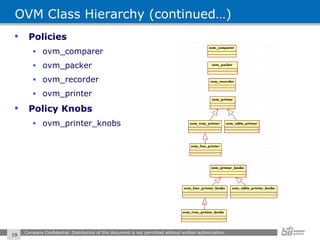
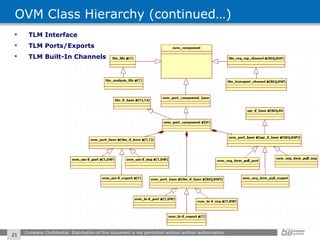
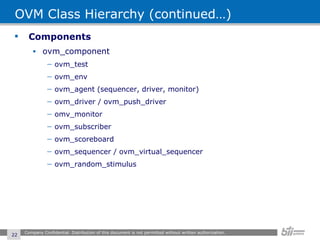
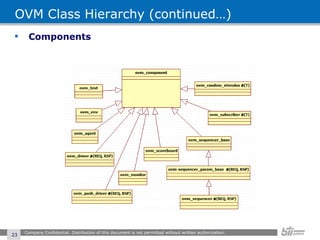
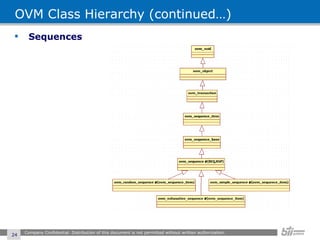
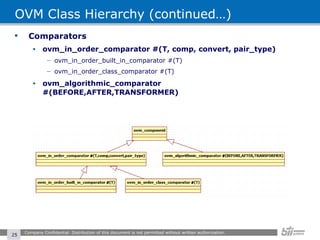
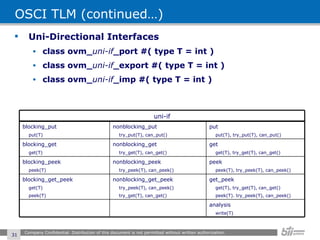
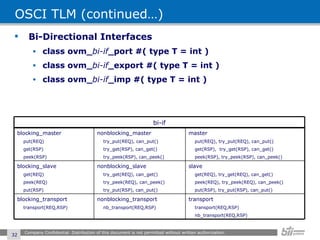
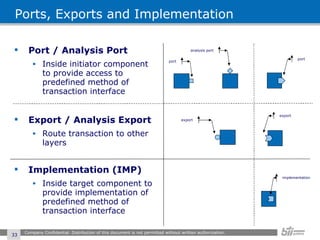
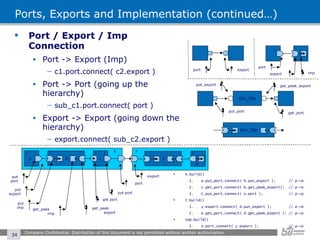
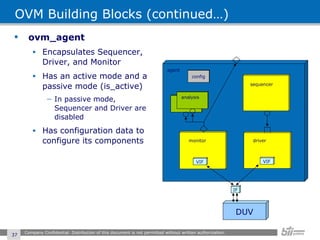
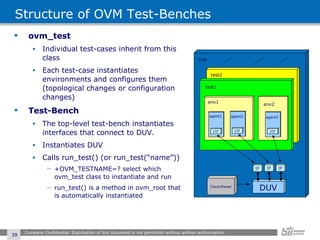
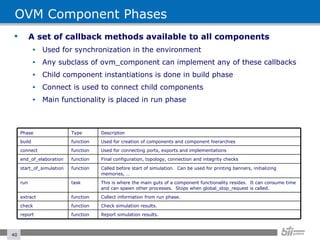
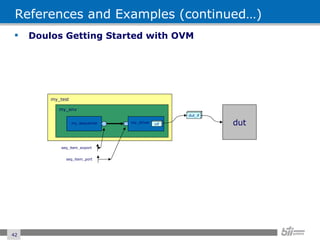
The document provides an overview of the Open Verification Methodology (OVM) framework. OVM is a SystemVerilog library that implements object-oriented design patterns to provide base classes for verification components. It includes features for component hierarchy, configuration, phasing, reporting, transaction recording, and interfaces based on the Open System C Initiative Transaction Level Modeling 2.0 standard.


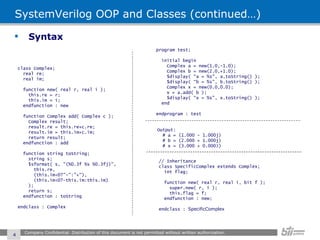


![SystemVerilog OOP and Classes (continued…) Parameterized Classes Company Confidential. Distribution of this document is not permitted without written authorization. class stack #(type T = int); local T items[$]; task push( T a ); items.push_front(a); endtask : push task pop( ref T a ); a = items.pop_front(); endtask : pop endclass : stack program test; initial begin stack #(int) is = new; stack #(real) rs = new; for( int i=0; i<10; i++ ) begin $display( "Pushed -> %0d : %0.3f", i, i*3.14 ); is.push( i ); rs.push( i*3.14 ); end $display( "--------------------" ); for( int i=0; i<10; i++ ) begin int x; real y; is.pop(x); rs.pop(y); $display( "Popped -> %0d : %0.3f", x, y ); end end endprogram : test # Pushed -> 0 : 0.000 # Pushed -> 1 : 3.140 # Pushed -> 2 : 6.280 # Pushed -> 3 : 9.420 # Pushed -> 4 : 12.560 # Pushed -> 5 : 15.700 # Pushed -> 6 : 18.840 # Pushed -> 7 : 21.980 # Pushed -> 8 : 25.120 # Pushed -> 9 : 28.260 # -------------------- # Popped -> 9 : 28.260 # Popped -> 8 : 25.120 # Popped -> 7 : 21.980 # Popped -> 6 : 18.840 # Popped -> 5 : 15.700 # Popped -> 4 : 12.560 # Popped -> 3 : 9.420 # Popped -> 2 : 6.280 # Popped -> 1 : 3.140 # Popped -> 0 : 0.000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ovm-features-summary-external-1228514223150940-8/85/SystemVerilog-OOP-Ovm-Features-Summary-7-320.jpg)