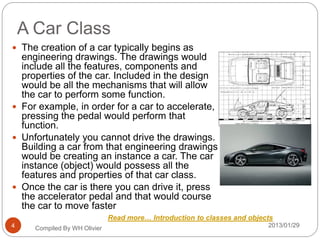
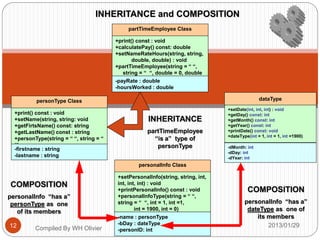
The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts including classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism and more. It defines a class as a blueprint for an object, and an object as an instance of a class. Classes can inherit properties and behaviors from other classes. Encapsulation groups an object's data and methods together. Polymorphism allows the same operation to be performed in different ways through method overloading and overriding.