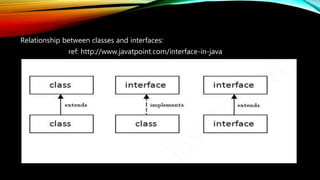
The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming principles in Java, including encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It explains key concepts through code examples and describes exception handling in Java, detailing keywords used for managing exceptions. The material serves as a foundational introduction for understanding Java programming concepts.



![EXAMPLES
Encapsulation:
public class Student{
private String name;
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s=new Student();
s.setname("vijay");
System.out.println(s.getName());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapresenation-160802212212/85/Object-Orinted-Programing-OOP-concepts-4-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLES
Inheritance:
class Employee{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapresenation-160802212212/85/Object-Orinted-Programing-OOP-concepts-5-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLES
Polymorphism:
class Bike{
void run(){
System.out.println("running");
}
}
class Splender extends Bike{
void run(){
System.out.println("running safely with 60km");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike b = new Splender();
b.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapresenation-160802212212/85/Object-Orinted-Programing-OOP-concepts-6-320.jpg)


![ Example: ( Abstract class )
abstract class Bike{
abstract void run();
}
class Honda4 extends Bike{
void run(){
System.out.println("running safely..");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike obj = new Honda4();
obj.run();
}
} ref: http://www.javatpoint.com/abstract-class-in-java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javapresenation-160802212212/85/Object-Orinted-Programing-OOP-concepts-9-320.jpg)