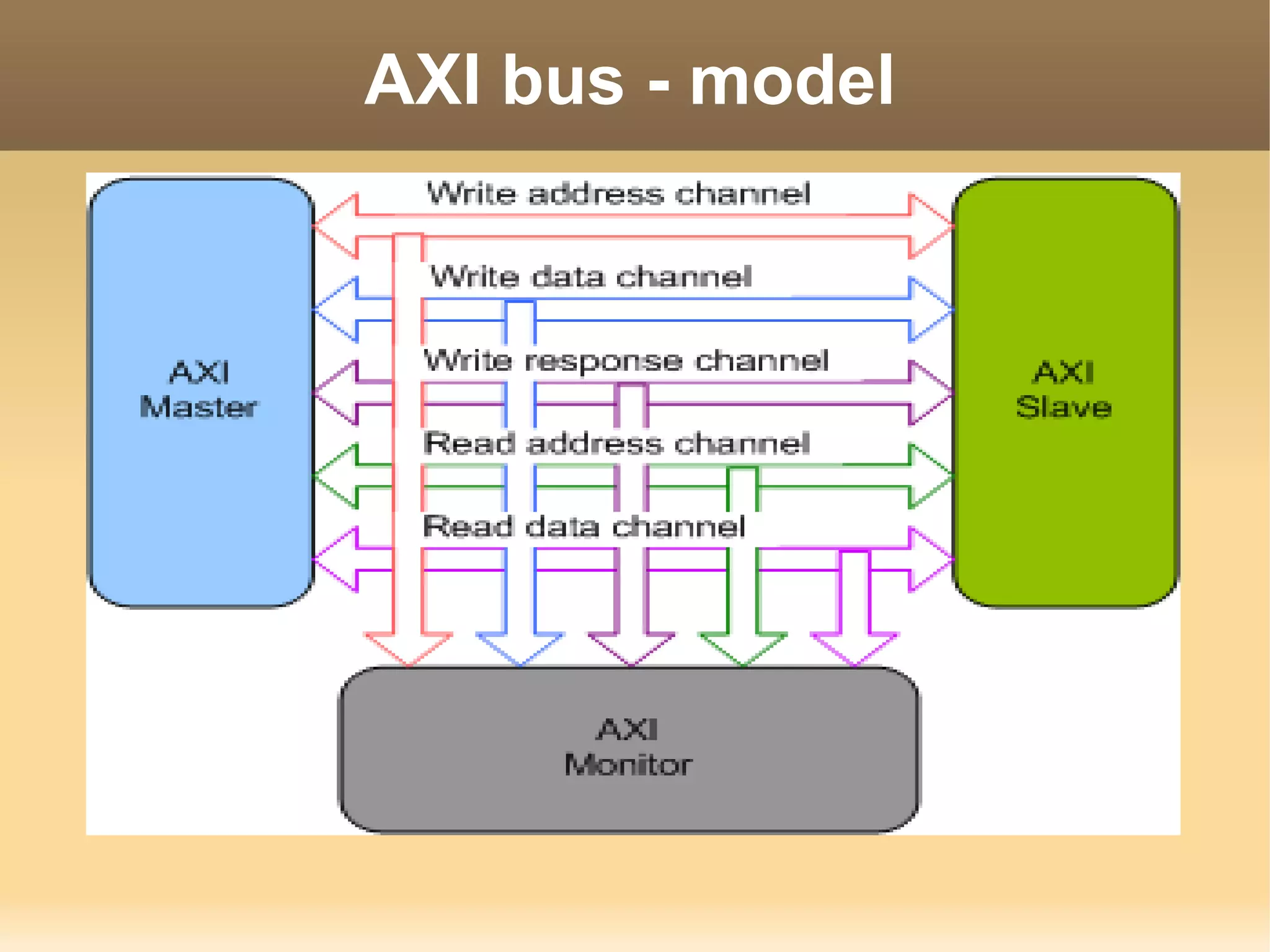
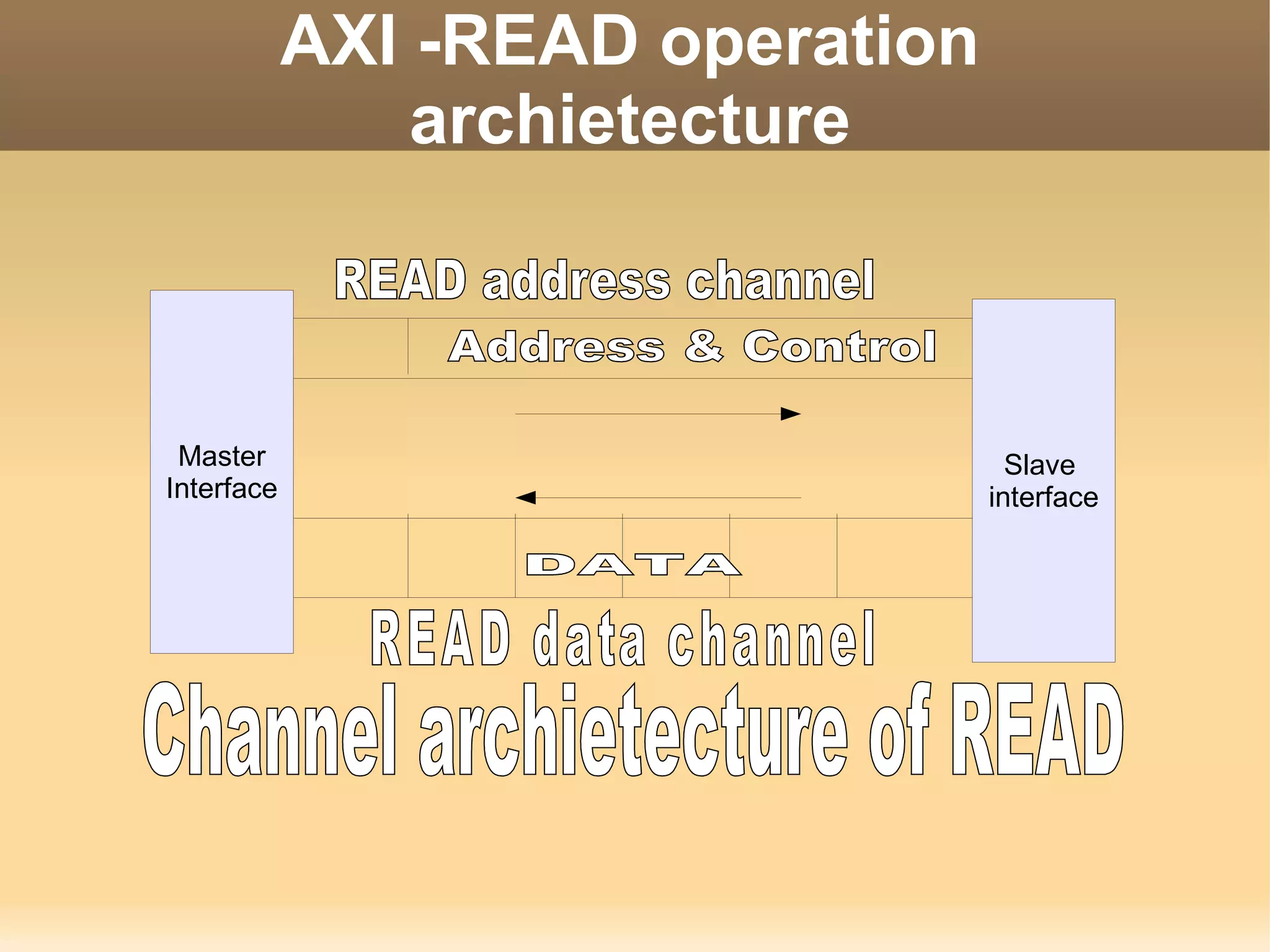
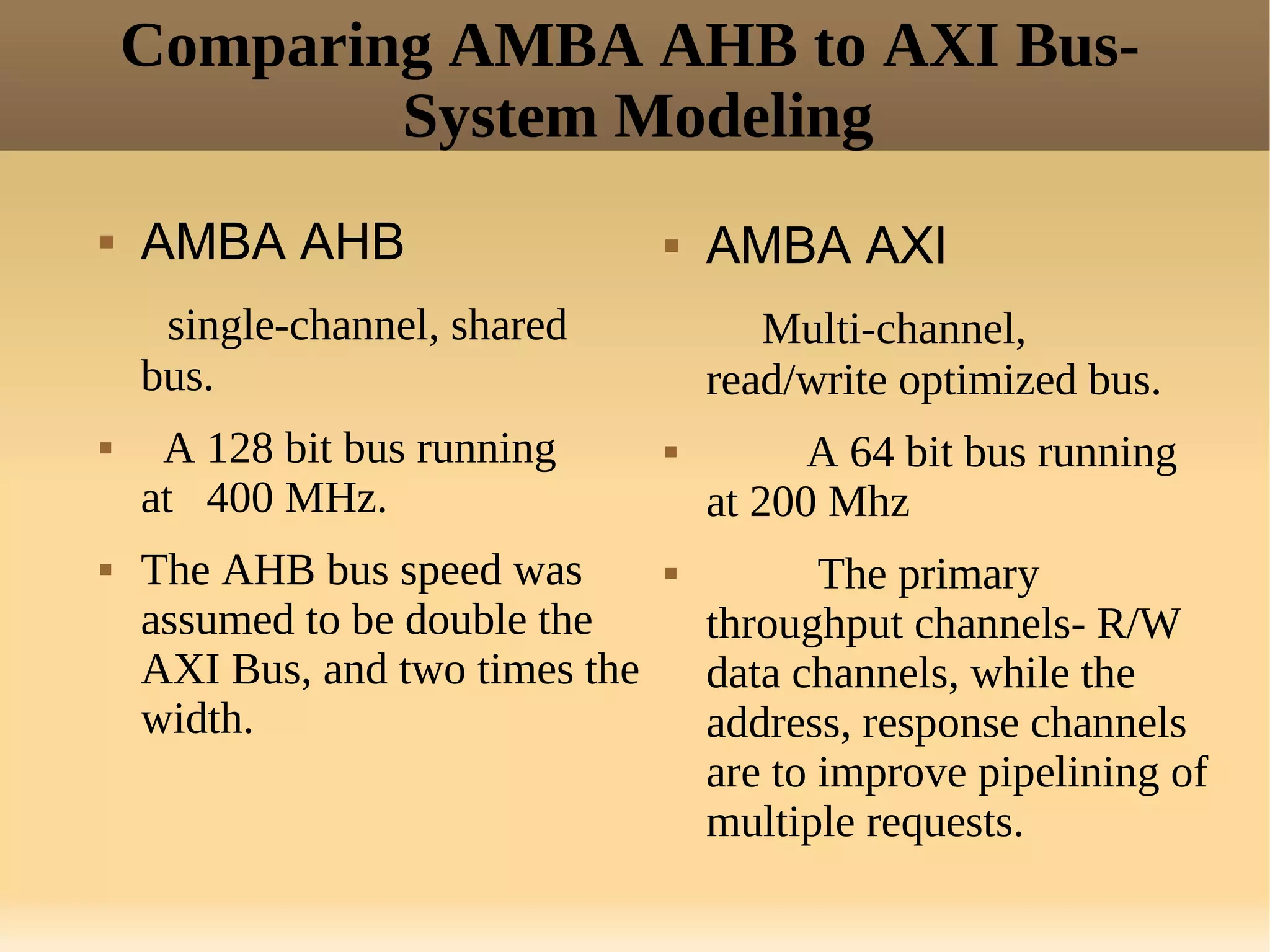
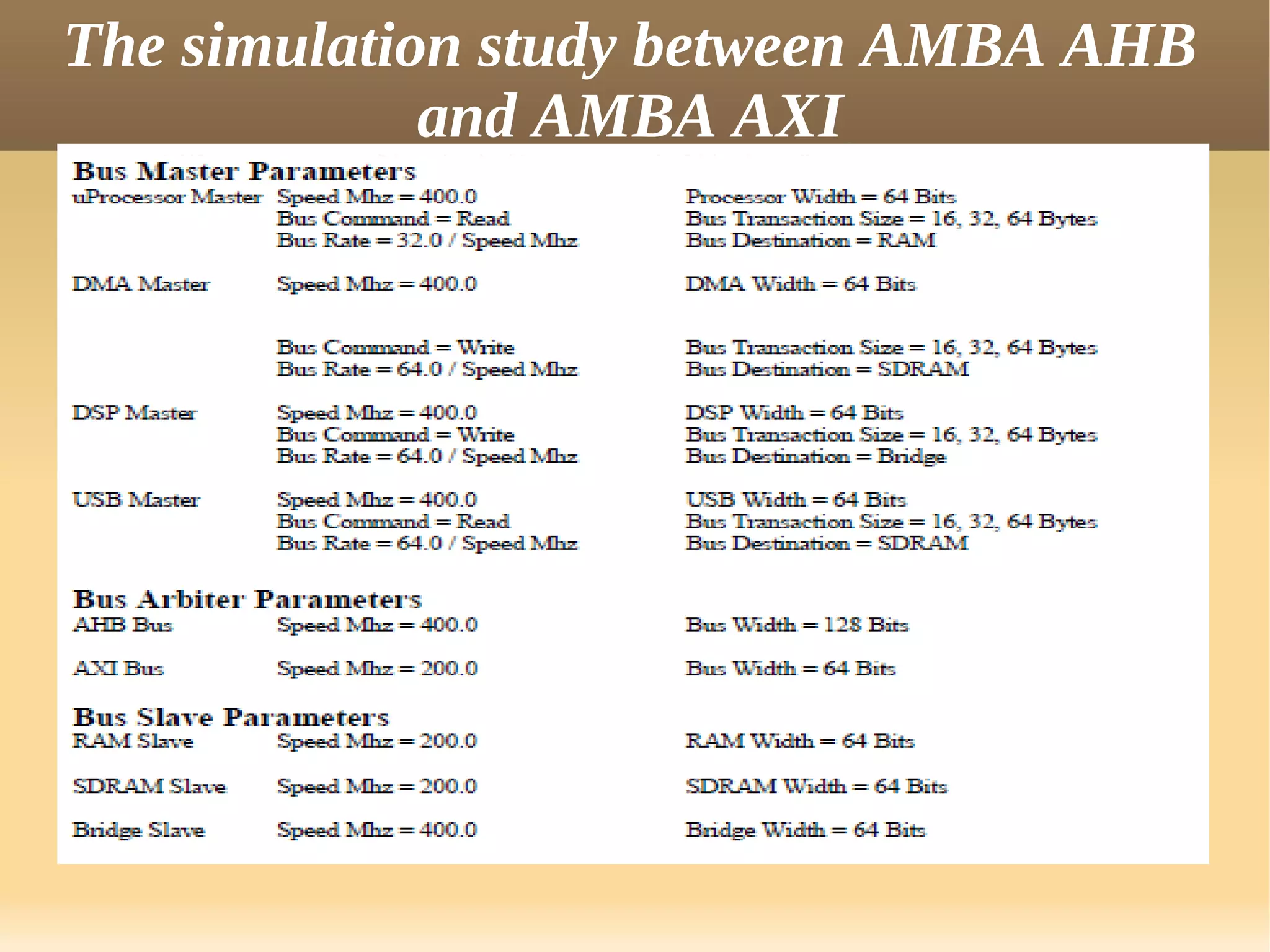
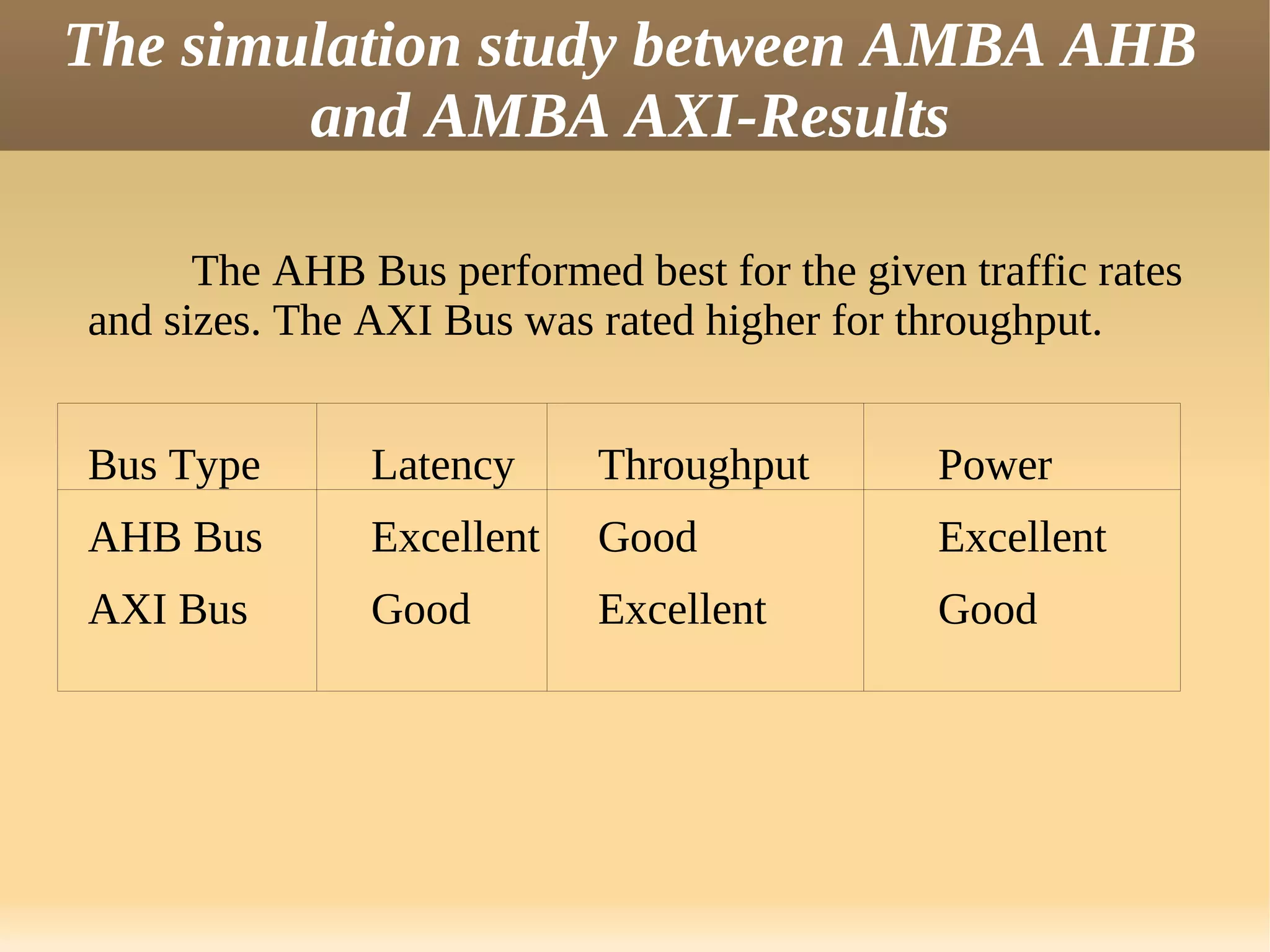
The document discusses the Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI) bus. AXI is a high-performance interface that supports high clock frequencies and burst transactions. It separates address/control and data phases and allows for multiple outstanding addresses. AXI consists of five channels for read/write address, data, and responses. It provides benefits like increased throughput and flexibility over older interfaces. Some limitations are burst size constraints and overhead from separate channels.