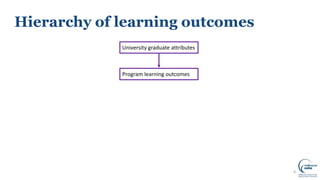
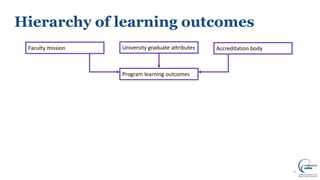
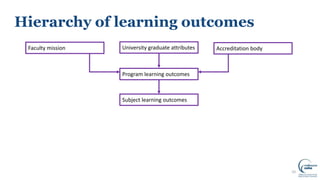
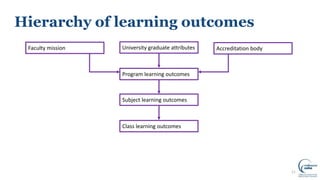
This document discusses writing intended learning outcomes for university courses. It explains that learning outcomes should state what students are expected to know or be able to do after completing a subject. Learning outcomes help provide transparency for students and need to be observable and measurable. The document outlines key components of learning outcomes, including using action verbs and specifying the expected knowledge or skills. It also describes how learning outcomes fit within a hierarchy from university-level graduate attributes down to class-level outcomes.







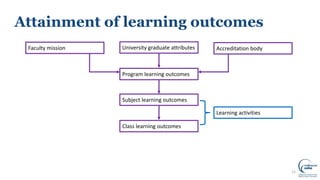
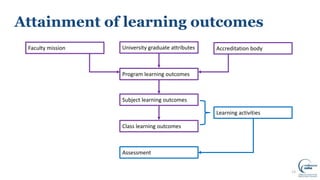
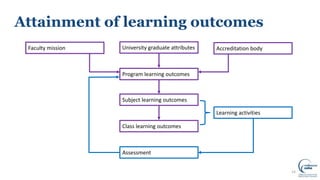


![17From: Elliot, K. (2019) Designing a Curriculum EDUC90516
Writing learning outcomes
• Begin with a stem –
After completing this class…
• Then, use an action verb that lets students know what is expected –
After completing this class, students are expected to be able to identify …
• Then, add the content and context –
After completing this class, students are expected to be able to identify
characteristic style features of early seventeenth-century opera.
By the end of this ________________________ , students are
[class, subject, programme of study]
expected to be able to ______ ________ ________.
[verb] [content] [context]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sp190305ss-190426071218/85/Sp190305ss-17-320.jpg)





