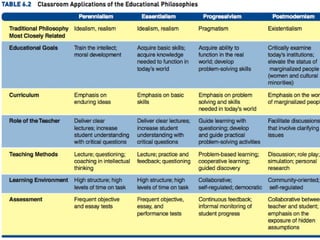
The document outlines various philosophies of education, highlighting key theories such as idealism, realism, pragmatism, and existentialism, and their implications for teaching practices. It emphasizes the importance of developing a personal philosophical framework as a teacher to inform educational decisions and promote student growth. Additionally, it discusses the criticisms and focuses of different educational philosophies, including perennialism, essentialism, progressivism, and postmodernism.