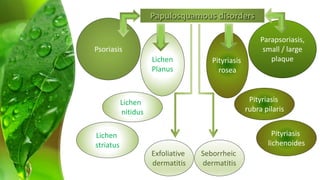
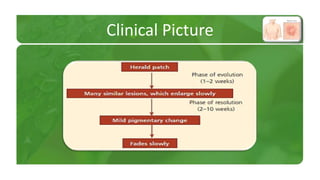
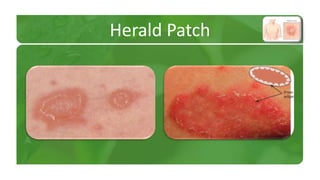
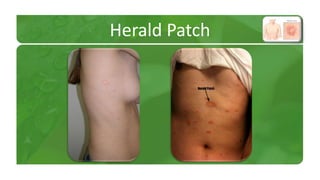
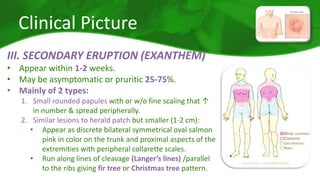
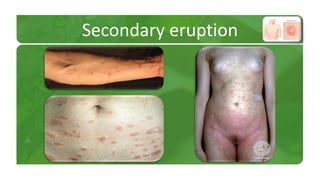
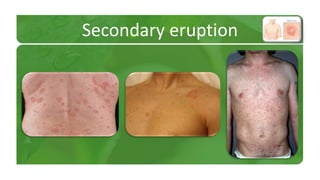
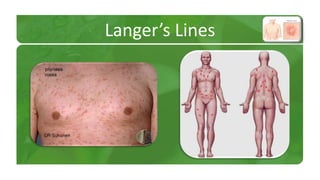
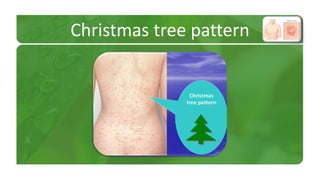
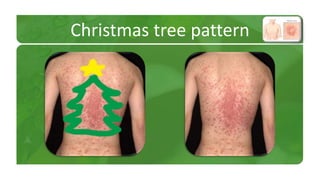
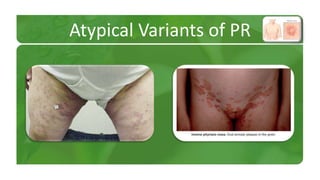
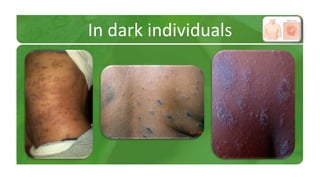
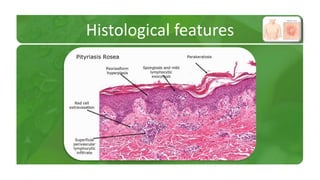
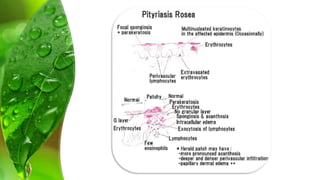
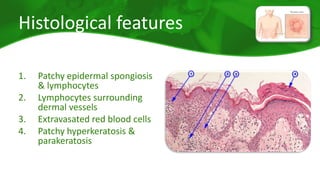
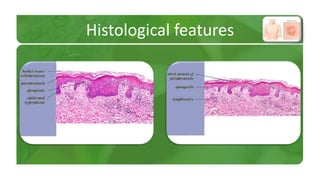
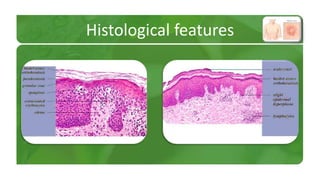
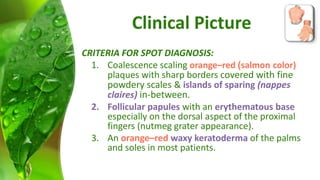
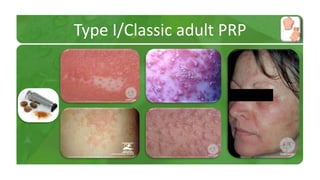
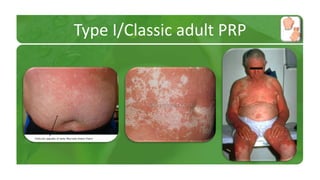
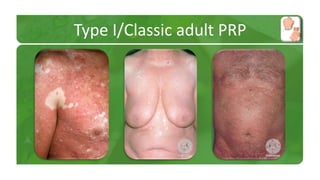
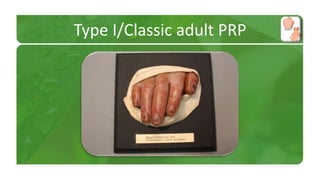
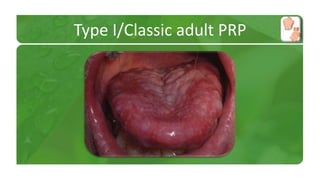
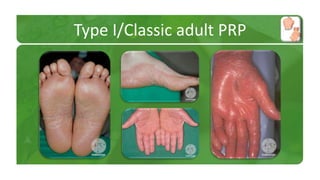
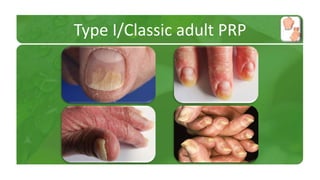
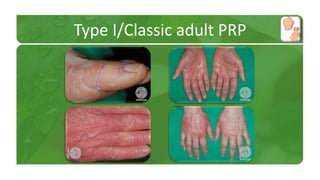
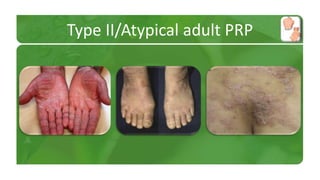
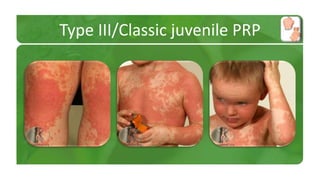
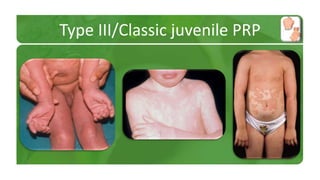
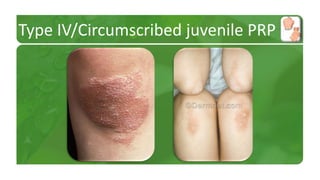
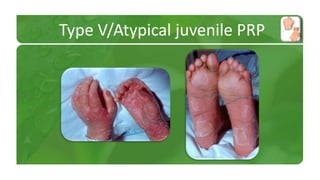
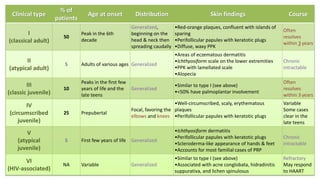
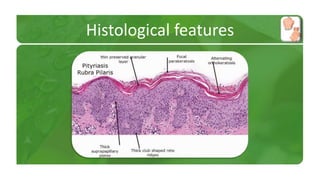
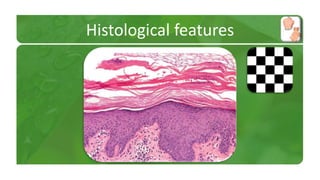
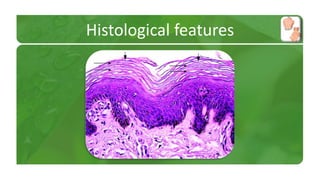
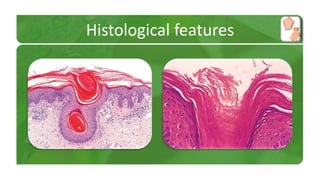
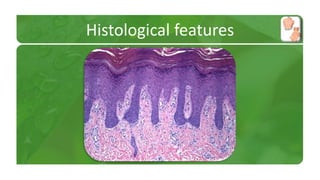
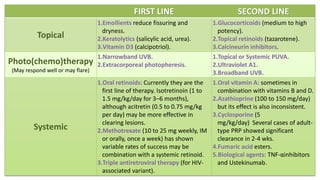
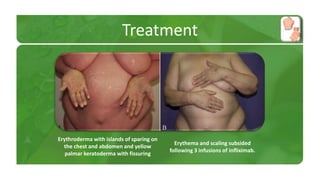
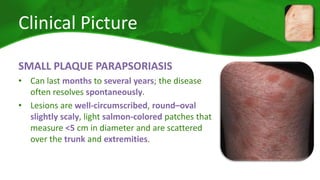
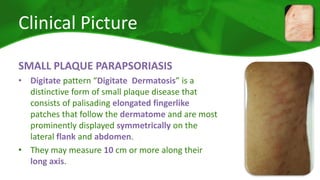
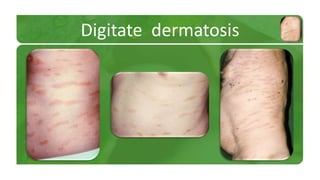
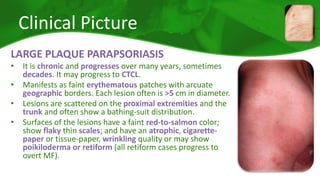
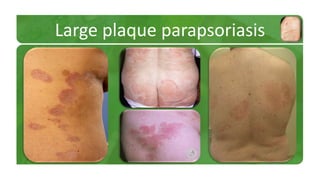
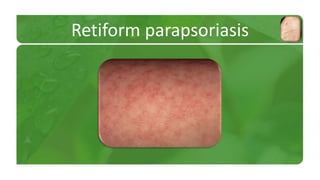
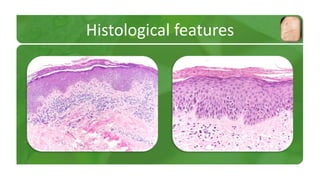
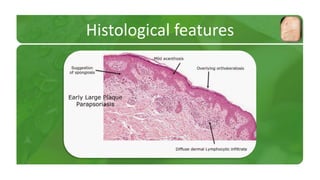
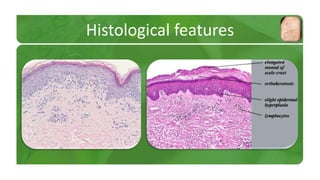
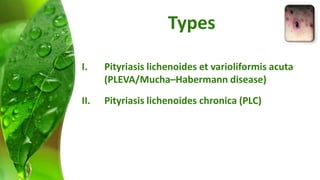
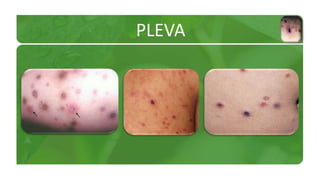
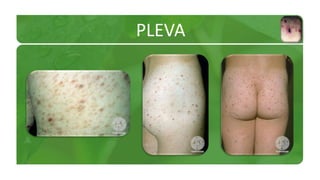
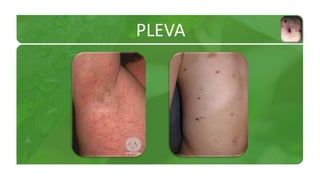
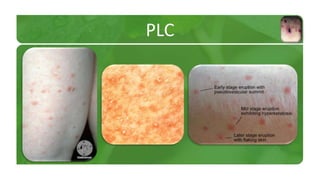
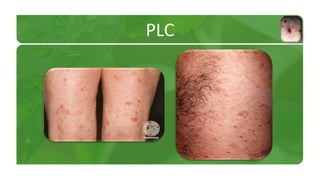
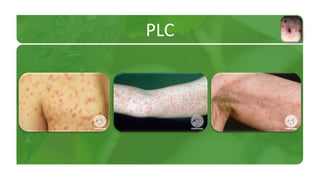
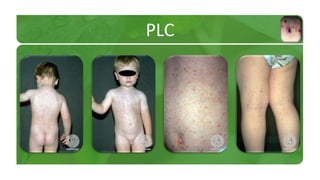
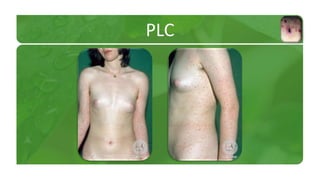
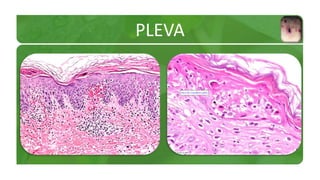
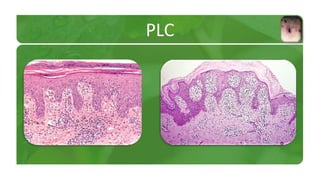
The document covers various papulosquamous disorders, focusing on conditions such as pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rubra pilaris, detailing their definitions, epidemiology, clinical pictures, differential diagnoses, histological features, and treatments. Pityriasis rosea is characterized by a herald patch and self-limiting course, while pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare chronic skin disease with distinct lesions. It also discusses parapsoriasis, outlining its classifications and clinical characteristics, with some cases linked to T-cell dysregulation.