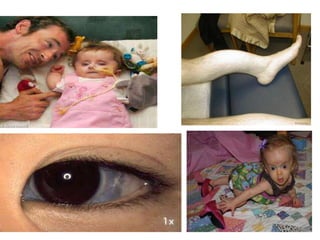
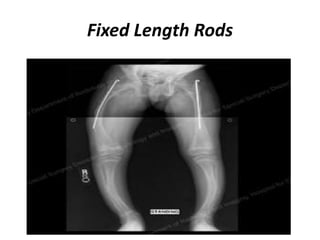
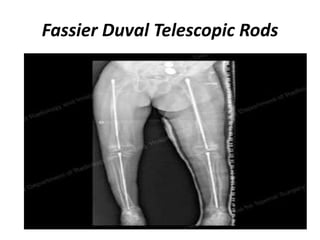
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI), or brittle bone disease, is a genetic disorder characterized by fragile bones that fracture easily. It is caused by a defect in the body's production of type 1 collagen, which is important for bone strength. The majority of OI cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, though some are the result of spontaneous genetic mutations or are inherited autosomally recessively. OI has been classified into eight types based on severity and symptoms, which can include multiple fractures, skeletal deformities, short stature, and in severe cases, lethality in infancy. While there is no cure for OI, treatment aims to increase bone strength and prevent fractures through medications, physical therapy,