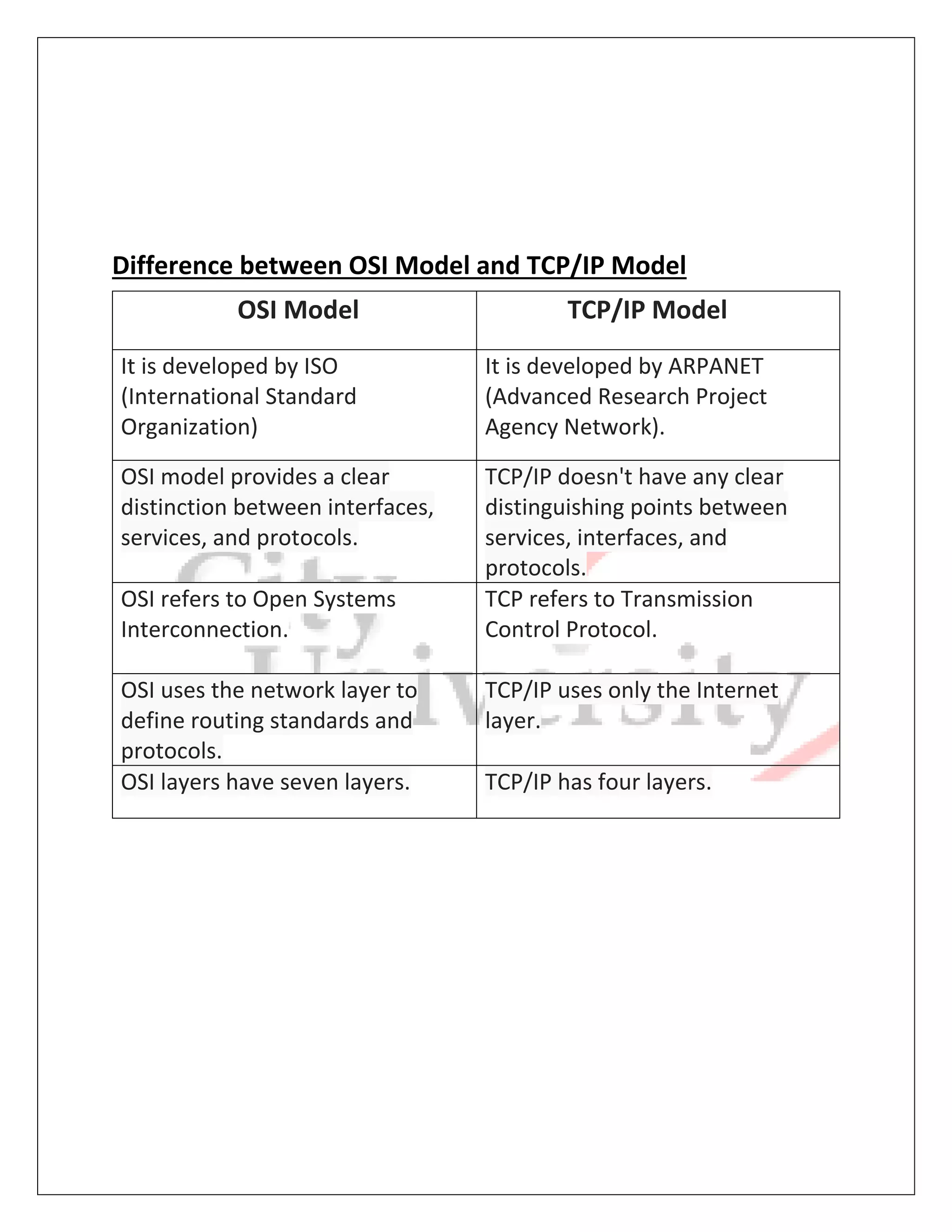
The document provides information on the OSI and TCP/IP network models. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model and its advantages such as standardizing interfaces and facilitating modular engineering. It also outlines the four layers of the TCP/IP model and advantages like enabling internetworking between organizations. Key differences between the two models are that OSI was developed by ISO and provides clearer distinctions between layers, while TCP/IP was developed by ARPANET and does not separate services, interfaces, and protocols as clearly.