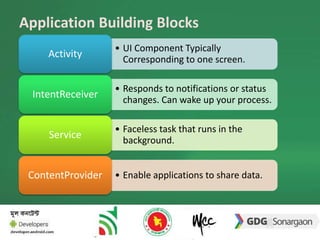
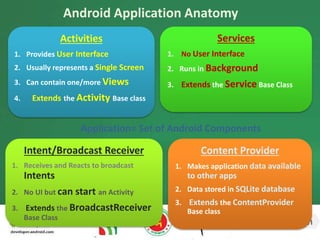
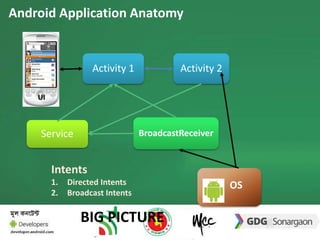
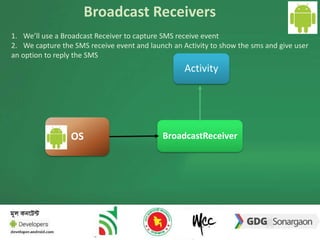
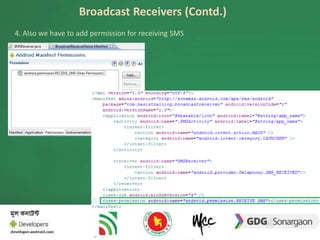
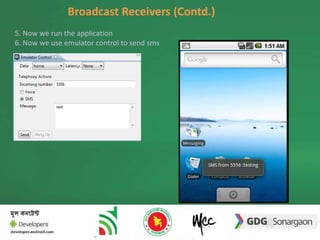
The document discusses the different building blocks of an Android application including activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers. It provides details on broadcast receivers, describing them as components that respond to system-wide broadcasts and application-initiated broadcasts. The document gives an example of using a broadcast receiver to capture the SMS receive event and launch an activity to display the SMS with an option to reply. It also discusses programmatically sending SMS from an application.




![Receiving SMS
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
SmsMessage[] msgs = null;
String str = "";
String address="";
if (bundle != null)
{
//---retrieve the SMS message received---
Object[] pdus = (Object[]) bundle.get("pdus");
msgs = new SmsMessage[pdus.length];
for (int i=0; i<msgs.length; i++)
{
msgs[i] = SmsMessage.createFromPdu((byte[])pdus[i]);
str += "SMS from " + msgs[i].getOriginatingAddress();
str += " :";
str += msgs[i].getMessageBody().toString();
str += "n";
address=msgs[i].getOriginatingAddress();
Toast.makeText(context, str, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-5broadcastreceiver-141001023810-phpapp02/85/Broadcast-Receiver-11-320.jpg)


