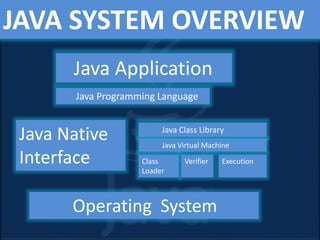
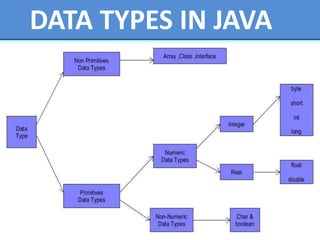
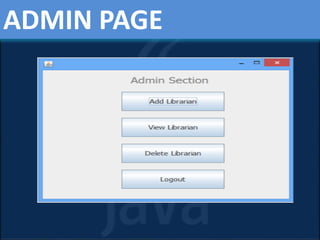
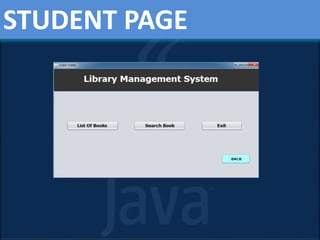
This presentation provides an overview of core Java concepts. It introduces Java as a popular programming language due to its portability across platforms. It then outlines the contents to be covered, including what Java is, where it is used, its features, how Java programs are translated and executed, and an overview of the Java system. Key topics like the Java Virtual Machine, object-oriented programming concepts in Java, data types, and garbage collection are explained. The advantages and disadvantages of Java are also presented. Finally, a library management system project built in Java is described as an example.