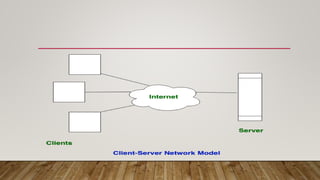
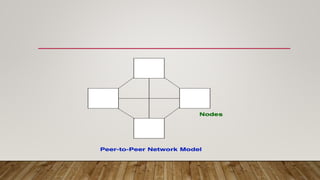
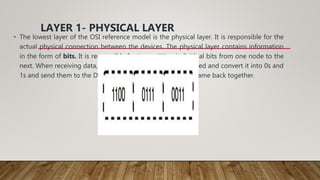
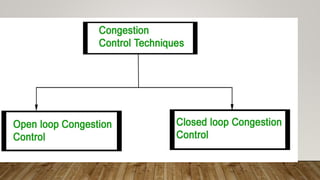
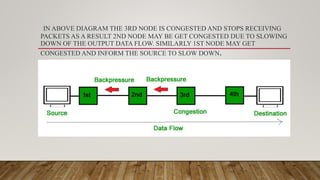
The document discusses different network models and their key differences. A client-server network uses centralized servers to store data and respond to client requests. In a peer-to-peer network, each node acts as both a client and server by sharing its own resources and consuming resources from other nodes. The document also covers congestion in networks and different techniques for congestion control, including open loop methods like adjusting transmission policies and closed loop methods that react to congestion like backpressure.