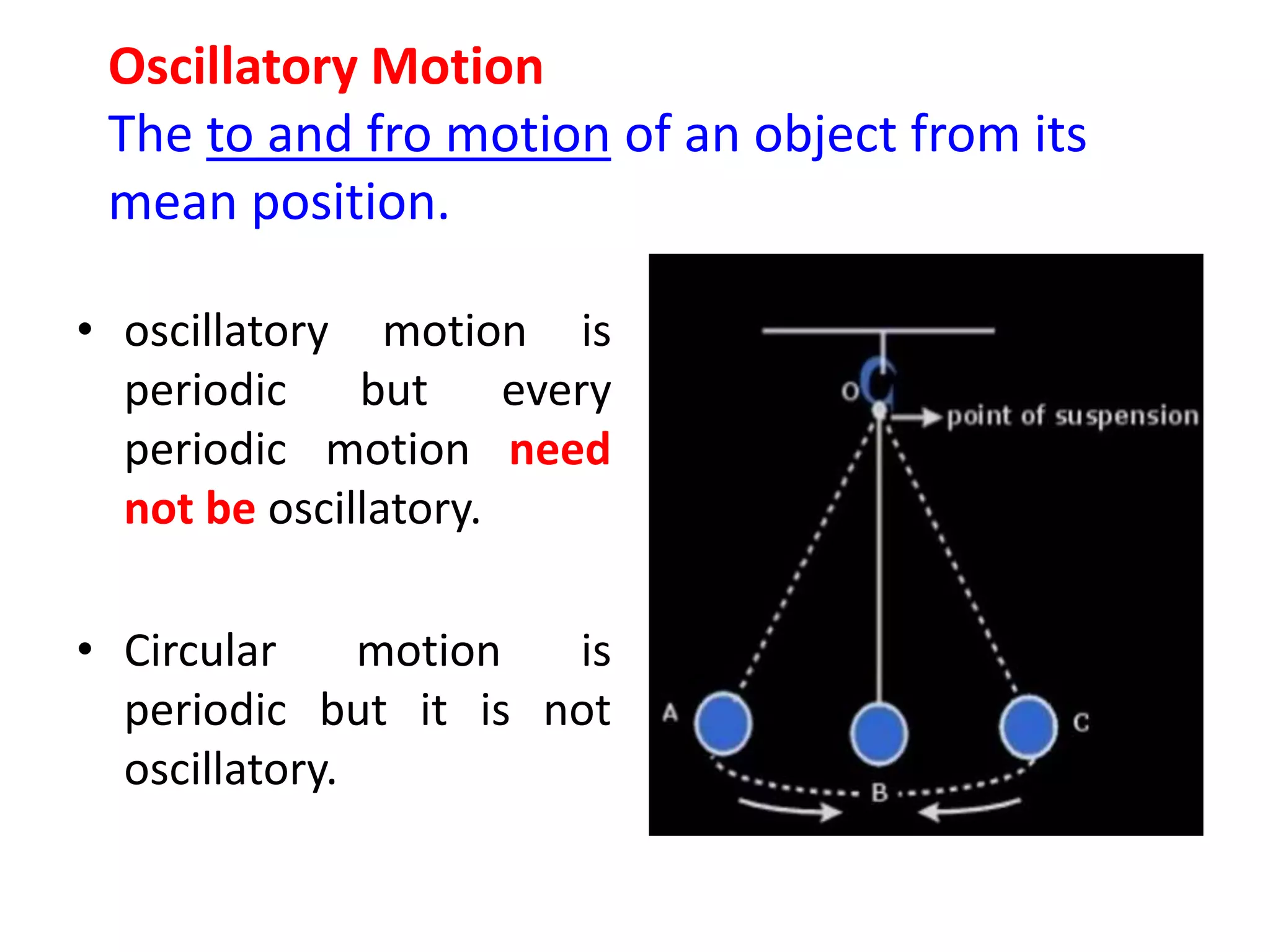
1. Periodic motion repeats itself after a definite interval of time, called the periodic time or period. Oscillatory motion involves to-and-fro movement around a mean position.
2. Linear simple harmonic motion (S.H.M.) involves a body moving along a straight line path, where the restoring force is proportional to and opposite of the displacement from the mean position.
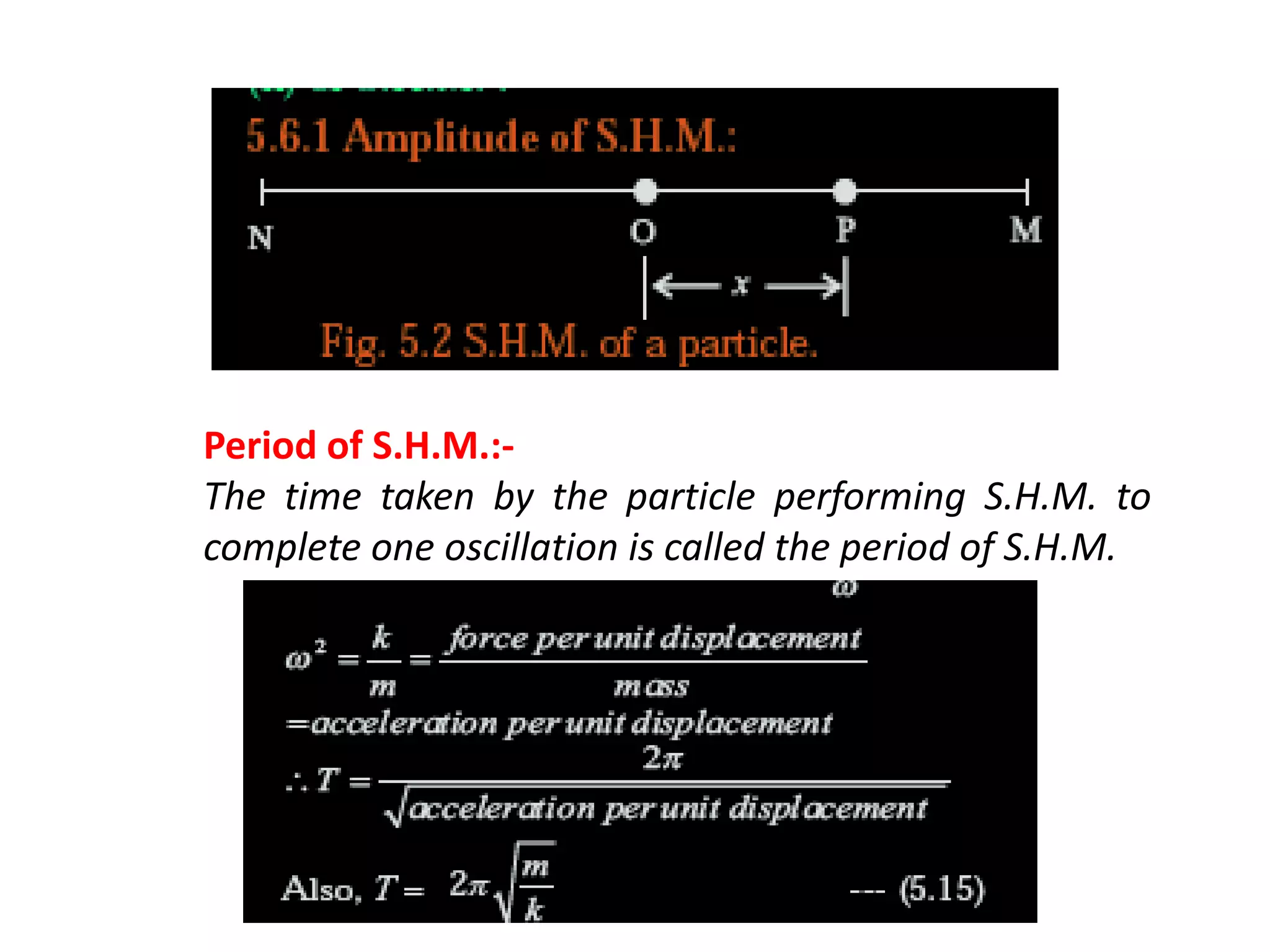
3. For S.H.M., the displacement, velocity, and acceleration can be expressed as sinusoidal functions of time with maximum amplitudes occurring at the extremes and zero at the mean position. The period and frequency are determined by properties of the system.