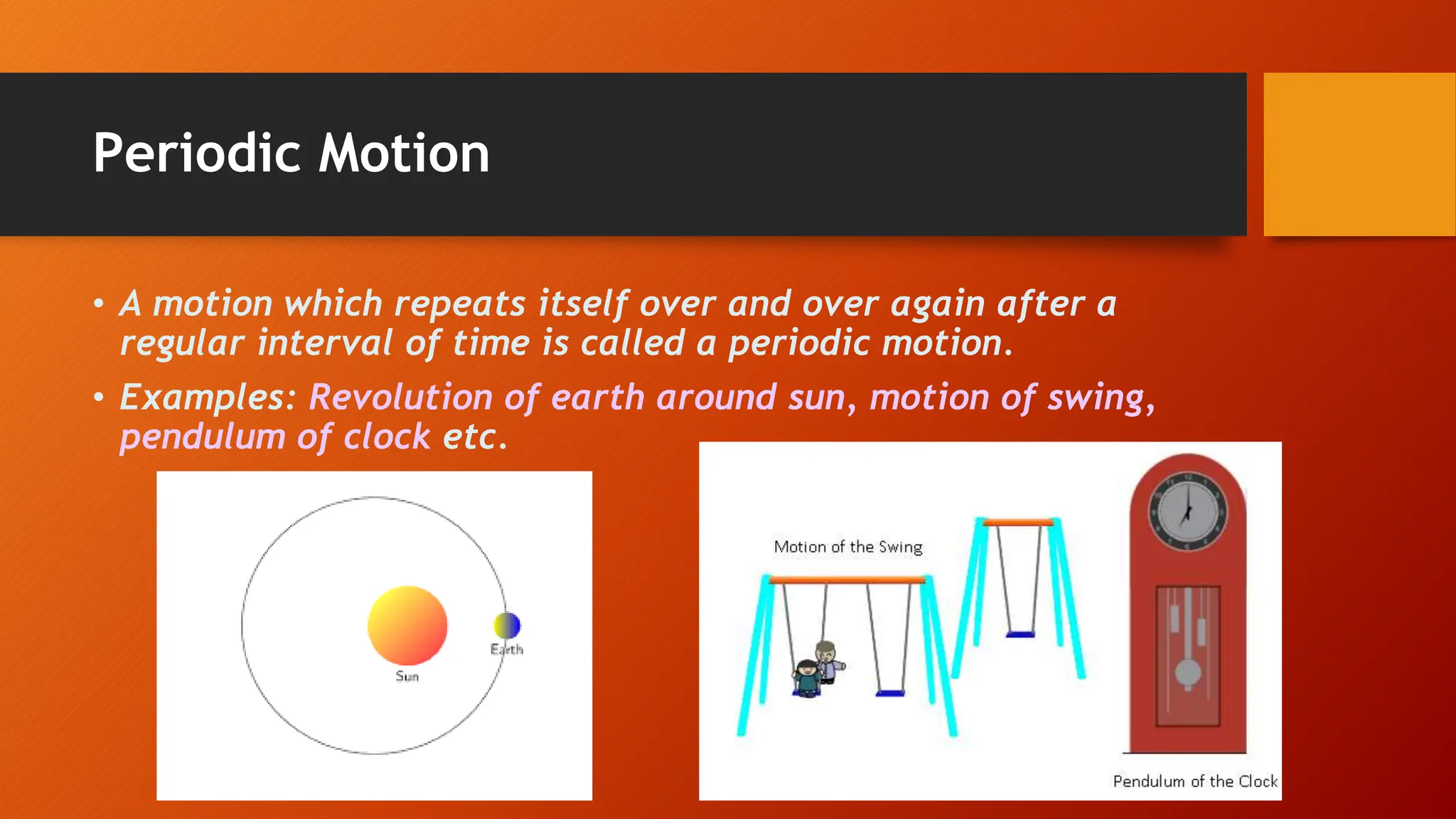
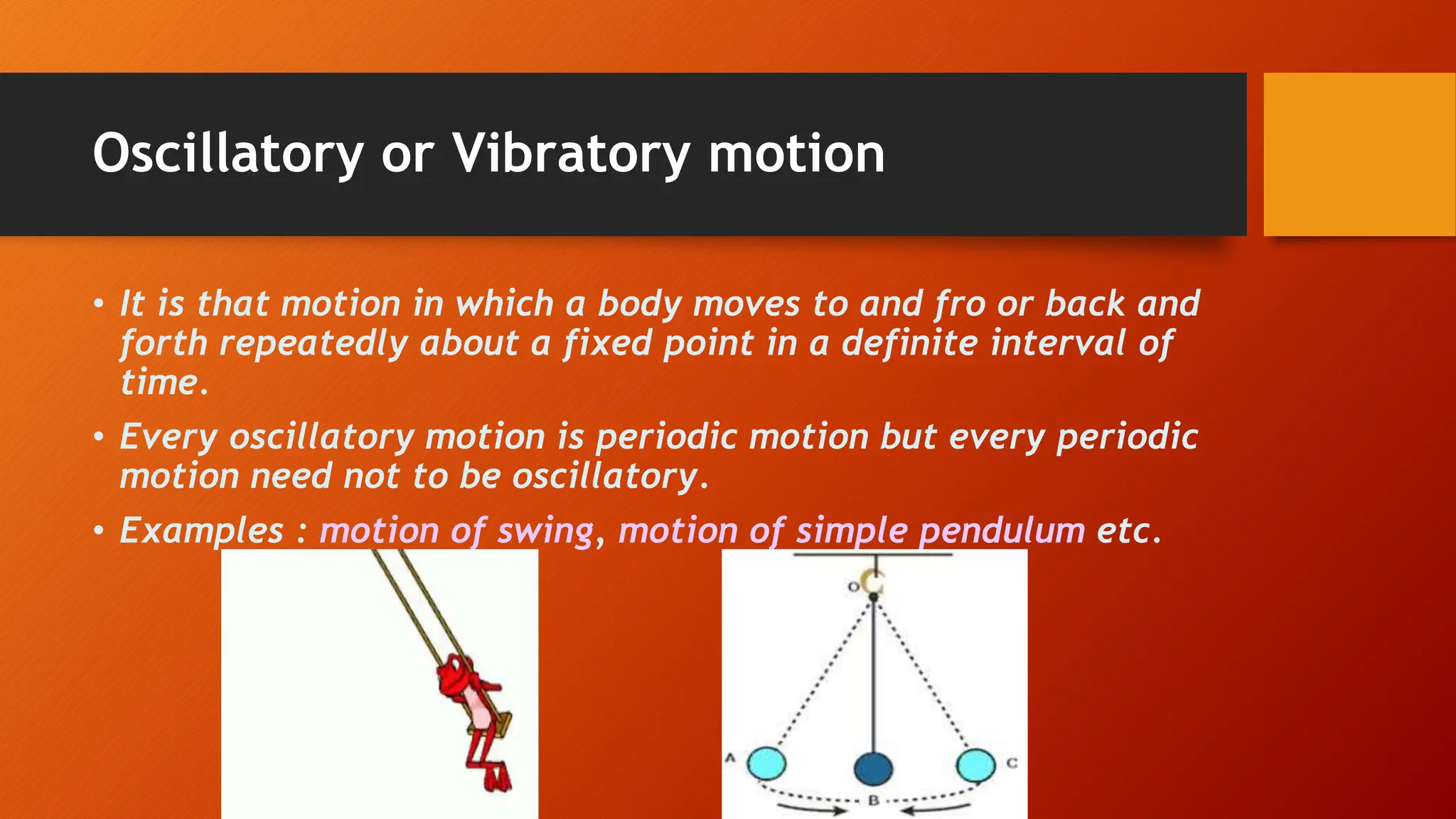
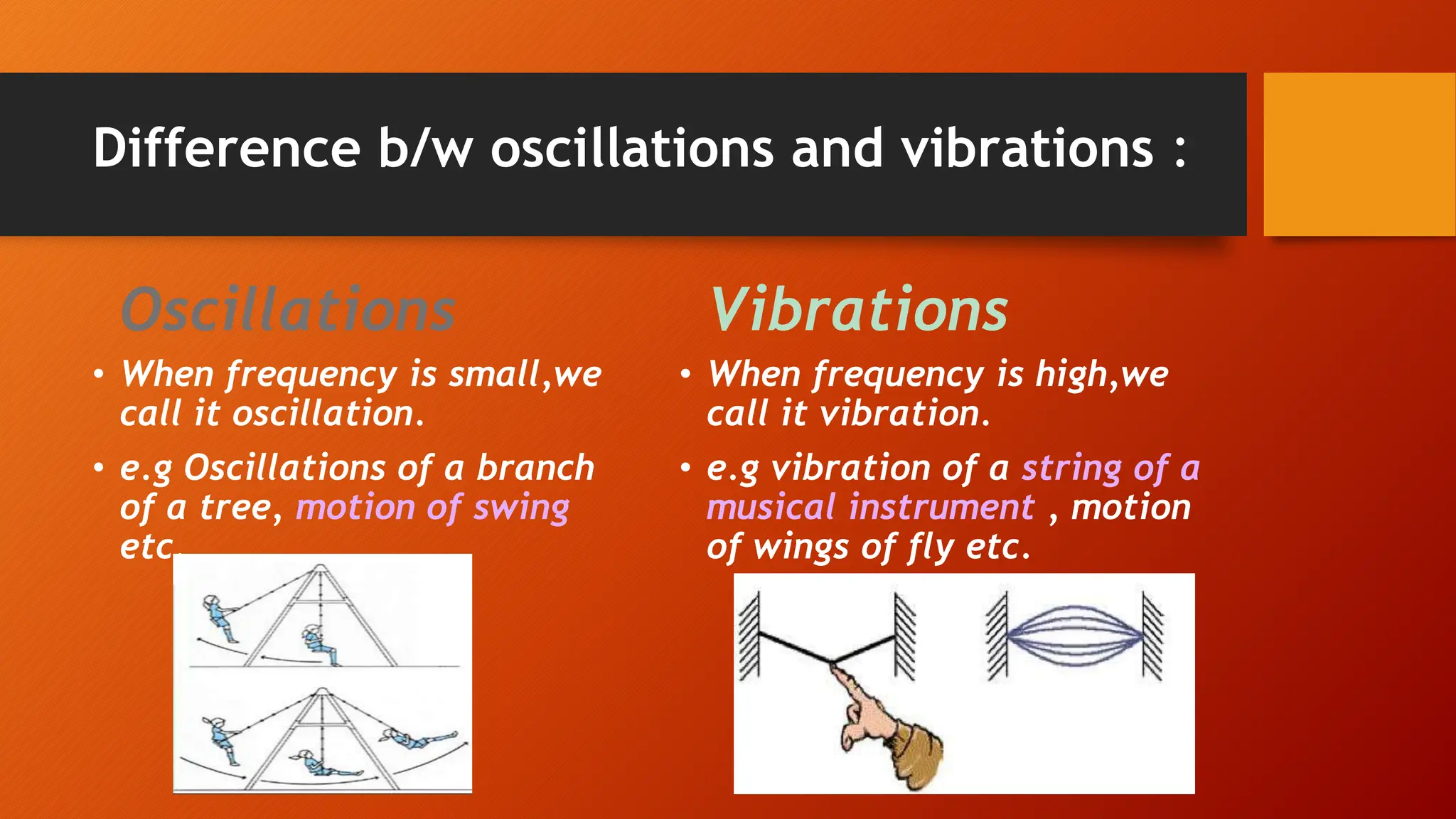
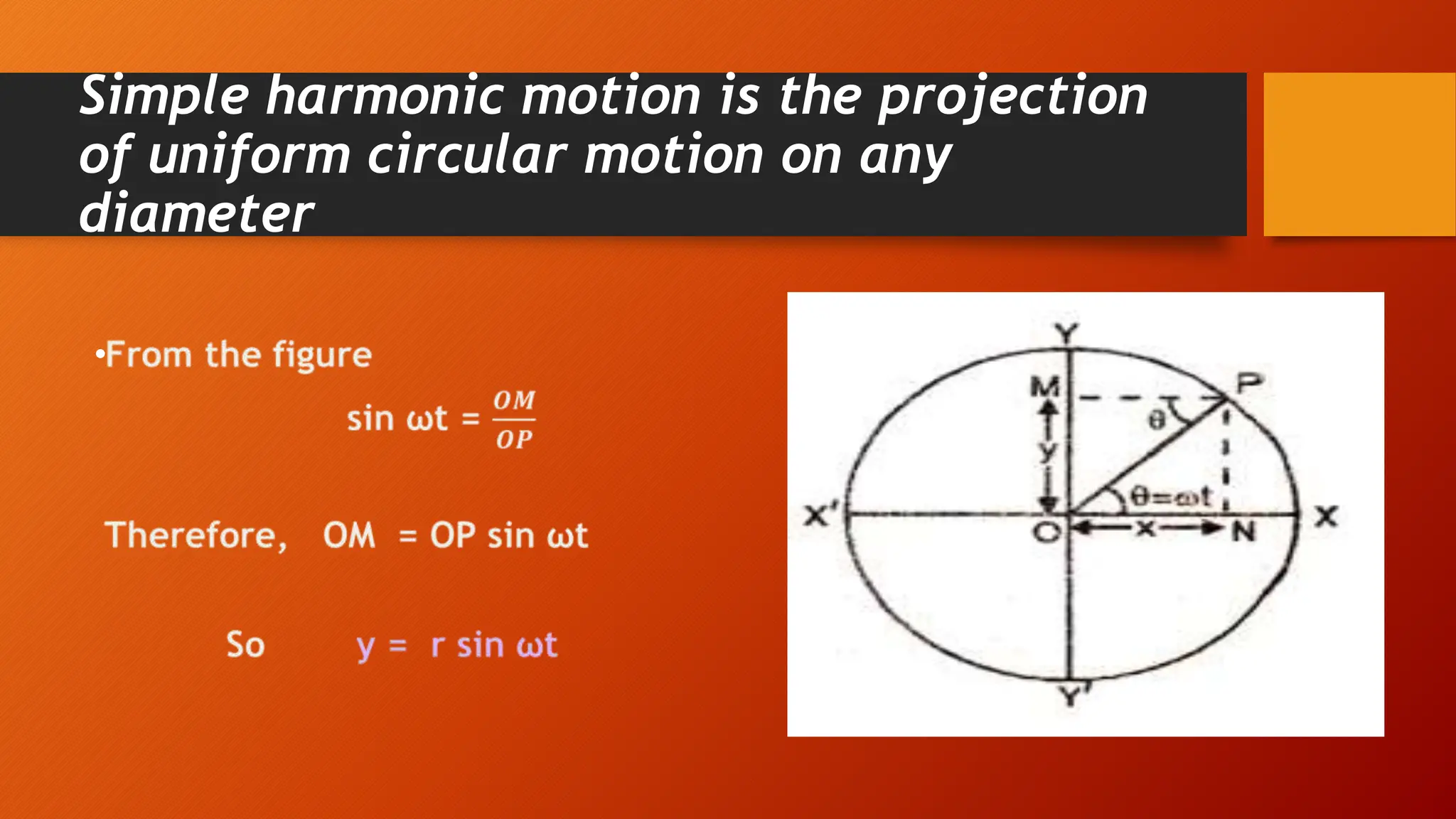
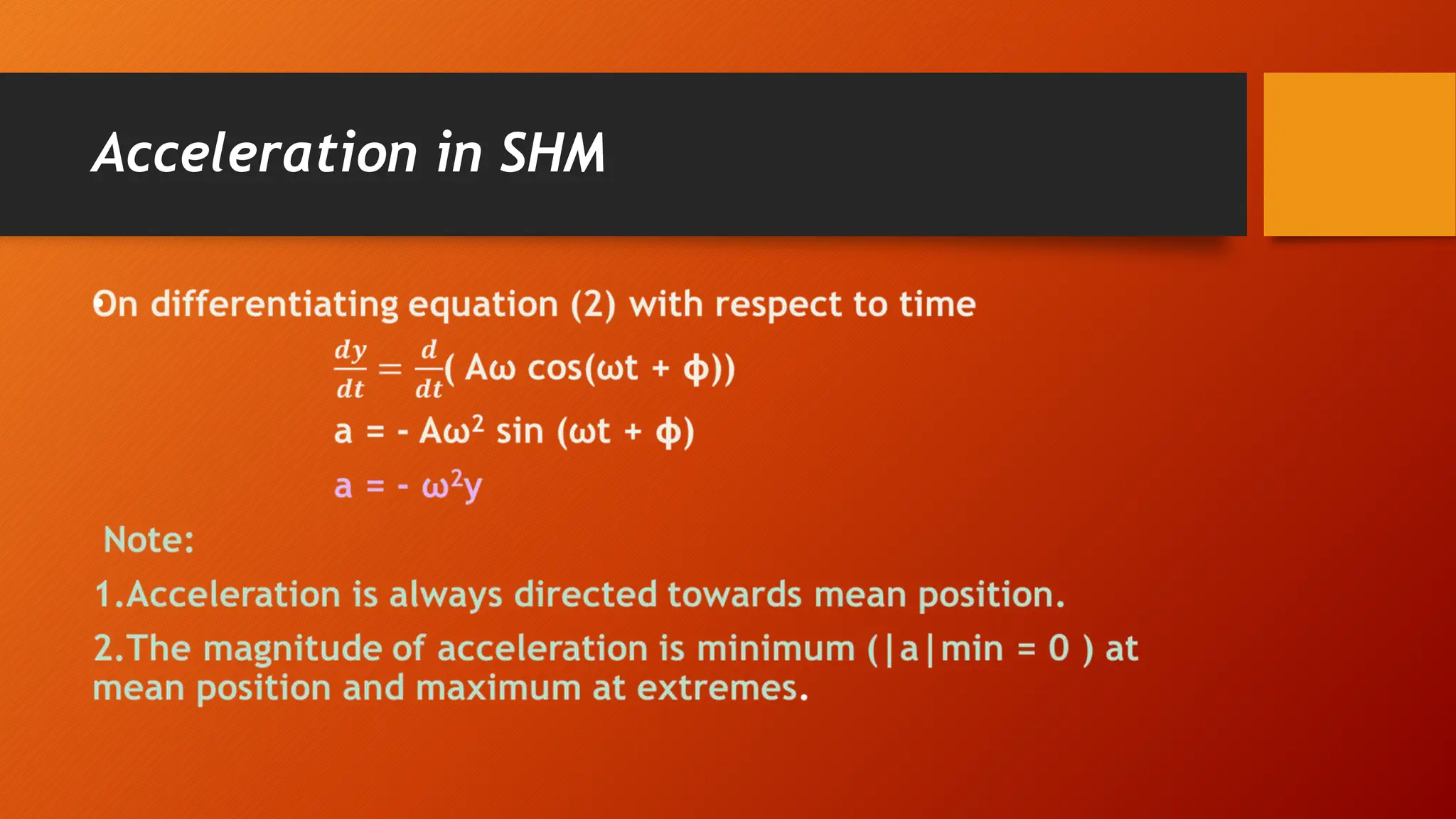
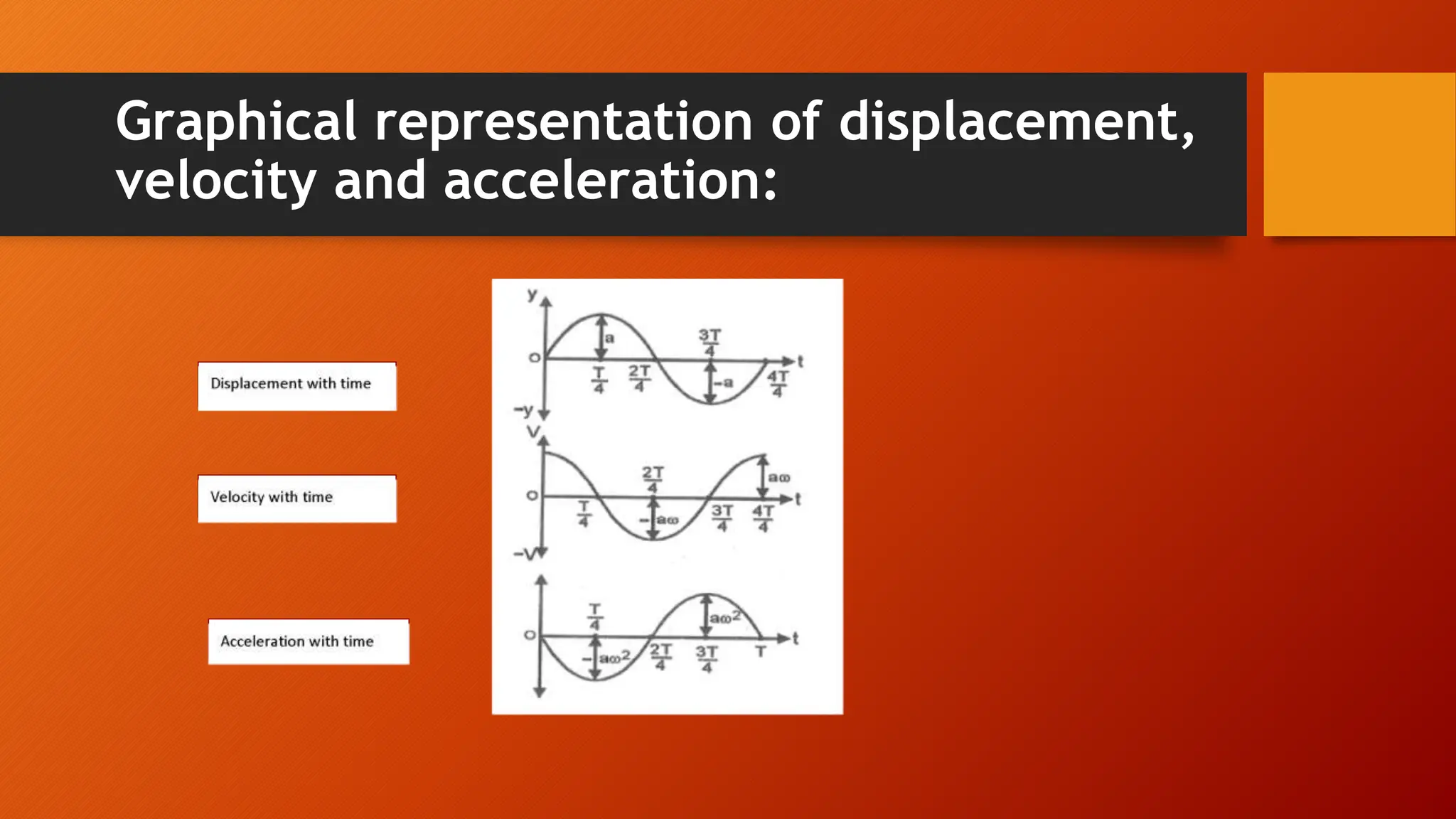
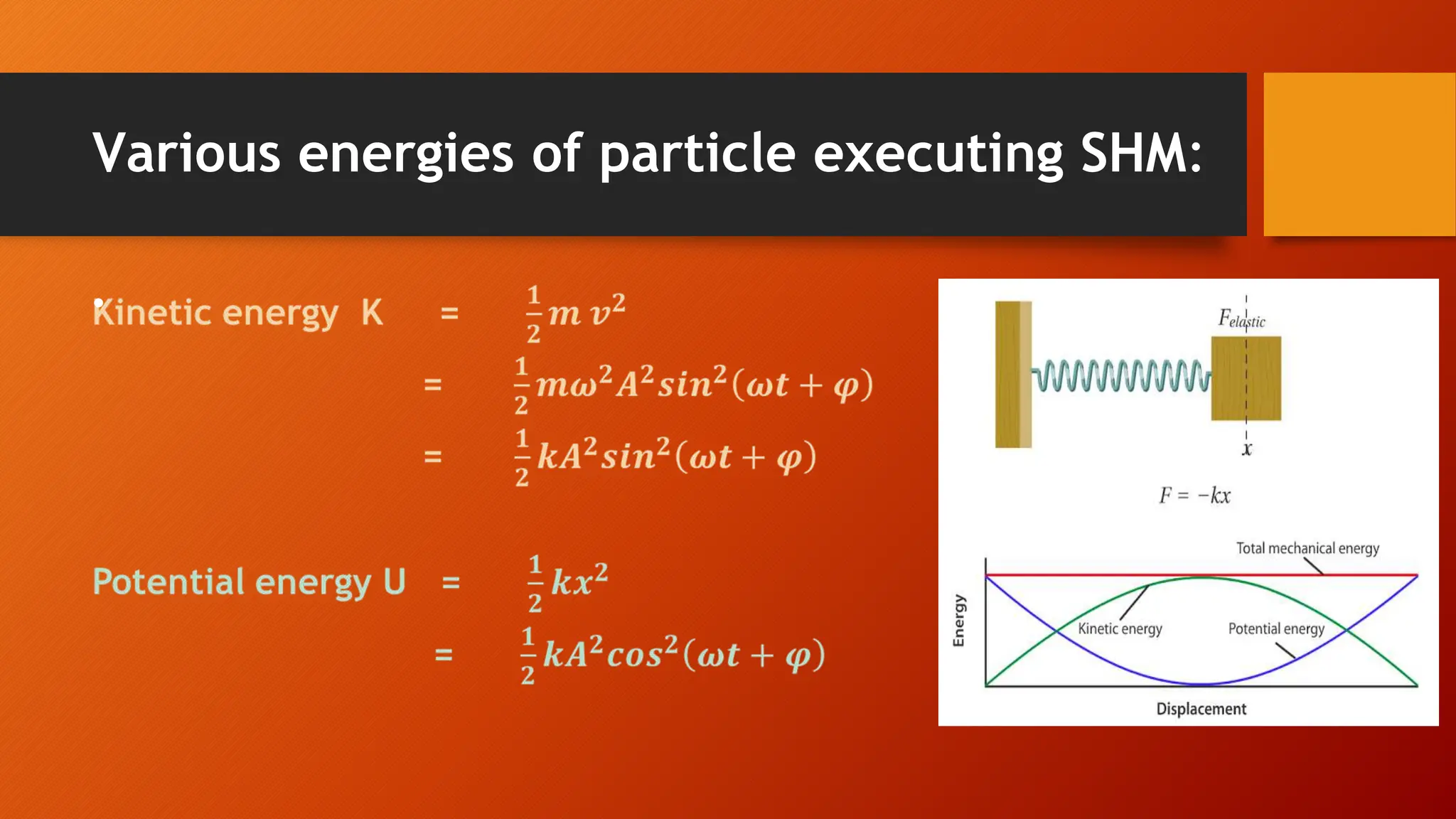
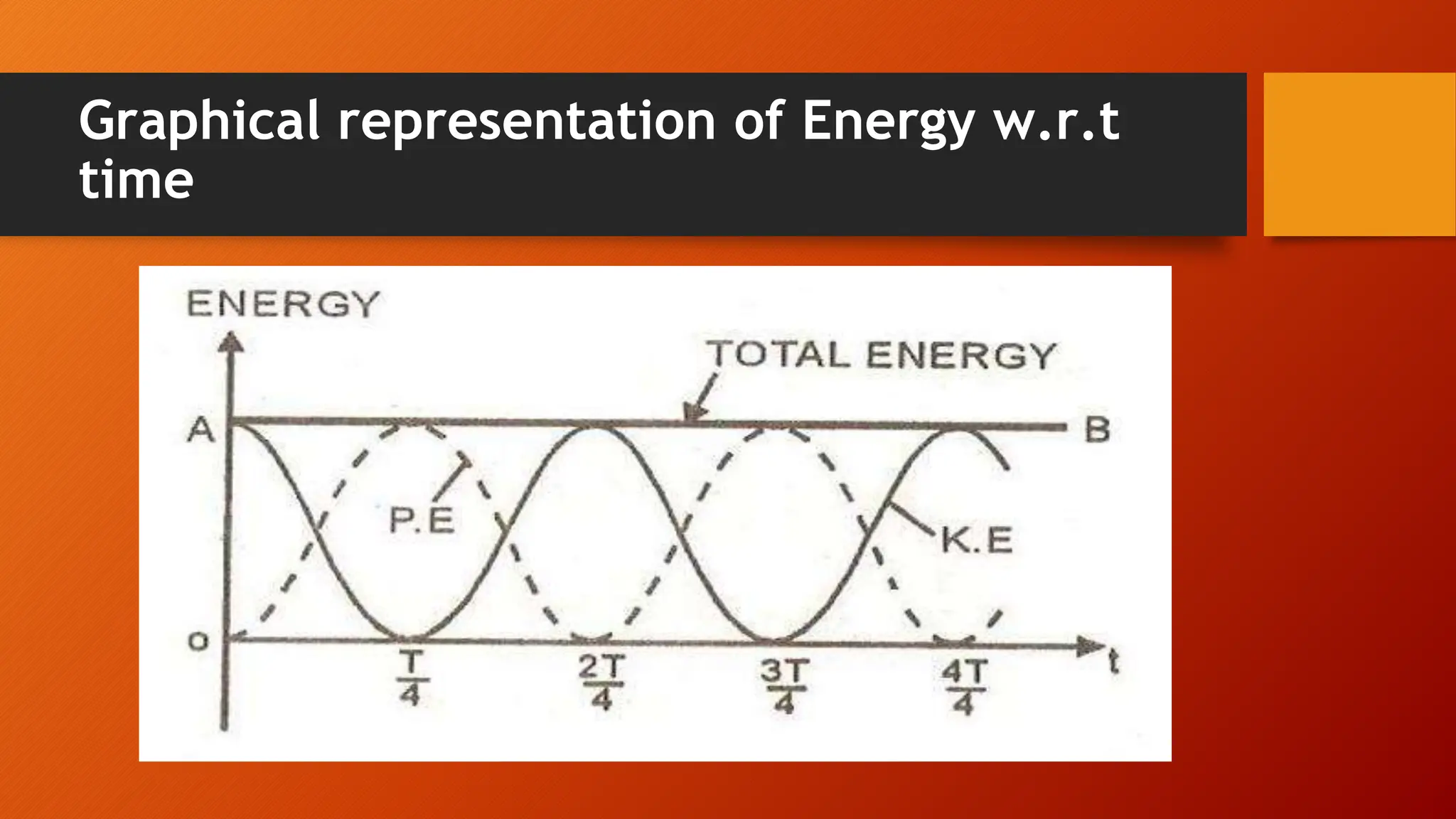
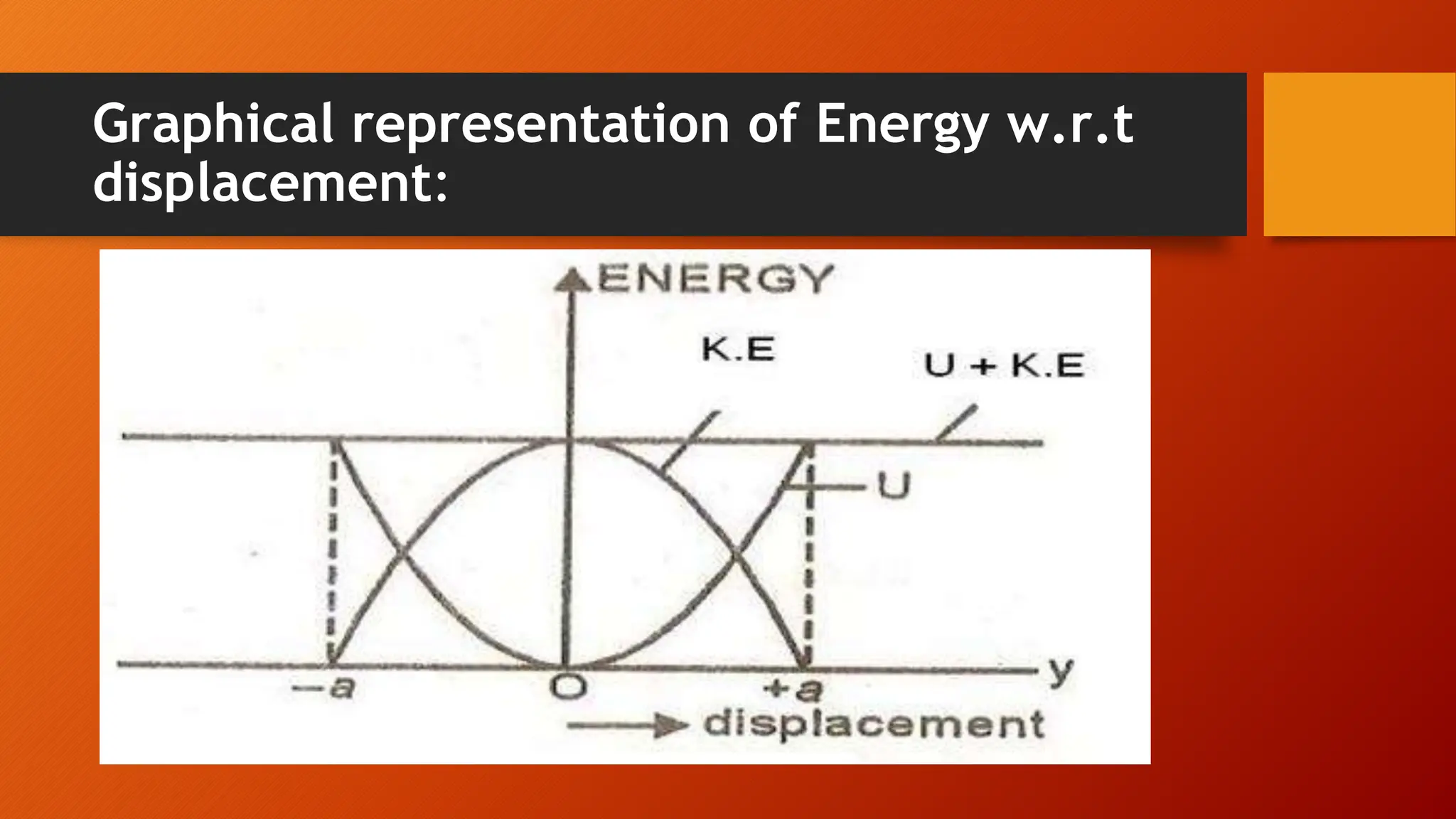
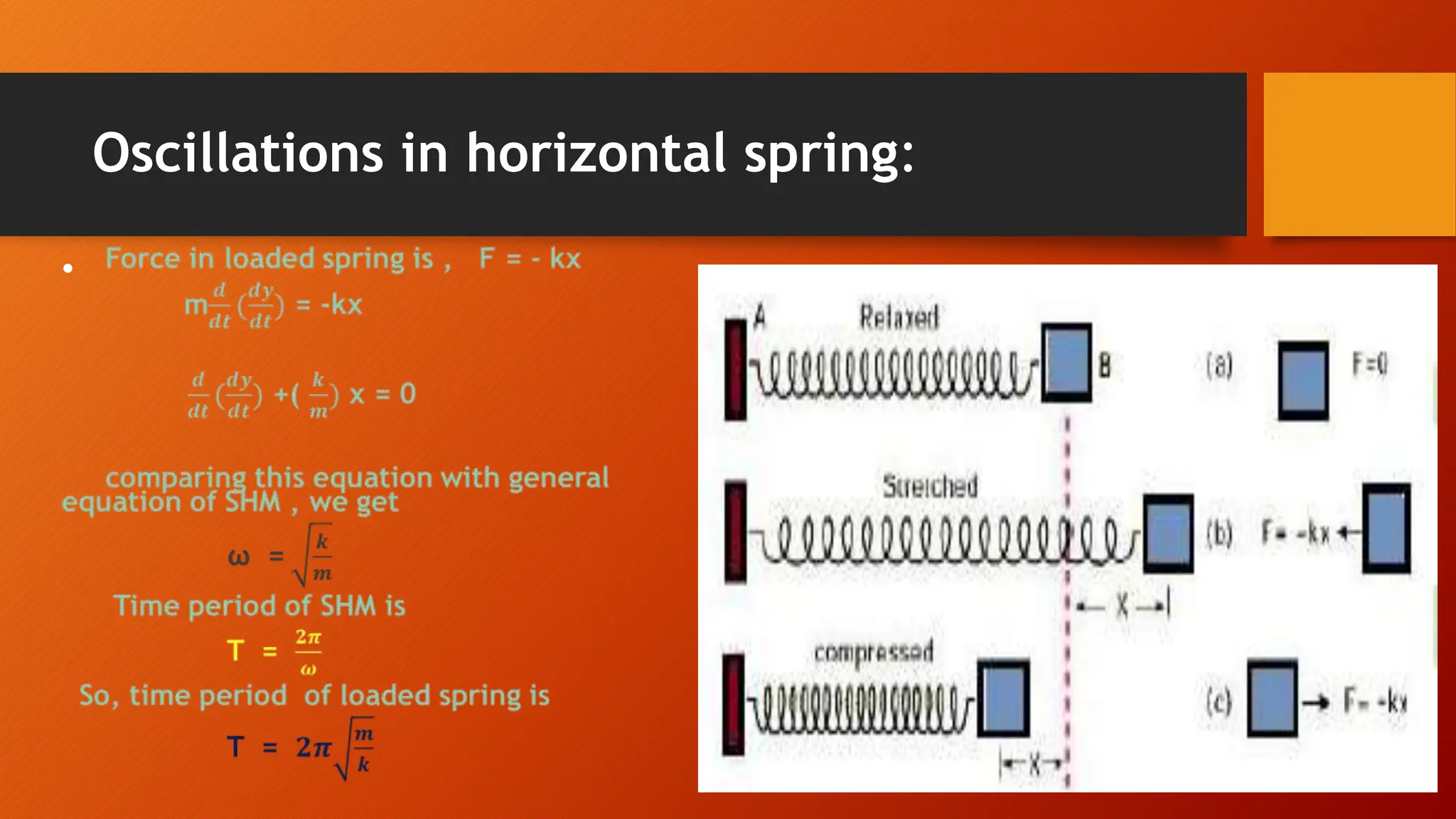
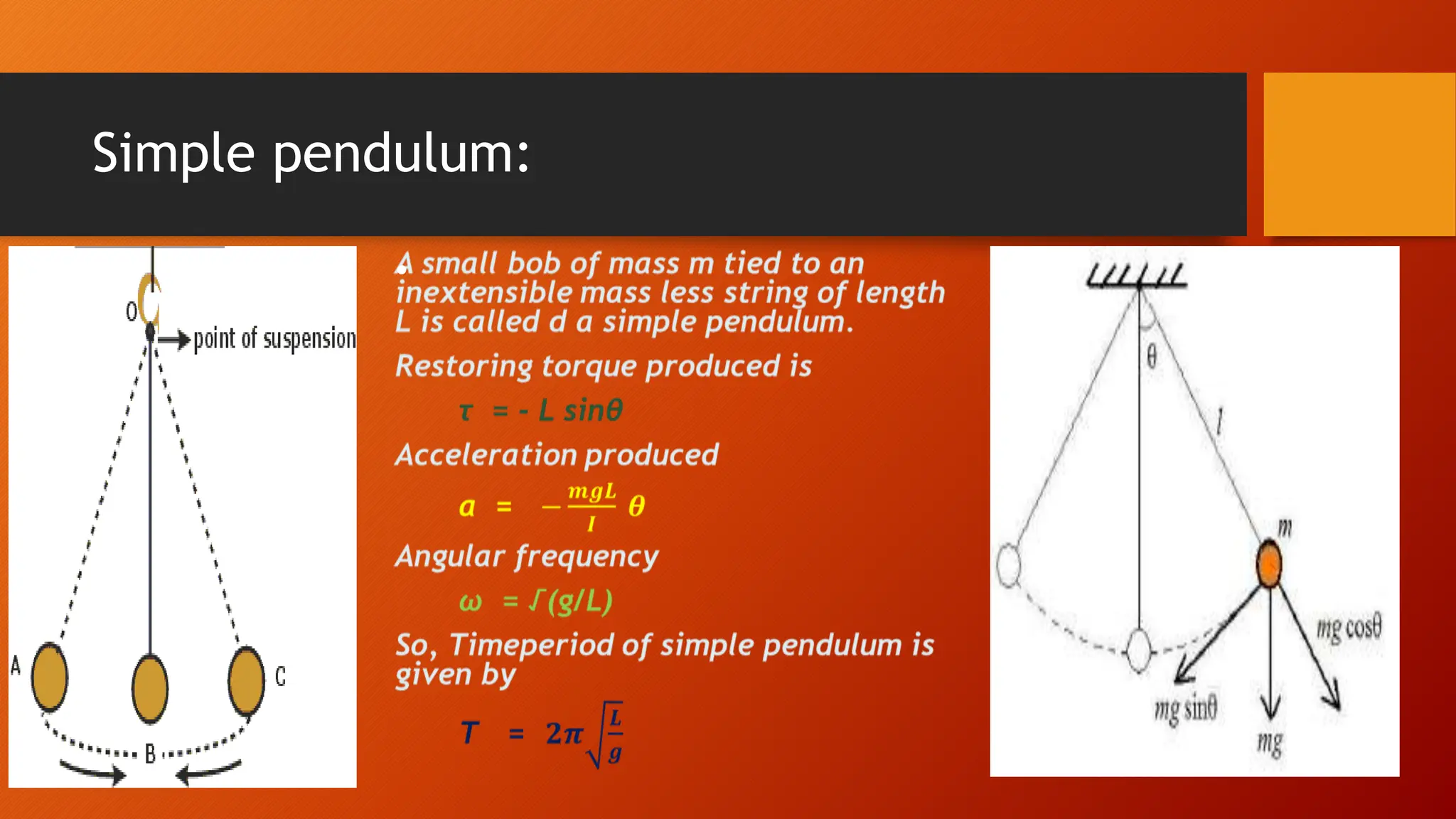
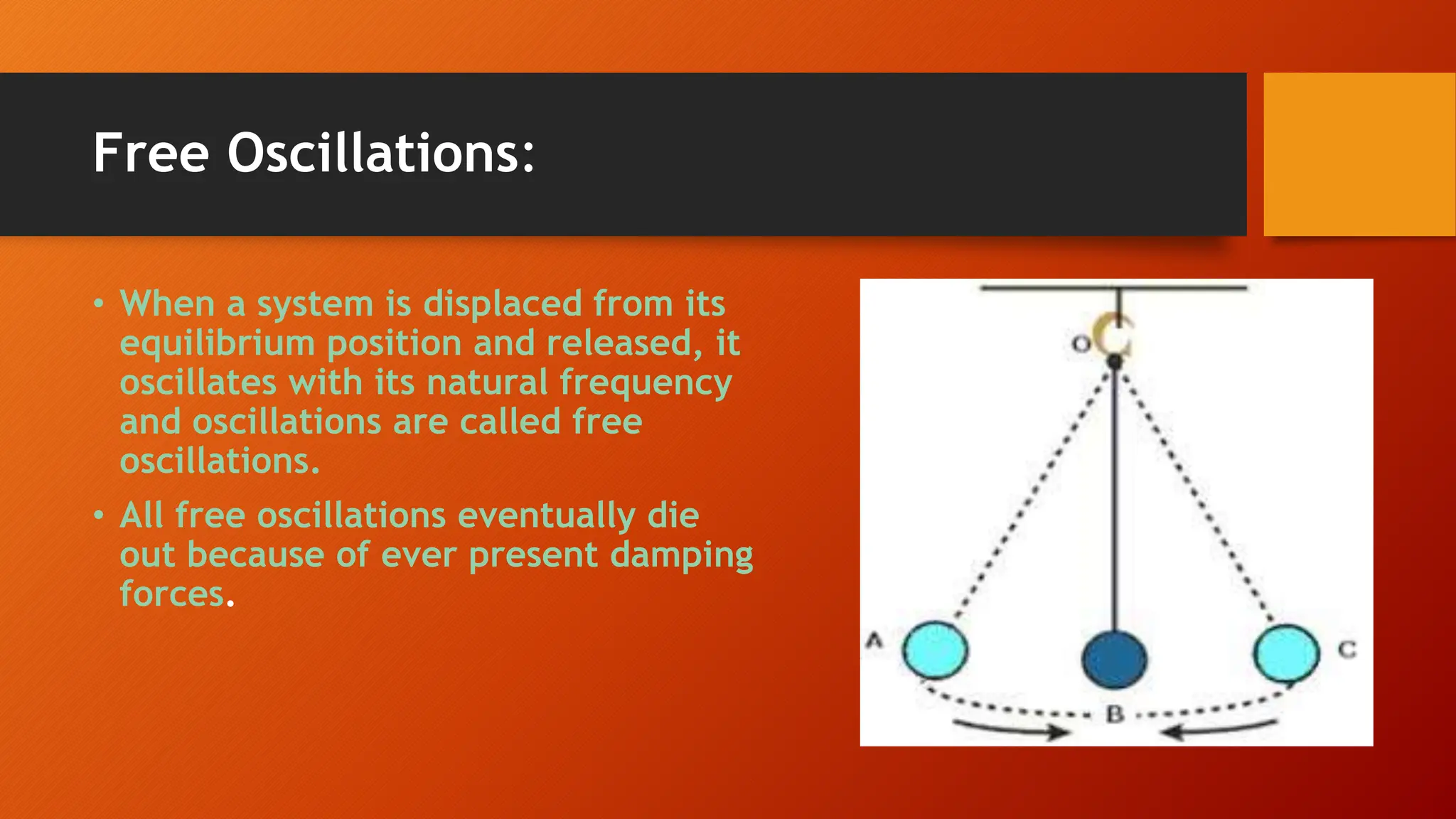
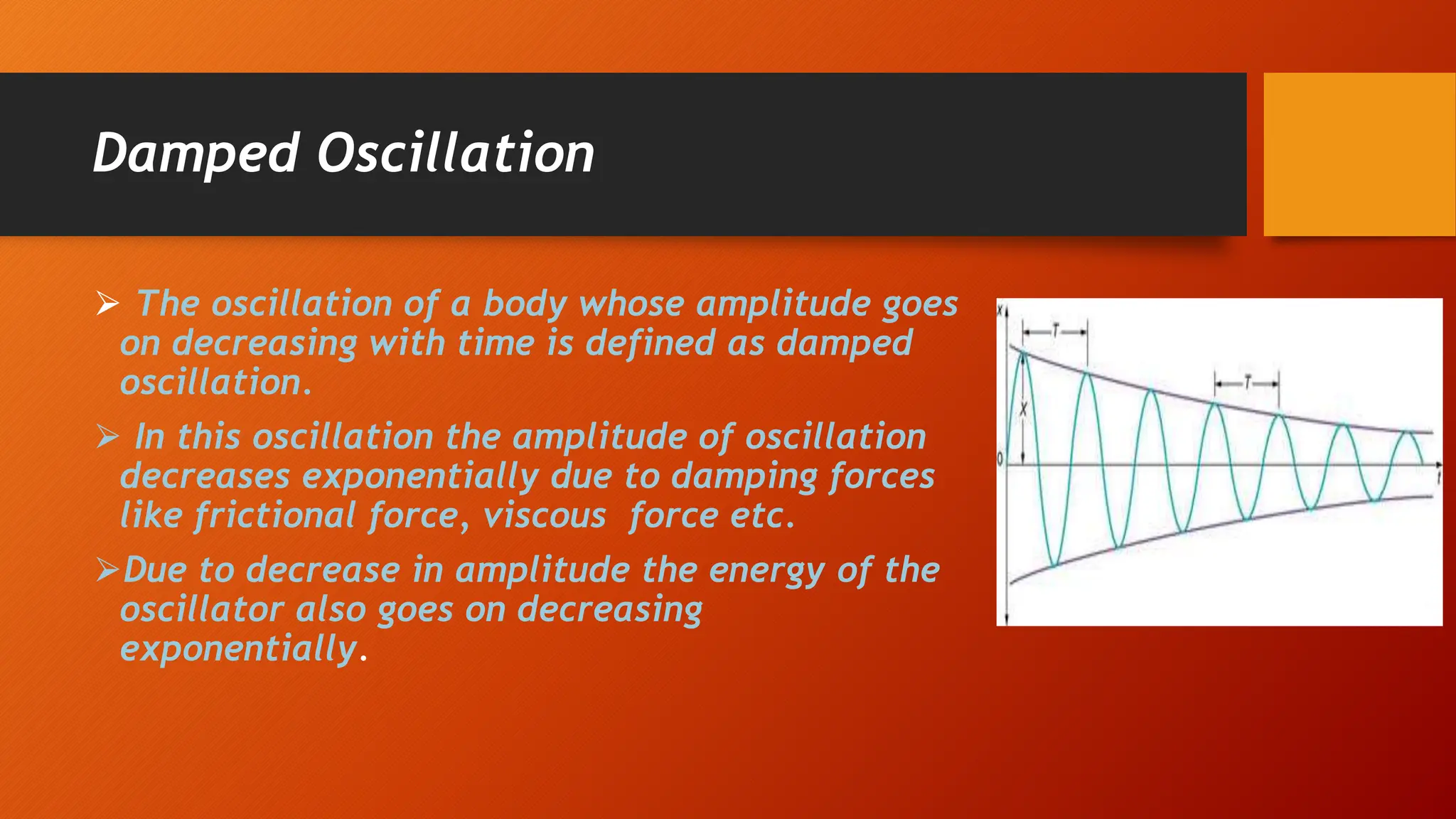
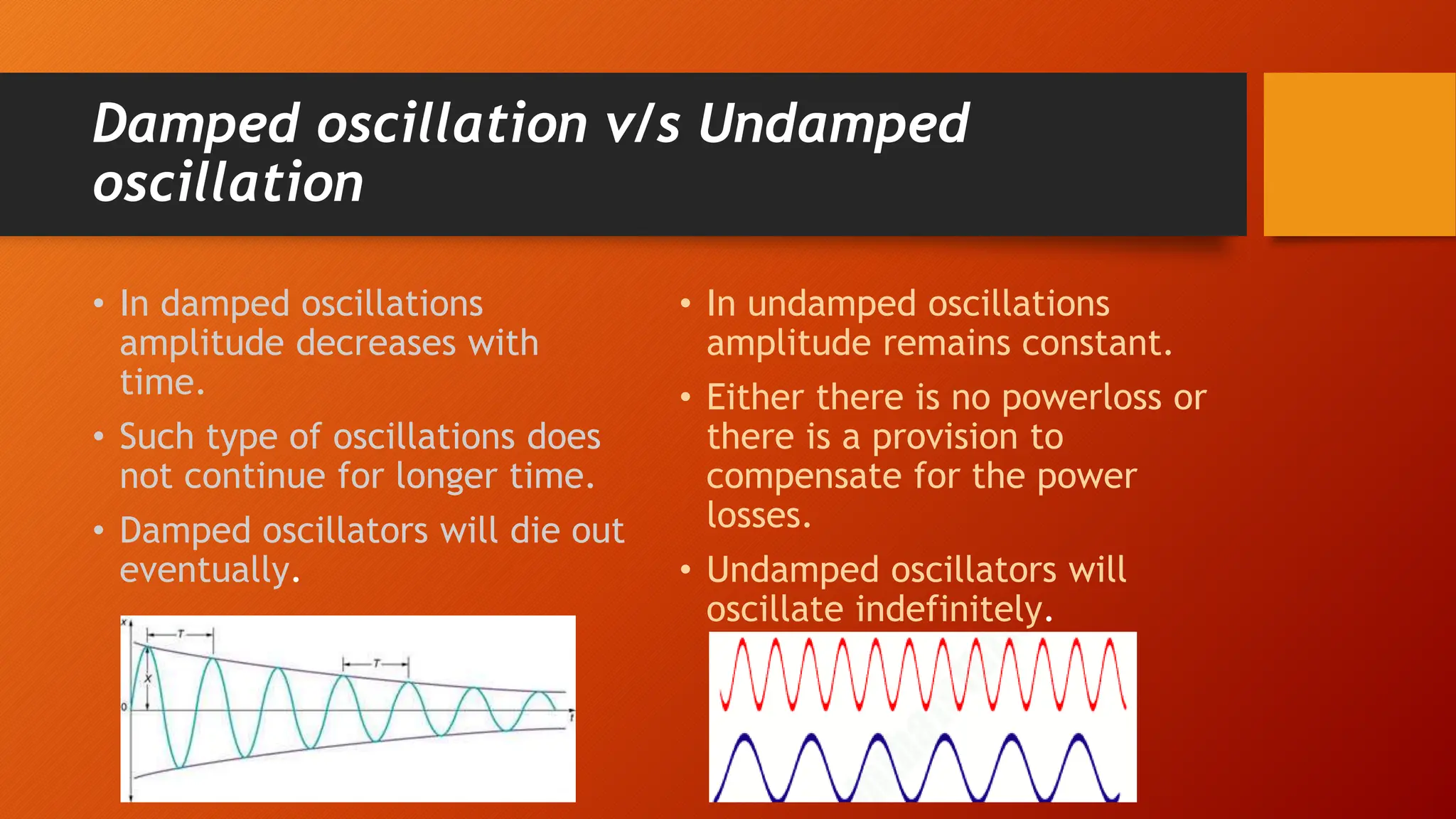
The document discusses oscillations and simple harmonic motion (SHM), defining periodic motion and the distinction between oscillatory and vibratory motion. It covers key concepts such as amplitude, time period, frequency, and phase, while explaining SHM characteristics and its relationship to uniform circular motion. Additionally, it describes free, damped, and forced oscillations, as well as the concept of resonance.